- Trending Now
- Foundational Courses
- Data Science
- Practice Problem
- Machine Learning
- System Design
- DevOps Tutorial

Open and Short Circuit Test of Transformer
In this article, we will go through the Open and Short circuit tests of a Transformer. Open and short circuit tests are performed on a Transformer to evaluate its performance characteristics and parameters which mainly determine the Voltage regulation of the transformer, the Transformer's efficiency, and the Equivalent circuit of the Transformer. They determine Iron and copper losses in the transformer. In this tutorial, we will go through the open and short circuit tests on a transformer with their circuit diagrams and an example and also we will tabulate the differences between the two.
Basic Terminologies
- Short circuit : An electrical connection in which current flows along a path that has very little resistance. This may result in high current flow, damage to the equipment, heating, etc.,
- Open circuit: It is an electrical connection in which there is a break in the path in which electric current flows. This may result in High resistance, no current flow, etc.,
- Transformer: An electrical device that is used to transfer electrical energy from one circuit to another without physical connection through electromagnetic induction. Now, let us learn open circuit tests and short circuit tests step by step with an example for each.
Open Circuit Test of Transformer
It is a method in electrical engineering used to determine the iron or core loss and it determines the exciting current of the transformer when it operates at rated voltage. The circuit diagram of this is shown below. In this, the secondary winding or the high voltage side is left open and the low voltage side is used to perform the test completely. Using this test we calculate no-load circuit parameters(X 0, R 0 ) and iron loss.

In the circuit diagram, the voltmeter(V), ammeter (A) and wattmeter(W) were all connected on the low-voltage side of the transformer, which is supplied at rated voltage(V1). The secondary winding side is left open, so which a small amount of current(I 0 ) is flowing in primary winding. Here, I 0 is called as no - load current. The reading of the wattmeter gives the iron loss.
The iron loss of transformer is given by (P i ),
where (P i ) = V 1 I 0 cosΦ 0 (where, cosΦ 0 is called as no - load power factor. )
True power(P) is given as , ( P) = E 2 p / R 0
so, no - load resistance (R 0 ) = E 2 P /P = V 1 / I 0
Apparent power(S) is given as , (S) = E P I 0
also, S = sqrt(P 2 + Q 2 ) (where P=true power, Q=reactive power )
so, Q = sqrt((E P I 0 ) 2 - P 2 --------- eq1)
no- load reactance (X 0 ) can be calculated as,
(X 0 ) = E 2 P / Q
Example: An open circuit test is conducted on a transformer and noted the following recordings E S = 57V, E P = 110V , I 0 = 150mA , P= 9.0W, Calculate the no load resistance(R 0 ) and no load reactance(X 0 )
Given, R 0 ,I 0 ,E p , E s , P now, according to the formula R 0 = E 2 P / P so, R 0 = (110V) 2 / 9 => 1.35 kΩ now, on substituting the required values in eq1 , we have sqrt((110V*150mA) 2 -(9W) 2 = 14.41vars and, X 0 = E 2 P / Q = (110v) 2 / 14.41vars = 840Ω
Short Circuit Test of Transformer
It is a method in electrical engineering used to determine the copper or winding loss and also it determines the impedance of the transformer . The circuit diagram of this is shown below. In this, the secondary winding (low voltage side is shorted by a thick conductor) and on primary side(high voltage side) Ammeter(A), Voltmeter(V) and wattmeter(W) are connected.
-768.png)
so, generally short circuit test is performed on high winding side and short circuited on low winding side. It will read copper losses because of high current passing through windings.
we have Power losses ( W s. c ) = I 2 s. c * R e Hence, R e = W s c / I 2 s.c we know that, Impedance( Z e ) = V s .c / I s. c Reactance(X e ) = sqrt((impedance) 2 - (resistance) 2 )
A short circuit test is conducted on a transformer and noted the following recordings V s .c = 7V , I s .c = 1.5mA , W s .c = 4W, Calculate the Reactance(X e ) , resistance(R e ) ?
Given that, V s. c = 7V , I s. c = 1.5mA , W s . c = 4W now, resistance ( R e ) = W s. c / I 2 s. c so, Resistance (R e ) = 1.8Ω Impedance(Z e ) = V s .c / I s. c => 7/1.5 Now, Reactance( X e ) = sqrt((impedance) 2 - (resistance) 2 ) X e = 1.46Ω
Differences Between Open Circuit Test and Short Circuit Test
Both the open circuit test and short circuit test are done to measure the efficiency of the transformer through various parameters in each case, voltage regulation. In this article, we have covered this topic in detail. We have covered Open CIrcuit Test and Short Circuit Test both separately with proper example.

Similar Reads
- Open and Short Circuit Test of Transformer In this article, we will go through the Open and Short circuit tests of a Transformer. Open and short circuit tests are performed on a Transformer to evaluate its performance characteristics and parameters which mainly determine the Voltage regulation of the transformer, the Transformer's efficiency 5 min read
- Fourier Transform in Circuit Analysis In this article, we will study about the Fourier transform analysis or Fourier Transform in Circuit Analysis. The Fourier transform is basically a mathematical operation that decomposes a signal into its constituent frequency components. In simple words, it converts a signal from the time domain to 10 min read
- Step-Up and Step-Down Transformer The device used for transferring electrical energy from one circuit to another is known as a transformer. A transformer works on the principle of mutual induction. A transformer is further of 2 types based on the number of turns in the windings or coil of the transformer. These are called step-up tr 12 min read
- Theory of Transformer on Load and No Load Operation In this article, we will study the theory of transformer on load and no load operation. A transformer is a static electrical machine used to increase or decrease the value of voltage and current in an electrical circuit. The transformer operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction and mutu 14 min read
- Step-Up and Step-Down Transformers: Simulation and Calculations The transformer is the simplest device that is used to transfer electrical energy from one alternating-current circuit to another circuit or multiple circuits, through the process of electromagnetic induction. A transformer works on the principle of electromagnetic induction to step up or step down 7 min read
- Laplace Transform in Circuit Analysis The analysis of circuit analysis is a fundamental discipline in electrical engineering. It enables engineers to design and construct electrical circuits for several purposes. The Laplace transform is one of the powerful mathematical tools that play a vital role in circuit analysis. The Laplace trans 7 min read
- How To Find Voltage In A Series Circuit Voltage in a series circuit is distributed among all the components connected in series. A series circuit is one of the important circuits in electric circuits. To find the voltage in a series circuit we add all the voltages across each component connected in series. In this article, we will discuss 8 min read
- Applications of Transformer A transformer is an electrical device that transfers energy between circuits through electromagnetic induction. It consists of coils wrapped around a core and is used to change voltage levels. In this article, we are going to learn about transformers in detail, including their function, types, compo 5 min read
- Applications of Transformers Transformers are like silent giants in the world of electricity. They're used to change the voltage levels, which helps electricity move smoothly through circuits. They're like guardians, making sure power flows safely and efficiently in our electric-powered world. Whether it's lighting up our homes 10 min read
- Current Transformers In this article, we will discuss what is A current Transformer?, Construction of the Current Transformer, Its Working, Phasor Diagram, Errors in the current Transformer, and Its Types, and At last we will conclude this article With its advantages, disadvantages, Application, and FAQs. Table of Conte 10 min read
- Auto Transformer An Auto Transformer refers to a transformer that features a single winding wound around a laminated core. An autotransformer is like a two-winding transformer however contrast in the manner the primary winding and secondary winding are interrelated. A piece of the winding is common to both the prima 10 min read
- What Is Step-Down Transformer? - Definition, Formula, Working and Construction Step Down Transformer - A device that is used to transfer electrical energy from one alternating-current circuit to another or multiple alternating-current circuits is known as a transformer. Transformers work on the principle of electromagnetic induction. During this process of transfer, if the AC 10 min read
- What is an Ideal Transformer? In this article, we will look into a special type of transformer known as the Ideal Transformer which is designed in ideal condition with no loss and 100% efficiency. We will discuss what is a transformer, ideal transformer. We will look into the working principle, properties, and equations of the i 6 min read
- How to Solve Parallel Circuit A parallel circuit is one of the important electric circuits. To solve parallel circuits, we use different formulas accordingly. We can calculate the total current, total resistance, voltage, and current through specific resistors accordingly to solve parallel circuits. The total current in a parall 8 min read
- Different Types of Transformer Transformers are crucial components of electrical engineering that are important for the powerful distribution and transmission of electrical power. Their most crucial pastime is to regulate the voltage levels among circuits to keep protection and energy overall performance. Transformers were essent 8 min read
- Transformer Testing Transformer testing is a process of examining a transformer to determine its health i.e., whether it is working properly or not. On an electrical transformer, we can perform various types of tests to measure its performance and efficiency and to take corrective actions. As we know, in electrical sys 15+ min read
- Difference between Ideal Transformer and Practical Transformer Transformers use the concept of electromagnetic induction to transmit electrical energy between two or more circuits. There are two types of transformers which are Ideal Transformer and Practical Transformer. We will discuss the operational differences between an ideal and practical transformer in t 5 min read
- Quarter Wave Transformer To match impedances, a quarter-wave transformer is a basic tool in electrical engineering and RF circuit design. Basically, it's a section of transmission line that helps guarantee effective power transfer from a source to a load. It has a set length. In radio frequency (RF) and microwave engineerin 10 min read
- How to run Cypress Tests in Chrome and Edge? Cypress is a popular testing framework that provides end-to-end testing for various web applications. It can provide testing in various browsers like Chrome, Firefox, etc. In this article, we will learn how to run tests in Chrome and Edge. What is Cypress Framework?Cypress is an end-to-end testing f 3 min read
- Electrical Engineering
- Geeks Premier League
- Electrical Machines
- Geeks Premier League 2023
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?

- Laboratory Practice
- Safety Rules
ECE 494 - Electrical Engineering Laboratory III
Lab 3: power transformer open and short circuit tests.
- To conduct standard open and short circuit tests in order to find the parameters of the equivalent circuit of a transformer.
- Evaluate the regulation and efficiency of the transformer at a given load.
- Check the excitation characteristics of the transformer.
- One Power Quality meter from the stockroom.
- Two scope leads from the stockroom.
- One McLean Engineering Transformer EP-Trio with .1 MOHM-1 microfarad integrator and two 25 Watt 1 Ohm resistors built into back.
- 3-phase AC Variac.
- One four-winding single phase transformer. (Model # T-1000)
- One oscilloscope.
- A. Fitzgerald, C. Kinsley, Jr., S. Umans, Electric Machinery, Ch. 1, 6th Edition, McGraw-Hill Inc., 2005.
- P.C SEN, Principles of Electric Machines and Power Electronics , 3rd Edition, John Wiley, 2013
A power transformer is usually employed for the purpose of converting power, at a fixed frequency, from one voltage to another. If it is used for converting power from a high voltage to a low voltage, it is called a step-down transformer. The conversion efficiency of a power transformer is extremely high and almost all of the input power is supplied as output power at the secondary winding.

Consider a magnetic core as shown in figure 3.1, carrying primary and secondary windings having N 1 and N 2 turns, respectively. When a sinusoidal voltage is applied to the primary winding, a flux Φ will exist in the core which links both the primary and secondary windings, inducing the RMS voltages
The transformer is said to have a transformation ratio
Determine how to connect the meters into the circuits:
- Figure 3.4 (Open Circuit Test) to measure the voltage ( V 1 ), current ( I p ), and power ( W oc ) of the transformer.
- Figure 3.5 (Short Circuit Test) to measure the voltage ( V sc ), current ( I sc ), and power ( W sc ) of the transformer.
Show connections for each circuit with (a) regular Wattmeter (4 terminals) (b) Power Quality Meter (Fluke 43B)
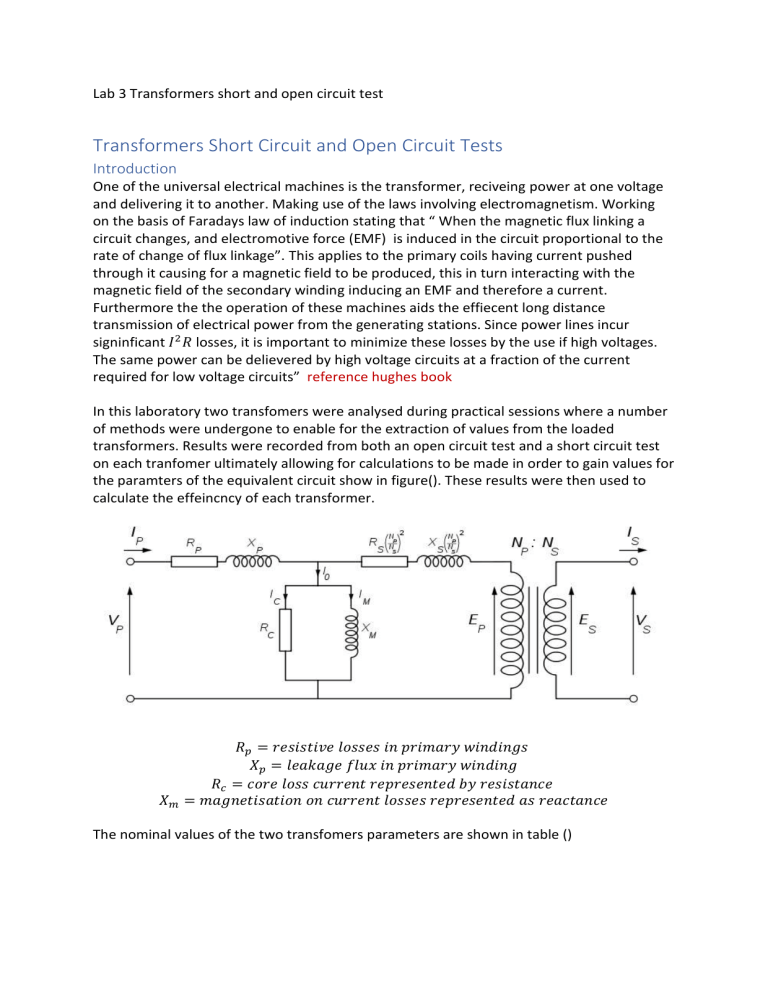
Equivalent Circuit
The transformer may be represented by the equivalent circuit shown in figure 3.2. The parameters may be referred to either the primary or the secondary side. The series resistances R 1 and R 2 represent the copper loss in the resistance of the two windings. The series reactances X 1 and X 2 are leakage inductances and account for the fact that some of the flux established by one of the windings does not fully couple the other winding. These reactances would be zero if there were perfect coupling between the two transformer windings.
The shunt resistance R p accounts for the core losses (due to hysteresis and eddy currents) of the transformer. The shunt inductance X p is representative of the inductances of the two windings and would be infinite in an ideal transformer if the number of turns of the two windings were to be infinite.
A knowledge of the equivalent circuit parameters permits the calculation of transformer efficiency and of voltage regulation without the need to conduct actual load tests. But experimental data must first be obtained in order to determine those parameters.
It will be confirmed at the conclusion of the first two parts of this experiment that the impedances of the series branch of the transformer equivalent circuit are substantially smaller than the impedances of the parallel branch. Because of this large discrepancy in the magnitudes of the elements we can redraw the equivalent circuit shown in figure 3.2 into that shown in figure 3.3. The errors introduced into calculations using figure 3.3 in place of figure 3.2 are quite insignificant. Furthermore, the large difference in the magnitudes of the transformer parameters allows for the determination of the elements in the series branch using one set of measurements and the elements in the parallel branch using another set of measurements.


Open Circuit Test
The open circuit test is used to determine the values of the shunt branch of the equivalent circuit R p and X p . We can see from figure 3.3 that with the secondary winding left open, the only part of the equivalent circuit that affects our measurement is the parallel branch. The impedance of the parallel branch is usually very high but appears lower when referred to the low voltage side. This test is therefore performed on the low voltage side of the transformer terminals 1 − 1' in figure 3.3) to increase the current drawn by the parallel branch to a readily measurable level. Besides, the rated voltage on the low voltage side is lower and therefore more manageable.
T-1000 transformer has four windings. Create a 1:2 ratio step up transformer by connecting the two primary windings in series and the two secondary windings in series.
This transformer will also be used in the next part of the experiment, so leave the connections intact when the present part is finished.
This transformer is rated at 1.0 KVA. The rated current is 1000 VA/240 V = 4.16A on the 240 V side and 1000 VA/120 V = 8.32A on the 120 V side.
Instructions
- Connect the circuit as shown in figure 3.4. Make sure that the low voltage side of the transformer corresponds to the left side of the connection diagram. A low power factor wattmeter should be used.
- Connect the Power Quality Meter to the left side (primary) of the transformer. If a low Power Factor Wattmeter is used, it should be connected also to primary and DVM’s connected to allow measurement of phase voltage (V 1 ) and primary current (I P )
- Connect the power supply from the bench panel to the INPUT of the three-phase variac and connect the OUTPUT of the variac to the circuit.
- Vary the input voltage starting at 0 V in 20 V increments to go up to 120 V. At each step change, record I p , W 0 and V 1 in table 3.1.
- Turn off the variac.
- Complete table 3.1
- Compute the parameters R p and X p at the rated voltage by using

These parameters are referred to the low voltage side.
- Find the value s of R p and X p as referred to the high voltage side.
- Plot the no-load current I p , magnetizing current I m , core loss W 0 and no-load power factor cos Φ , against the applied voltage V 1 on the same graph paper.
Short Circuit Test
The short circuit test is used to determine the values R s and X s of the series branch of the equivalent circuit. These impedances are usually very low, but appear higher in value when referred to the high voltage side. This test is consequently performed on high voltage side of the transformer (terminals 2 − 2ʹ in figure 3.3) in order to keep the current drawn by these impedances at a manageable level.
- Using the 2:1 ratio transformer of the previous part connect the circuit as shown in figure 3.5. Make sure that the high voltage side of the transformer corresponds to the left side (primary) of the connection diagram. Use the voltage terminals ± and 150 V of the standard AC wattmeter, if used.
- Make sure that the variac is turned all the way down before starting this experiment. Turn on the variac.
- Turn the variac up slowly until the current I s (consult figure 3.5) is at the rated value (about 4 amps). Record I s , V s and W s in table 3.2.
- Repeat the previous step by reducing the current I s in 0.5 A and record all values in table 3.2.
- Plot the copper losses W s against the current I s .
- Compute the equivalent circuit parameter R s and X s at the rated high voltage winding current by first calculating

- Calculate the values of R s and X s referred to low voltage side.
- Now that we have all the parameters for the transformer equivalent circuit, compute the voltage regulation at the rated power and at a lagging power factor of 0.8.
- Calculate the per unit efficiency at the rated power and at a lagging power factor of 0.8.

Excitation Characteristics
- Return the T-1000 transformer and get a McLean Engineering Transformer from the cabinet.
- Connect the circuit as shown in figure 3.6.
- Apply 20 volts (peak to peak) to the primary side of the transformer. Display and record the voltage and phase shift polarity waveform of both primary and secondary sides on a two channel oscilloscope.
- Display the voltage across the 1 Ω resistor (which represents the excitation current of the primary winding) and the voltage of the secondary side on an oscilloscope and record their waveforms. Notice the non-sinusoidal of the excitation current waveform and the phase shift relative to the secondary voltage.
- Disconnect the secondary side scope leads from transformer.
- Use the optically coupled usb cable to connect your meter to the computer. Start the Flukeview software on the computer and make certain that it connects with your meter. If not, look at the device manager to determine the port that it is connected to and then choose that port for the Flukeview software.
- Vary the applied voltage and observe the change in the non-sinusoidal nature of the excitation current. At 20 V rms and at 120 V rms examine the voltage and current harmonics. Determine THD and the principle one or two harmonic numbers. Use the Fluxview software to capture this waveform for your report. It is best to capture the data into an excel spread sheet so that you can manipulate the plot for best viewing.
- Apply the excitation current to channel I of the oscilloscope. Display the voltage across the capacitor of the R-C passive integrator available on the back of the transformer on channel II of the oscilloscope. The purpose of the integrator is to integrate the voltage in order to get the flux since e = N (d Φ /dt) .
- Press the X-Y button on the oscilloscope to see the hysteresis loop.
- Increase the voltage applied to the primary winding and record the change in the shape of the hysteresis loop.
Show the captured waveforms and THD information.
Discussion Questions
- Calculate the value of the maximum efficiency of the Hampden Transformer and determine the current at which it occurs.
- Explain the differences in the harmonic contents of the current at 20 V and 120 V. Why are some harmonics missing from the current waveform at 120V?
- Using the laboratory data, determine percent efficiency of the Hampden Transformer at half rated power and 0.8 lagging power factor.
- Engineering & Technology
- Electrical Engineering
Lab 3 Transformers short and open circuit test
Related documents

Add this document to collection(s)
You can add this document to your study collection(s)
Add this document to saved
You can add this document to your saved list
Suggest us how to improve StudyLib
(For complaints, use another form )
Input it if you want to receive answer

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
From short circuit test data, the equivalent resistance, reactance and impedance of the transformer can be found out with respect to high voltage side as well as the low voltage side. Circuit Diagram: Experimental Setup for the Short Circuit Test on a 1-Φ Transformer:
the core loss is very small. Hence, the power input on short circuit is dissipated as heat in the winding. The circuit diagram to conduct this test is shown in Fig.6 (a). In this test, the LV terminals of the transformer are short circuited. The primary voltage is gradually applied till the rated current °ows in the winding.
list of experiments sl.no name of the experiment page no 1 open circuit & short circuit test on a single phase 3 transformer 2 sumpners test 10 3 scott connection of transformers 15 4 no load and blocked rotor test on a 3- ɸ 18 induction motor 5 regulation of alternator using synchronous 23 impedance method
Oct 18, 2023 · Now, let us learn open circuit tests and short circuit tests step by step with an example for each. Open Circuit Test of Transformer. It is a method in electrical engineering used to determine the iron or core loss and it determines the exciting current of the transformer when it operates at rated voltage. The circuit diagram of this is shown ...
Figure 3.4 (Open Circuit Test) to measure the voltage ( V 1), current ( I p), and power ( W oc) of the transformer. Figure 3.5 (Short Circuit Test) to measure the voltage ( V sc), current ( I sc), and power ( W sc) of the transformer. Show connections for each circuit with (a) regular Wattmeter (4 terminals) (b) Power Quality Meter (Fluke 43B ...
The results obtained from the practical can be seen in table () Transformer Frequency 𝑉1𝑜𝑐 𝑃𝑜𝑐 1 50 Hz 240.5Vrms 26.2W 2 50.02 Hz 239.8Vrms 38.11W 𝑉𝐴𝑜𝑐 𝑝𝑓𝑜𝑐 67.61VA 0.387 109.2VA 0.349 𝐼1𝑜𝑐 0.281 0.456 𝑉20𝑐 248.7Vrms 35.92Vrms The second test was the short circuit (sc) the circuit of ...
2.2: Short Circuit Test The short circuit test is performed for determining the below mention parameter of the transformer. • It determines the copper loss occur on the full load. The copper loss is used for finding the efficiency of the transformer. • The equivalent resistance, impedance, and leakage reactance are known by the short ...
Short Circuit Test: Connect as shown in the circuit diagram. Short circuit the secondary and apply a low voltage to the primary through an auto transformer. The iron losses are negligible since the flux will be very low on account of the primary and secondary. Increase the voltage gradually till full load current flows in the primary.
Jun 26, 2024 · Short Circuit Test on Transformer. The connection diagram for the short circuit test on the transformer is shown in the figure below. A voltmeter, wattmeter, and an ammeter are connected in HV side of the transformer as shown. A low voltage of around 5-10% is applied to that HV side with the help of a variac (i.e. a variable ratio auto ...
Sep 9, 2022 · A transformer could be tested under no-load and full-load conditions to determine its turns ratio, regulation, and efficiency. However, without fully loading the transformer, it is possible to perform two tests (open-circuit and short-circuit) from which all the important data can be derived. In this article, learn how to analyze the results of open-circuit and short-circuit transformer tests ...