
Technology Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky
Technology Business Plan
This sample technology company business plan, created by the experts at PlanBuildr.com, is a launchpad for your success. With over 20 years of experience helping entrepreneurs bring their concepts to life, the plan covers everything from market positioning to revenue models, ensuring you can create a technology business that thrives.
Technology Business Plan Example & Template
Below is a Technology business plan template and sample to help you create each section of your own business plan.
Executive Summary
Business overview.
Kearney Tech Inc., located in Houston, Texas is a tech startup that focuses on developing and commercializing new artificial intelligence (AI) technology applications designed for small-to-medium sized businesses. The company has created proprietary technology that helps businesses improve their profitability by using AI to increase customer engagement. We offer multiple products, including AI hardware, marketing AI software, and CRM AI software. Many of our most basic services are free, but the rest can be accessed by paying a subscription fee. By providing flexible and affordable subscription options for our clients, Kearney Tech Inc. aims to be the next big technology company in the AI space for small and medium-sized businesses.
Kearney Tech Inc. was founded and is led by Abigail Kearney. Abigail has been a senior software engineer for nearly 10 years and has extensive experience in artificial intelligence and machine learning. In addition to her experience, she has a bachelor’s degree in computer science and an MBA. Her education and experience are sure to lead Kearney Tech Inc. to success.
Product Offering
Kearney Tech Inc. will showcase a variety of different applications for its AI technology that companies can utilize to increase their customer engagement from day one. Businesses can choose the platform package that works for them, based on a freemium subscription pricing structure.
The following are the services that Kearney Tech Inc. will provide:
- AI Hardware
- Marketing AI Software
- Customer Relationship Management AI Software
- Customer Support AI Software
- Technology Training: Training sessions on how to use our AI solutions and integrate them into their businesses
Customer Focus
Kearney Tech Inc. will serve small to medium-sized businesses within a 30-mile radius of Houston, Texas. Many of the businesses in our target demographic are startups looking to expand their reach and thus would benefit from technology that can increase their customer base.
Management Team
Kearney Tech Inc. will also employ an experienced assistant to work as a business analyst and help with various administrative duties around the office. She will also hire several developers, salesmen, and other administrative staff to assist her.
Success Factors
Kearney Tech Inc. will be able to achieve success by offering the following competitive advantages:
- Management: Abigail Kearney has been extremely successful working in the technology industry and will be able to use her previous experience to provide the best service experience. Her unique qualifications will serve customers in a much more sophisticated manner than Kearney Tech Inc.’s competitors.
- Relationships: Abigail Kearney knows many of the local leaders, business managers, and other influencers within Houston, Texas. With her 10 years of experience and good relationships with business leaders in the area, she will be able to develop an initial client base.
- Proprietary technology : The company has developed proprietary AI technology that will be used to add new data sources, expand on valuable insights, launch advanced features like benchmarking, provide predictive and prescriptive analytics, and ensure self-guided data discovery.
- Client-oriented service: Kearney Tech Inc. will have full-time customer service and sales managers to keep in contact with clients and answer their everyday questions.
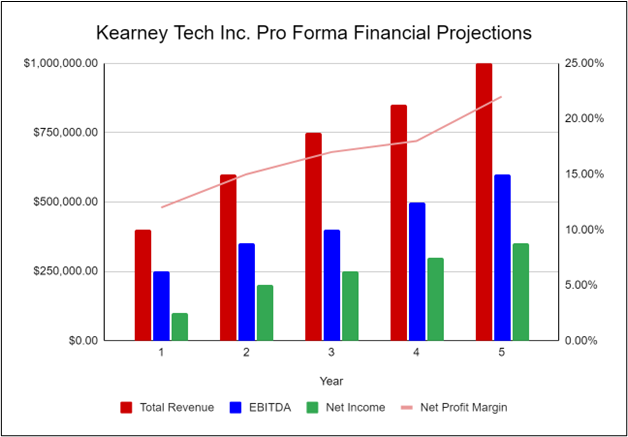
Financial Highlights
Kearney Tech Inc. is seeking a total funding of $400,000 of debt capital to open its office. The funding will be dedicated to office design, software development, marketing, and working capital. Specifically, these funds will be used as follows:
- Office design/build: $50,000
- Software development: $150,000
- Three months of overhead expenses (payroll, rent, utilities): $150,000
- Marketing costs: $25,000
- Working capital: $25,000
The following graph below outlines the pro forma financial projections for Kearney Tech Inc.:
Company Overview
Who is kearney tech inc..
Abigail began researching what it would take to create her own technology company and did a thorough analysis of the costs, market, demographics, and competition. Abigail has compiled enough information to develop her business plan in order to approach investors.
Kearney Tech Inc.’s History
Once her market analysis was complete, Abigail Kearney began surveying the local vacant office space and located an ideal location to house the technology company. Abigail Kearney incorporated Kearney Tech Inc. as a Limited Liability Corporation in April 2023.
Since incorporation, the company has achieved the following milestones:
- Located available office space for rent
- Developed the company’s name, logo, and website
- Determined equipment and necessary supplies
- Began recruiting key employees
Kearney Tech Inc. Services
Industry analysis.
As of 2021, the global technology industry was valued at approximately $5.2T. Of all countries worldwide, the United States currently has the largest technology market, with 32% of the market share at $1.7T. The technology industry in the U.S. accounts for a large part of the nation’s economy.
The Information Technology market can be segmented by categories such as software, devices, infrastructure IT and business services, emerging technology, and telecom services. In the United States, IT and business services hold the greatest market share (30%), followed by software (20%) and telecom services (20%).
Market drivers include the economy, employment rates, and the digital transformation of daily life for a growing number of people and businesses worldwide. Corporations and organizations are seeking IT service providers that can help improve their software, cybersecurity, data, and infrastructure. Technology companies that can provide products and services that cater to these issues can be competitive in the constantly evolving market.
Technology is an integral part of society. Developments in AI and machine learning are essential to keep society moving forward and make businesses more efficient. Therefore, businesses will always be in need of AI solutions to bring in more customers and streamline their services and products. According to Market Watch, the Technology industry is set to grow at a CAGR of 25.73% from now until 2027. Very few industries see this growth, which shows how much demand there is for technological solutions. Therefore, we expect Kearney Tech Inc. to see great success in our local market.
Customer Analysis
Demographic profile of target market.
Kearney Tech Inc. will serve the small and medium-sized businesses of Houston, Texas, and the surrounding areas.
Many small businesses in the community are startups or established enterprises looking to expand their reach and thus would benefit from technology that can increase their customer engagement.
Customer Segmentation
Kearney Tech Inc. will primarily target the following customer profiles:
- Small businesses
- Medium-sized businesses
Competitive Analysis
Direct and indirect competitors.
Kearney Tech Inc. will face competition from other companies with similar business profiles. A description of each competitor company is below.
Tekuserv has been a reliable technology company in Houston, Texas for more than fifteen years. The company is known for its wide range of technology solutions that serve many small-to-medium-sized businesses. With its large number of experts focused on delivering customer satisfaction, the organization maintains its high standard of developing quality products and providing exceptional customer service. Tekuserv provides business software on a freemium subscription basis. It develops enterprise technology solutions with a focus on customer relationship management.
Prime AI Business Solutions
Prime AI Business Solutions is a technology development company in Houston, Texas. In business for several years, the company has developed highly-rated AI solutions used by many well-known businesses in a variety of industries. Prime AI Business Solutions now offers a range of AI hardware and software products geared toward helping businesses of all sizes increase their customer base. The company has also introduced a “pay-as-you-grow” pricing model that scales to provide users with more support as they scale up.
AICE Developments
AICE stands for Artificial Intelligence for Customer Engagement. AICE Developments is also a local technology company that manufactures and distributes a variety of technology products. AICE Developments was established in 2009 in Houston, Texas, providing integrated AI applications and platform services. Its products include applications and infrastructure offerings delivered through various IT deployment models, including on-premise deployments, cloud-based deployments, and hybrid deployments. The company serves automotive, financial services, healthcare, hospitality, retail, utilities, construction, etc. It provides AI solutions for enterprise marketing and customer engagement.
Competitive Advantage
Kearney Tech Inc. will be able to offer the following advantages over the competition:
- Proprietary technology: The company has developed proprietary AI technology that will be used to add new data sources, expand on valuable insights, launch advanced features like benchmarking, provide predictive and prescriptive analytics, and ensure self-guided data discovery.
Marketing Plan
Brand & value proposition.
Kearney Tech Inc. will offer a unique value proposition to its clientele:
- Service built on long-term relationships
- Big-firm expertise in a small-firm environment
- Thorough knowledge of the clients and their varying needs
- Proprietary technology developed by skilled software engineers
Promotions Strategy
The promotions strategy for Kearney Tech Inc. is as follows:
Kearney Tech Inc. understands that the best promotion comes from satisfied customers. The company will encourage its clients to refer other businesses by providing economic or financial incentives for every new client produced. This strategy will increase in effectiveness after the business has already been established.
Social Media
Kearney Tech Inc. will invest heavily in a social media advertising campaign. The brand manager will create the company’s social media accounts and invest in ads on all social media platforms. It will use targeted marketing to appeal to the target demographics.
Website/SEO
Kearney Tech Inc. will invest heavily in developing a professional website that displays all of the features and benefits of the technology company. It will also invest heavily in SEO so that the brand’s website will appear at the top of search engine results.
Direct Mail
Kearney Tech Inc. will blanket businesses with direct mail pieces. These pieces will provide general information on Kearney Tech Inc., offer discounts, and/or provide other incentives for companies to use the AI platform.
Kearney Tech Inc.’s pricing will be on par with competitors, so clients feel they receive great value when purchasing the technology.
Operations Plan
The following will be the operations plan for Kearney Tech Inc.:
Operation Functions:
- Abigail Kearney will be the Owner and CEO of the company. She will oversee all the operations and executive functions of the company. In the beginning, she will also provide customer support and market/sell AI products to potential clients.
- Abigail will employ an experienced assistant to work as a business analyst and help with various administrative duties around the office.
- Abigail will also hire several developers to maintain and develop AI products and services.
- Abigail will also hire a solid sales team to sell our products to potential clients. As the company grows, she will also hire a team that is solely dedicated to customer service.
Milestones:
Kearney Tech Inc. will have the following milestones completed in the next six months.
5/2023 – Finalize lease agreement
6/2023 – Design and build out Kearney Tech Inc.
7/2023 – Hire and train initial staff
8/2023 – Kickoff of promotional campaign
9/2023 – Launch Kearney Tech Inc.
10/2023 – Reach break-even
Financial Plan
Key revenue & costs.
Kearney Tech Inc.’s revenues will come primarily from its technology solution subscription sales. The company will use a freemium subscription model, in which basic functions can be used by any company for free. Additional solutions and support will be available in a tiered package model based on the enterprises’ size and the number of users.
The office lease, equipment, supplies, and labor expenses will be the key cost drivers of Kearney Tech Inc. Ongoing marketing expenditures are also notable cost drivers for Kearney Tech Inc.
Funding Requirements and Use of Funds
Key assumptions.
The following outlines the key assumptions required in order to achieve the revenue and cost numbers in the financials and pay off the startup business loan.
- Average number of clients per month
- Annual rent: $20,000
Financial Projections
Income statement, balance sheet, cash flow statement, technology business plan faqs, what is a technology business plan.
A technology business plan is a plan to start and/or grow your technology business. Among other things, it outlines your business concept, identifies your target customers, presents your marketing plan and details your financial projections. You can easily complete your Technology business plan using our Technology Business Plan Template here .
What are the Main Types of Technology Businesses?
There are a number of different kinds of technology businesses, some examples include: Network technology, Software technology, and Customer relationship technology.
How Do You Get Funding for Your Technology Business Plan?
Technology businesses are often funded through small business loans. Personal savings, credit card financing and angel investors are also popular forms of funding.
What are the Steps To Start a Technology Business?
Starting a technology business can be an exciting endeavor. Having a clear roadmap of the steps to start a business will help you stay focused on your goals and get started faster.
1. Develop A Technology Business Plan - The first step in starting a business is to create a detailed technology business plan that outlines all aspects of the venture. This should include potential market size and target customers, the services or products you will offer, pricing strategies and a detailed financial forecast.
2. Choose Your Legal Structure - It's important to select an appropriate legal entity for your technology business. This could be a limited liability company (LLC), corporation, partnership, or sole proprietorship. Each type has its own benefits and drawbacks, so it’s important to do research and choose wisely so that your technology business is in compliance with local laws.
3. Register Your Technology Business - Once you have chosen a legal structure, the next step is to register your technology business with the government or state where you’re operating from. This includes obtaining licenses and permits as required by federal, state, and local laws.
4. Identify Financing Options - It’s likely that you’ll need some capital to start your technology business, so take some time to identify what financing options are available such as bank loans, investor funding, grants, or crowdfunding platforms.
5. Choose a Location - Whether you plan on operating out of a physical location or not, you should always have an idea of where you’ll be based should it become necessary in the future as well as what kind of space would be suitable for your operations.
6. Hire Employees - There are several ways to find qualified employees including job boards like LinkedIn or Indeed as well as hiring agencies if needed – depending on what type of employees you need it might also be more effective to reach out directly through networking events.
7. Acquire Necessary Technology Equipment & Supplies - In order to start your technology business, you'll need to purchase all of the necessary equipment and supplies to run a successful operation.
8. Market & Promote Your Business - Once you have all the necessary pieces in place, it’s time to start promoting and marketing your technology business. This includes creating a website, utilizing social media platforms like Facebook or Twitter, and having an effective Search Engine Optimization (SEO) strategy. You should also consider traditional marketing techniques such as radio or print advertising.
Learn more about how to start a successful Technology business: How to Start a Tech Company
Don't bother with copy and paste.
Get this complete sample business plan as a free text document.
Educational Software Business Plan
Start your own educational software business plan
Third Degree I.D.
Executive summary executive summary is a brief introduction to your business plan. it describes your business, the problem that it solves, your target market, and financial highlights.">.
Third Degree I.D. is a limited-liability company (LLC) with three founding partners, located in Savannah, Georgia. The company designs, develops, and markets instructional products and services for the corporate, education, government, and healthcare e-learning industries. It is committed to high quality instructional design and educational new media development, and provides a core deliverable of programs, courses, and learning objects for the distance education, distributed learning, and e-learning markets.
The company employs an object-oriented design methodology that yields flexible, scalable, and reusable content, supporting clients with rich, targeted solutions that are easily replicated and maintained. It seeks a balanced portfolio of clients from a variety of industry sectors, and plans to mitigate business fluctuations with an appropriate number of local, national, and international clients.
Third Degree I.D. develops strategic relationships and builds its business on a returning customer base and an accumulation of educational content that can be re-purposed and re-sold.
The three founding partners of Third Degree I.D. will each invest $35,000 into the company, and are seeking an additional two-year loan of $30,000 to complete the start-up funding. Roughly $19,000 of this initial funding is required for start-up expenses and assets; the remainder will provide a cash basis for the initial year of operations, during which Third Degree I.D. will provide some at-cost work to influential clients to create a solid reputation for our work and capabilities; this reputation forms the necessary basis for marketing and sales strategies after the first year.
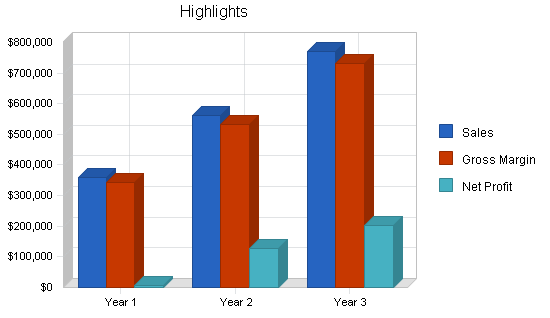
Our market research shows our sales goal of $360,000 in the first year is conservative, for a start-up educational software company with our combined expertise. Growth estimates in years 2 and 3 are based on data from comparable businesses in the same industry.
1.1 Objectives
Key objectives for Third Degree I.D. in the first year are as follows:
- Establish a legal business through appropriate licensing.
- Complete business planning and pursue funding–via venture capital, bank loans, grants, and contracts.
- Establish a web presence and list products and services in industry-relevant websites and publications.
- Contract with six to eight clients requiring consulting, training, design or development work of an appropriate scope ($50,000 or more).
1.2 Mission
Third Degree I.D. designs, develops, and markets instructional products and services for the corporate, education, government, and healthcare e-learning industries. It affords companies and institutions cost-effective, progressive, flexible and well supported solutions to their instructional design and e-learning operational needs. Its principal goal is client satisfaction, serving client interests as an ally and loyal business partner. The company operates on a for-profit basis and provides an engaging and equitable work environment for its owners, employees, and contractors.
1.3 Keys to Success
Success will be dependent upon:
- persistent and creative client development efforts
- exceptional product and service quality
- time-efficient and cost-effective development processes
- expert management and knowledgeable staff
- cash-savvy growth strategies
Company Summary company overview ) is an overview of the most important points about your company—your history, management team, location, mission statement and legal structure.">
Third Degree I.D. is located in Savannah, Georgia. It sells instructional design products and services to the corporate, education, government and healthcare e-learning markets. The company is committed to high quality instructional design and educational new media development. It sells program/curriculum design and development, course design and development, program/curriculum and course evaluation, content analyses and revision, rich-media production, e-learning training, e-learning consulting, and additional services, such as market research, editing, document workflow, and translation. Third Degree I.D. employs an object-oriented design methodology that yields flexible, scalable, and reusable content. This approach provides clients with rich, targeted solutions that are easily replicated and maintained.
2.1 Start-up Summary
To begin the business, we require $5,924 in start-up expenses, and another $13,000 in non-cash assets. Details of these requirements can be found below.
Legal Expenses
- Attorney Consultation — $300
- Initial Filing Fee for LLC — $400
- Name and Logo Trademark — $300
Website Expenses
- Website Domain (2 Years) — $14
- Website Hosting (1 Year) — $96
Communications
- Stationery/Letterhead + Envelopes (500 set) — $500
- Business Cards (500 x 3) — $300
Memberships and Subscriptions
- Coastal Beta — $75
- eLearning Guild — $95
- Faculty Finder.com — $745
- Authoring and Multimedia Software for Sony Vaio — $1,000
- Authoring and Multimedia Software for Mac Powerbook — $1,000
- Authoring and Multimedia Software for SH Desktop — $300
Long-term Assets
Computer Hardware
- DS Laptop (Sony Vaio) — $2,500
- MH Laptop (Mac 15″ Powerbook — $2,500
- SH Desktop + Laser Printer + Scanner — $2,000
- Networked Content Server — $6,000
Start-up Investment
Each of the the founding partners will make an equal investment of $35,000 in starting the business. In addition, the partners intend to secure a 2-year commercial loan in the amount of $30,000 to cover the working capital requirements for the initial period of operations.
All startup expenses and funding requirements are summarized in the tables below.

2.2 Company Ownership
Third Degree I.D. is structured as a limited-liability company (LLC), consisting of three executive partners: Susan Hines, Mona Meyer, and Daniel Stanford, who will function in the roles of chief executive officer (CEO), chief learning officer (CLO), and chief creative officer (CCO).
Third Degree I.D. focuses on the following deliverables: program/curriculum design and development, course design and development, program/curriculum and course evaluation, content analyses and revision, rich-media production, e-learning training, e-learning consulting, and additional services, such as market research, editing, document workflow, and translation. For purposes of billing, project management, and client relations, these services are broken down as follows:
- Program/Curriculum Design & Development
- New Program Services
- Existing Program Services
- Course Design and Development
- Learning Object Development
- Other Services
3.1 Program Design & Development
Third Degree I.D. provides development services for clients in accordance with educational best practices and client specifications. It employs a systematic design and development process that produces instructionally sound, engaging programs/curricula that are aligned with institutional goals and exceed applicable accreditation and/or compliance standards.
3.1.1 New Program Services
New program services are available to clients who do not yet possess an e-learning infrastructure or who do not yet possess robust programming that would adequately leverage the infrastructure.
Needs Analysis Report The needs analysis report is the end result of a client-partnered consulting and research effort. The report articulates technology, workforce, and policy/procedure needs for e-learning programs in the general context of any institutional and/or accreditation and/or compliance constraints. Clients are charged according to the scope of the project, which is generally tied to the length and/or number of programs/curricula to be developed. For example, a needs analysis report for an e-learning certificate or academic “minor” (or group of related courses of no more than six) would conclude with a base charge of $3600.
Clients developing multiple curricula receive a 50% discount on the base charge of the lesser fee. For example, an institution or company developing an MA and an undergraduate minor would be charged the full fee for the MA plus half of the fee charged for the undergraduate minor ($4500 + $1800 = $6300).
Funding Assistance Funding assistance is a deliverable provided to institutions or companies that wish to raise funds externally in order to underwrite or mitigate their e-learning start-up and operation expenses. Assistance would include research, reporting, grant and business proposal efforts. The charge for initial consulting is $75 per hour, with subsequent research, reporting, grant and business proposal efforts charged at $50 per hour. Clients may indicate a “not to exceed” clause in all funding-assistance efforts.
Program/Curriculum Prospectus The program/curriculum prospectus is the end result of a client-partnered consulting and research effort. The prospectus outlines the objectives and viability of a given program/curriculum and critiques any development dependencies or any potential implementation constraints; it also includes a market study and a program/curriculum evaluation plan.
Clients who purchase a needs analysis report are given a 20% discount on each program/curriculum prospectus.
Program/Curriculum Development Plan The program/curriculum development plan is the end result of a client-partnered consulting and research effort. The development plan is a report that articulates the program/curriculum specifications according to institutional needs. The document includes a full articulation of curriculum design, including course-series or individual course “look and feel” and functionality requirements. It characterizes the significant development/delivery features of the courses and identifies any course developers, subject matter experts (SMEs), or consultants associated with the individual course projects. The development plan includes a time horizon for the overall program/curriculum with timelines for individual courses and delineated fees associated with project development and management.*
Clients who purchase a curriculum prospectus report are given a 20% discount on each corresponding program/curriculum plan.
*Clients are charged a monthly project management fee of 5% on the overall curriculum design and development charge for the duration of the project development period. A project development period runs from the date of the program/curriculum development plan implementation to the date of program/curriculum development plan completion.
Program/Curriculum Implementation Strategy The program/curriculum implementation strategy is the end result of a client-partnered consulting and research effort. It is a report that recommends ways to optimize program/curriculum support and to leverage the program/curriculum in order to maximize learning and revenues. The report recommends enrollment goals, scheduling, instructor recruitment, content-reuse, and technical support strategies.
Clients who purchase a program/curriculum development plan are given a 20% discount on each corresponding program/curriculum implementation strategy report.
Program/Curriculum Evaluation Plan The curriculum evaluation plan is the end result of a client-partnered consulting and research effort. It is a report that articulates qualitative and quantitative strategies which satisfy accreditation and/or compliance standards and assist institutions and companies in procuring feedback that informs and improves upon their curricula. The evaluation plan includes survey collection instruments for curriculum-level and course-level analysis.
Clients who purchase a curriculum prospectus report are given a 20% discount on each corresponding program/curriculum evaluation plan.
3.1.2 Existing Program Services
Existing program services are available to clients who possess an e-learning infrastructure and deliver programs/curricula, but who wish to enhance or improve upon their offerings. Clients with existing programs may select from the New Program Services, if they wish to add new programs to their offerings.
Program/Curriculum Evaluation Report The program/curriculum evaluation report includes a top-level analysis of a given program/curriculum relevant to institutional or company goals and relative to comparable institutional and company programs/curricula. It includes a systematic analysis of each course within the program/curriculum and provides recommendations for revision of content, structure, and delivery. Recommendations are informed by educational best practices and any institutional, accreditation and/or compliance standards.
Program/Curriculum Strategy Report The program/curriculum strategy report is the end result of a client-partnered consulting and research effort. It is a report that analyzes the institution or company’s current implementation and operations strategy and recommends ways to optimize program/curriculum support and to leverage the program/curriculum in order to maximize learning and revenues. The report recommends enrollment goals, scheduling, instructor recruitment, content-reuse, and technical support strategies.
Clients who purchase a curriculum evaluation report are given a 20% discount on each corresponding program/curriculum strategy report.

3.2 Course Design and Development
Third Degree I.D. provides course- or project-development services for clients in accordance with established curriculum plans. The company employs a systematic instructional design process that produces instructionally sound, engaging course work, systematically aligned with program goals and learning outcomes and designed to exceed institutional accreditation standards.
Course-design cost estimates are based upon the following assumptions:
- A course or training project contains one or more units of instruction.
- A “unit” consists of approximately 8 pages of content and represents 3-5 hours of instruction.
- A “page” of content covers a single topic and represents information that would be presented to a learner “at once” (e.g. between clicks of a “Next” button).
- A “page” of content contains from 150-1500 words (as dictated by lesson flow and audience requirements).
- A typical unit contains approximately:
- 16 content-related photos or illustrations (an average of 2 per page)
- 1 collaborative discussion assignment
- 2 hands-on or research-focused “homework” assignments, and
- 1 standard assessment (e.g. 20-question multiple choice, true/false, or matching quiz).
Note: A unit may also contain one or more interactive learning objects, which are priced separately under topic 3.3, below.
Development Options
Type A: Courses are developed “from scratch.” Third Degree I.D. is responsible for providing subject-matter expertise, researching relevant content, and developing courses with limited support from the client partner. This is the most expensive development option. Type B: Courses are developed with the aid of a dedicated subject-matter expert employed by the client for the scope of the project (e.g. a faculty member for higher-ed institutions, or a seasoned field professional for corporate clients). Type C: The client partner provides raw content in an existing medium (e.g. textbooks, articles, PowerPoint slides, training manuals, etc.) Third Degree I.D. develops courses that re-purpose and/or supplement the existing content. Type D: The client partner provides both existing content in an alternate medium and a dedicated subject-matter expert. Third Degree I.D. works with the dedicated subject-matter expert over the course of the project to produce courses that re-purpose or supplement the raw content.
Delivery Options
Type 1: Content is designed for delivery by nonprofit institutions under the rules of the TEACH Act. This is the least restrictive option in terms of copyright and, therefore, requires limited investment in new media development and permissions acquisition. Type 2: Content is designed for delivery by nonprofit institutions and education clients under the “Fair Use” guidelines for copyrighted works. Fair Use strictly limits the amount of copyrighted content that can be used within the context of an online course. Therefore, courses developed for this standard require additional investment in new media development and permissions acquisition. Type 3: Content is developed for commercial delivery. This is the most restrictive option and requires that all course content (including media) be developed from scratch or obtained via purchase or agreement with the copyright holder.
Cost Estimates
*Note: A typical course for a higher-ed client is 10 to 12 units in length (representing 30-50 hours of instruction). Multiply the unit price by 10 or 12 to calculate average course cost.
Additional Development Services and Pricing
Third Degree I.D. also offers the following additional services related to course/program development:
*1 audio “clip” = 60 seconds of digital audio
**1 video “clip” = 30 seconds of digital video
3.3 Learning Object Development
Third Degree I.D. designs and develops rich-media learning objects, designed to motivate learners, to increase course interactivity, to provide novel and interesting views of course content, to simulate real-world scenarios, and to provide stimulating alternatives to drill-and-practice instruction. Learning objects are typically authored in Macromedia Flash and range in complexity from single-screen interactions with no evaluation to rich, simulated environments that respond to a variety of user inputs.
Object Types
Level 1: Level 1 objects are typically single-screen environments that respond to user actions but do not evaluate responses. Examples include:
- X-Ray Machine: A custom cursor reveals a hidden layer as the user rolls his mouse over an image. Imagine, in an anatomy course, being able to peer “inside” a simple, illustrated diagram of the human body, revealing the skeletal system, the circulatory system, etc.
- Overlay Engine: Users can toggle various image “layers” on and off, similar to the way transparency overlays can be used with an over head projector. Imagine a map with highways, lakes, and gas station markers that could be hidden and revealed as needed.
- Simple Image Gallery : Users cycle through images with corresponding text. Imagine a menu with five buttons, each displaying a single work of art, the title of the piece, the artist’s name, and the date it was created.
Level 2: These objects are typically 1-2 screen engines, with evaluation and feedback, and are typically used as assessment vehicles. Examples include:
- Media-Rich Quiz: For instance, a multiple-choice or fill-in-the-blank quiz with optional areas for displaying diagrams, photographs, or hints.
- Hint/Password Game: The user tries to guess the topic or item that is described by a growing list of clues.
Level 3: Level 3 objects are media-rich resources that are designed to display a variety of media in a unique format. They may combine text, illustrations, photographs, charts and graphs, audio/video clips, and web links to create rich, educational experiences. Examples include:
- Timelines: Imagine an interactive timeline designed to illustrate key points in the development of personal computing. For instance, one event on the timeline could provide photos of the early Apple II computers and later Macintosh models, text describing the growth of Apple as a major hardware manufacturer, sound-bytes from industry professionals, and a link to the Apple website.
- Image Magnifier: Imagine a display engine that allows users to interactively select and view magnified portions of a small image (e.g. a painting or other work of art). The engine could handle multiple images (with a page-turning metaphor), and a text area could provide a description of each work with links to museums featuring work by the same artist.
- Interactive Dictionary/Glossary: Imagine key words or terms hyperlinked from within a course. When a term is clicked, the glossary would open, displaying a basic text definition, supplemented by audio clips, animated diagrams, or illustrations.
Level 4: These are typically complex adaptive learning tools that modify content presentation, based upon user response. Examples include:
- Adaptive Assessments/Tutorials: Content presentation is adjusted based upon user responses. Imagine a quiz that supplies a more difficult question each time a user responds correctly or easier questions when the user responds incorrectly.
- Adaptive Simulations: These are typically games or simulations that replicate real-world problems. Imagine a game designed to test a learner’s understanding of the urban planning process. For example, users might control the rate and quality of road construction, public parks, and commercial/residential zoning. By choosing to spend a significant portion of her budget on parks and residential development, a user may receive feedback that traffic congestion and unemployment have driven potential buyers out of the city.
Cost Estimates—Engine Development
Cost Estimates—Engine “Population” and Media Editing
3.4 Training
Third Degree I.D. provides a number of training options for clients who wish to expand their e-learning skills and knowledge. Training sessions can benefit instructors, support staff and administrators.
3.5 Consulting and Other
Third Degree I.D. charges a flat fee of $75 per hour for consulting, and specializes in a variety of areas, including:
- e-learning strategic planning
- accreditation substantive change documentation
- learning-objects database planning
- content-reuse planning
- “best practices” consulting
- open-source e-learning assets consulting
Third Degree I.D. charges a flat fee of $60 per hour for work that may stem from consulting, such as:
- Copy editing
- Translation
- Illustration
Market Analysis Summary how to do a market analysis for your business plan.">
Third Degree I.D. is competing for e-learning instructional design business in the corporate, educational, healthcare and government sectors. Its emphasis will be on corporate and educational markets, as these sectors are likely to experience the greatest growth.
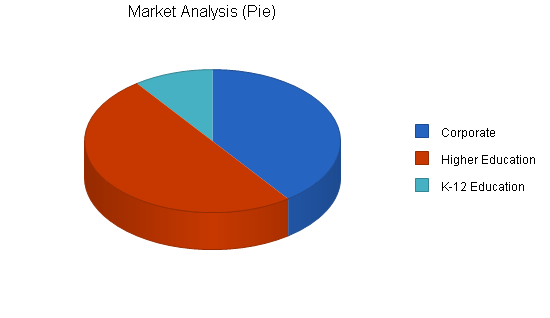
Third Degree I.D. projects it will do $360,000 worth of business in Year 1, which represents a development objective of at least three 7- to 12-course series (i.e. a professional certificate or masters degree). Of the $360,000, the partnership estimates that 50% will come from higher-ed clients, 40% from corporate clients, and 10% from K-12 clients.
According to the Booz Allen Hamilton white paper, Re-Learning E-Learning,[1] the compound annual growth rate for the three sectors is: higher ed = 25%, corporate=30%, and K-12=30%. These assumptions were used to estimate new-development revenue for each of the three sectors.
In addition, the partnership anticipates generating revenue through reuse and relicensure at a rate of 25% of cumulative revenue, from year to year.
——————————————————————————–
[1] Lee, Reggie with Sumita Bhattacharya, Tina Nelson, and Martin Kihn. “Re-Learning e-Learning” (Booz Allen Hamilton, 2002) <http://extfile.bah.com/livelink/livelink/108290/?func=doc.Fetch&nodeid=108290>.
4.1 Market Segmentation
The e-learning market continues to expand. According to ThinkEquity Partners and Eduventures, the global training and education market is a $2 trillion industry, with the United States accounting for 37.5% of the market.[1] The greatest demand for e-learning in the U.S. comes from the corporate sector, which according to Brandon-Hall realizes a “30 to 60 percent” savings over traditional classroom instruction.[2] Thus, businesses and corporations have invested—and continue to invest—in infrastructure that will require a steady supply of content.
Higher education and K-12 are substantial markets, as well—a combined industry representing over 100 billion dollars.[3] With the largest class of high school students in U.S. history graduating in 2009 and a brick-and-mortar system that cannot expand quickly enough to accommodate them, e-learning is becoming a necessity for institutions as much as it is becoming an expectation among students who are increasingly computer savvy.[4] Colleges and universities are also turning to e-learning as a way to increase their reach—to offer branded educational opportunities to students outside of their traditional geographical boundaries.
While the move to e-learning in the healthcare and government sectors remains slower than in the corporate and educational sectors, these industries are showing a strong interest nevertheless. According to Jones Knowledge, Inc. and CourseShare.com, the healthcare industry shows an 80% interest (with a 30% commitment) level while government shows 50% interest (with 39% commitment).[5]
[1] ThinkEquity Partners, Eduventures (quoted in “The Learning Markets: E-Learning” by eMarketer, Inc., 2003) <http://www.emarketer.com>.
[2] Adkins, Sam. “2002-2010 U.S. e-Learning Industry” (Brandon-Hall Marketing Series, 2002) <http://www.brandonhall.com>.
[3] Brandon-Hall (quoted in “The Learning Markets: E-Learning” by eMarketer, Inc., 2003) <http://www.emarketer.com>.
[4] Howell, Scott, Peter Williams, and Nathan Lindsay. “Thirty-two Trends Affecting Distance Education: An Informed Foundation for Strategic Planning.” The Online Journal of Distance Learning Administration (6.3) 2003 <http://www.westga.edu/~distance/ojdla/fall63/howell63.html>.
[5] Jones Knowledge, Inc. and CourseShare.com (quoted in “The Learning Markets: E-Learning” by eMarketer, Inc., 2003) <http://www.emarketer.com>. The ratio of interest to commitment is 75% to 64% in education and 80% to 60% in among corporations.
4.2 Target Market Segment Strategy
Third Degree I.D. is focusing on the corporate and educational markets because they represent the e-learning growth sectors. The partnership is well positioned to tap these markets locally and regionally. Savannah and the Lowcountry is experiencing genuine growth in high-tech businesses and is home to over 20 colleges, universities, technical institutes, and educational centers in higher education alone.
4.3 Service Business Analysis
The educational services industry is comprised of a large number of existing businesses competing in several segments. Historically, K-12, colleges/universities and corporate training providers utilized a traditional instructor-led approach for the delivery of short- and long-term courses. Over the last few years, e-learning has developed into a mature alternative to instructor-led course delivery, as it provides substantial cost savings in both development and delivery of the content and allows service providers to increase their geographical market.
4.3.1 Competition and Buying Patterns
Until recently, the competition in e-learning has been among large, proprietary course management or learning management system (CMS/LMS) vendors and IT-infrastructure companies. However, as less expensive systems and free, easy-to-install open-source systems emerge, the focus and interest is moving (appropriately) from delivery systems to the actual content delivered.
Third Degree I.D. is committed to leveraging the trend toward less expensive and open-source systems by emphasizing user-centered instructional design and by designing object-oriented content that facilitates easy installation and migration into almost any system. The company is dedicated to developing content that meets or exceeds interoperability (SCORM, OKI) and compliance standards (W3 Accessibility, ADA), so that clients can make better decisions about how to serve their content to virtually anyone.
However, the company has extensive experience with the most popular, proprietary CMS/LMS systems, and recognizes a continued investment by its clients in those systems. Thus, it also focuses on design and development for those systems (Blackboard, WebCT), while also maintaining interoperability and compliance standards that allow for easy migration of content (from system to system).
Strategy and Implementation Summary
Third Degree I.D. will focus on four e-learning markets– the corporate, educational, healthcare, and government sectors. While it seeks business from companies and institutions across the United States and abroad, it will make a concerted effort to develop long-term local and regional clients.
Third Degree I.D.’s target customers are the upper-level management of companies and institutions who are charged with the day-to-day operations of e-learning implementation and delivery.
5.1 Competitive Edge
Third Degree I.D. provides its clients the personal touch that large, proprietary systems vendors are ill-equipped to deliver. There is no universal recipe for a “good” instructional design. However, all effective instructional solutions share similar ingredients: a dash of market opportunity, a pinch of business goals, and a generous helping of user requirements. As its name implies, Third Degree I.D. is committed to “interrogating” the relevant stakeholders to determine the appropriate mix of ingredients.
Better questions yield better results. Third Degree I.D. will ask probing questions and deliver superior instructional solutions.
5.2 Marketing Strategy
Third Degree I.D.’s marketing strategy for the first year requires that the company:
- initiate as many personal contacts as possible
- demonstrate excellence with every personal contact
- identify six to eight key clients, and “win them over” through demonstration of expertise with limited initial client investment
- provide excellent custom development services with enthusiasm and a personal touch
- make a name for the company.
Identity Issues The first year of operations will present a marketing challenge for Third Degree I.D. The partnership and identity are newly formed; therefore, the company is relatively unknown in the marketplace. Although the founders have significant experience and many contacts within the e-learning and new media industries, they have worked mainly for corporate or institutional employers during the course of their careers. Therefore, Third Degree I.D. won’t benefit from immediate name recognition.
The challenge is mitigated somewhat, for name recognition isn’t especially prevalent among custom content developers in the industry—even among those who have been successful in the marketplace for years. Brandon-Hall surveyed over 200 chief learning officers, e-learning managers, and training directors to discover that the majority couldn’t name more than five custom content companies.[1]
Selling Services Another challenge stems from the nature of the business. In the first year, Third Degree I.D. will focus chiefly on marketing and selling instructional-design services, although the long-term plan is to obtain revenue from content re-packaging and re-licensure, at which time the focus will shift from selling services to selling products. Services are traditionally tough to market, as clients are wary of spending money for intangibles. They are more likely to buy from a well-known business that offers “good enough” service than to take a chance on an unknown organization that might provide exceptional service.
Photo processing is a suitable example. Many consumers routinely have their film developed at the local drugstore, despite the fact that they are often dissatisfied with the quality of the printing, the speed of the service, etc. In spite of their concerns, most consumers continue to use the drugstore’s service, rather than taking a chance on a non-chain photo lab, a mail-in service, or any of several less familiar options.
Selling Instructional Design (I.D.) The nature of the service provided by Third Degree I.D. presents yet another challenge in that “instructional design” is not exactly a household term. Although many organizations have experimented with e-learning, the field is still very young. Best practices are in their infancy, and every organization does online education a bit differently.
The market is dominated by a variety of course management system (CMS) and learning management system (LMS) vendors, each claiming their products will revolutionize the industry. Despite their lofty claims, most of these systems service providers are ill-equipped to help clients with their most daunting task—that of organizing, restructuring, and enhancing their content to provide meaningful web-based instruction.
Clients are overwhelmed by the choices and confused by the options.
Part of Third Degree I.D.’s strategy is to capitalize on that frustration as well as on the growing awareness of companies and institutions that they actually need instructional design services, especially the services of those who design and develop for the e-learning niche. In February 2004, Brandon-Hall published “Custom Content Developers: Comparative Analysis of 97 Outsource E-Learning Providers.” The study highlights and evaluates the best-known custom content development vendors in the e-learning marketplace. These are, arguably, Third Degree I.D.’s most traditional competitors. However, it also pays to consider a source that would normally be the last place one would look for competition—the clients themselves. When faced with unfamiliar tasks, clients often try to “do it themselves,” rather than take a chance on outsourcing services, which are traditionally difficult to quantify and measure.
To succeed in this environment, Third Degree I.D. will demonstrate, through cost analysis, that outsourcing content development to a well-equipped development house with streamlined processes is generally more cost-effective than in-house development.
The Personal Touch During the first year of operation, Third Degree I.D. will focus on developing relationships as a conduit for sales. Rather than mounting an advertising campaign that promotes a faceless service, the founders will strive to make as many personal or “insider” contacts as possible. According to Brandon-Hall’s custom content report, the majority of the companies surveyed “chose their outsource partner through simple ‘word of mouth or they selected companies that were in close geographic proximity to themselves.”[2]
Fortunately, Third Degree I.D. operates in a city that is known for its relationship networking. The founders have established and continue to establish their credibility among potential clients, particularly in the higher education and high-tech corporate sectors.
Higher Education Clients All of the company founders have worked for at least one institution of higher education in Savannah, and the company CEO, who has a 10-year employment history in Georgia at several colleges and universities, plans to extend that experience to another Savannah-based university in August. The potential clients for which personal contacts exist include:
- Armstrong Atlantic State University (Savannah)
- East Georgia College (Swainsboro)
- Middle Georgia College (Cochran)
- Georgia State University (Atlanta)
- Georgia Tech Regional Engineering Program (Savannah)
- Savannah College of Art and Design (Savannah)
- Savannah State University (Savannah)
- South University (Savannah)
- University of Georgia (Athens)
Other States:
- LaSalle University (PA)
- Matanuska-Susitna College (AK)
- Methodist College (NC)
- Tennessee Board of Regents Online Degree Program (TN)
- Thomas Edison University (NJ)
- Saint Thomas University (FL)
- San Diego State University (CA)
Another strategy of Third Degree I.D. is to read about and research the higher education e-learning market continuously. There will be no “cold calling.” Instead, institutions will be approached when there is a natural context for doing so. Institutions in likely need of instructional design products and services include those with high-volume e-learning programs, troubled or ineffective e-learning programs (that may be “on probation”), or ambitious curricula rollouts. Current candidates include:
- American InterContinental University
- Drexel eLearning
- Penn State World Campus
- University of Maryland University College
- University of Phoenix
- University of Illinois at Springfield
Other potential higher education clients may be non-American institutions wanting to establish themselves in the U.S. e-learning market and wanting to utilize designers and developers more familiar with regional accreditation and compliance standards. Countries with high-volume e-learning establishments, such as Canada and the U.K., stand to save substantially on design and development costs, as well.
Corporate Clients While Third Degree I.D. wants to build its reputation in education, it appreciates the need to keep a balanced client portfolio. Recognizing that industries fluctuate and that corporate e-learning is the sector predicted to show the largest growth, the company will work to establish a number of corporate relationships, as well, approaching potential clients through appropriate forums, and via a context that clarifies need (such as a news article or press release announcing a potential client’s new e-learning infrastructure). Third Degree I.D. has already begun to market its products and services to local companies—and particularly high-tech companies–through a number of forums, associations and businesses, including:
- Advanced Technology Development Center (ATDC)
- Coastal BETA
- Coastal Venture Investment Forum
- The Creative Coast
- OnPoint Digital
- Savannah Economic Development Authority
- Savannah Entrepreneurial Center
- Small Business Chamber of Savannah
It has begun to announce its products and services to the national and international communities through national and international e-learning forums and associations, including:
- eLearning Europa
- Eduventures
- The eLearning Guild
- World Wide Learn
Third Degree I.D. has already secured some limited “spec” work from the University of Ceramic Tile and Stone through The eLearning Guild.
Healthcare Clients Healthcare represents a small, but growing market (relative to the corporate and educational e-learning markets). Clients that are likely to develop e-learning infrastructures are large, university-affiliated hospitals that do a good deal of teaching and research. Third Degree I.D. has already established contacts with the University of Chicago Hospitals Academy and is planning to contact several of the local Savannah hospitals, one of which is Memorial Health, a “medical university” that has been listed as one of the “100 most wired hospitals” three years in a row by hospitalconnect.com.[3]
Government Clients Like healthcare, government e-learning is demonstrating some growth, especially in sectors where training is mandated by law. The recent Forecast of Contract Opportunities for FY 2004 issued by the Department of Homeland Security features a number of projects that will require training that is flexible, mobile and cost-effective. A number of the projects are also based in Georgia and South Carolina.
New and Key Clients While Third Degree I.D. seeks clients who have established e-learning programs and wish to improve upon or extend them, many of its potential clients (particularly the local clients) will be forging ground in unfamiliar territory as they move from traditional educational and training environments to the e-learning arena. They will be uncertain about the benefits of e-learning and protective of their subject-matter expertise. They will be wary of third-party content developers claiming to have the “answer to their prayers.”
The founders of Third Degree I.D. recognize the cautious environment they are likely to face and have realistic expectations for the first year of operation. The general goal is to establish a limited number of key clients and provide high-quality services and exemplary products. Key clients are best characterized as clients with genuine e-learning ambitions who are considering a number of large-scale projects and will require some training and maintenance. Key clients would be returning customers.
To acquire key clients, Third Degree I.D. is prepared to take limited-scope development projects at a reduced rate to prove its capabilities. For instance, the company may offer to develop a single course in a certificate program “at cost,” with the goal of winning a more lucrative through the demonstration of superior service and an exemplary product.
Seeking Excellence Third Degree I.D. will strive for excellence in all personal encounters and development transactions because it recognizes the validity of “the butterfly effect.” In much the same way chaos theorists posit that a butterfly flapping its wings in Brazil can affect global weather patterns, entrepreneurs know that a single client meeting handled with passion, enthusiasm, and excellence may be the catalyst for many future successful business dealings.
Looking Ahead After the initial year of selling predominantly services, Third Degree I.D. will reposition itself to market the products it has developed both as a result of the service deliverables and some in-house research and development. The central product is the “learning object,” a Flash-based course enhancement that raises the level of course engagement and interaction levels and raises the bar in the e-learning industry. The learning objects bring together high-quality instructional design with compelling, state-of-the-art media design. The objects are also exceedingly flexible, eminently re-purposable, and remarkably scalable.
Because the learning objects are likely to be copied quickly after their release, Third Degree I.D. will need to prepare a special campaign to become “the name” in reusable custom content development. The company will:
- write press releases
- get featured in articles and on websites
- register keywords with major search engines
- approach CMS/LMS vendors and professional organization about linking to our website
- advertise in industry-specific publications
- register with RFP exchanges
- investigate/initiate strategic partnerships
- attend trade shows (as exhibitors)
- present our solutions at conferences and seminars.
As the market demonstrates its needs, Third Degree I.D. will begin to narrow its focus, optimizing those products and services that are most useful, beneficial, and cost-effective. The company will invest in a market research strategy utilizing a number of evaluation and survey techniques to assure its understanding of the market and its staying power within that market.
[1] Chapman, Bryan. “Custom Content Developers: Comparative Analysis of 97 Outsource e-Learning Providers” (Brandon-Hall Marketing Series, 2004) <http://www.brandonhall.com>.
[2] Chapman, Bryan. “Custom Content Developers: Comparative Analysis of 97 Outsource e-Learning Providers” (Brandon-Hall Marketing Series, 2004) <http://www.brandonhall.com>.
[3] Hospitals Connect. “100 Most Wired.” <http://www.hospitalconnect.com/hhnmostwired/archives/100_most_wired.html>.
5.3 Sales Strategy
Third Degree I.D. promotes its products and services via its website and advertises strategically via portals and publications devoted to e-learning and distance education. Additionally, the company solicits likely customers through direct mailings targeted toward businesses or institutions that are planning large online program rollouts or that are experiencing accreditation problems related to e-learning.
5.3.1 Sales Forecast
While business began in May 2004 and will intensify through August 2004, September 2004 is the partnership’s first month of official operations. The sales forecast (from September 2004 to August 2005) represents a year of operations.
For the purpose of this plan, we treat our development costs as our staff costs. The only direct cost of sales listed here is software packaging, which we project at 5% of the sale price. Although this effectively brings our direct costs to zero, it reflects the fact that all three founding members will, in fact, be directly involved in the development of our products. Our staff costs are laid out in the Personnel Plan. On average, we’ll markup our development costs by 50% to set the final price.
During the first year of operations, all our sales will come from new content and curriculum development. We will strive to make this content re-usable and subsequently re-package it to meet the needs of additional clients. This should decrease our overall development costs in future periods. We plan that 25% of cumulative previous years’ sales will come from such re-used content.
The table below summarizes our sales forecasts.

5.4 Milestones
Our milestones for the initial period are summarized in the table below.
Web Plan Summary
The Third Degree I.D. website will help familiarize potential clients with the company’s unique approach to instructional design and e-learning content development. The website will establish Third Degree I.D. as a sophisticated yet approachable instructional design group with over 25 years of collective experience in educational new media development.
6.1 Website Marketing Strategy
Through sample learning objects and case studies, the website will showcase the type of detail-oriented instructional design that Third Degree I.D. provides. These examples will demonstrate how the company can leverage new media capabilities to create richer learning experiences. The work samples and promotional copy will help clients make the connection between engaging content and effective instruction, while emphasizing the company’s ability to identify and meet learning goals.
In addition to introducing prospective clients to the company, the website will provide supplementary information for those already familiar with Third Degree I.D., its products, and its services. Through a password-protected client extranet, the website will serve existing clients as a means to track project progress and to investigate new opportunities for curriculum development. Message boards in this portion of the site will offer a convenient location where clients can exchange ideas with project managers, subject matter experts, content developers, and instructional designers.
Internationally-known educational media organizations, such as the eLearning Guild, the Association for the Advancement of Computing in Education, and World Wide Learn, will provide cost-effective opportunities for exposure and drive traffic to the Third Degree I.D. website. Similarly, ads placed online in publications such as the Chronicle of Higher Education will allow the company to reach its target market and establish a network of links to the company website. These links will contribute to higher rankings in search engine result lists, which will lead to increased web traffic and name recognition for the company. Additional web-based advertising will be pursued as needed to improve company visibility and to generate interest in company services.
6.2 Development Requirements
The development of the Third Degree I.D. website will be the responsibility of the Chief Creative Officer. Tasks necessary for the completion of the site include:
- Domain name registration
- Purchase of Web hosting plan
- Development of site look and feel
- Backend programming and database integration for client extranet
The domain name ThirdDegreeID.com has already been registered and hosting has been established for the address. While the website look and feel will evolve over time, creating a web presence consistent with the company’s identity is an immediate priority. Equally vital to the success of the website as a promotional tool is the establishment of a collection of learning objects and other work samples. After meeting this need, the client extranet and other advanced features will be added to the site as resources become available.
Management Summary management summary will include information about who's on your team and why they're the right people for the job, as well as your future hiring plans.">
Third Degree I.D. is owned and operated by its founders. It is a small company with a lateral, non-hierarchical structure that cultivates mutual input and collective solutions. The company will operate with three full-time employees (also the founders) in the first year, hiring contractor and consultants as needed. As our business grows, we plan to add additional staff, as discussed below.
7.1 Personnel Plan
Third Degree I.D. will be formed with three executive partners, a Chief Executive Officer (CEO), a Chief Learning Officer (CLO), and a Chief Creative Officer (CCO). While a number of their job duties overlap, the CEO is primarily responsible for front-end consulting, planning, and project management, while the CLO and CCO are responsible for back-end product development, refinement, and implementation. The partners work together at promoting the business and managing office operations.
Susan Hines, CEO Susan has worked in the educational sector for twenty years. She has seventeen years of teaching experience across a broad range of institutions, including public and private universities, four-year colleges, community colleges, and college-preparatory facilities. She has taught at institutions both domestic and foreign, has been a traditional tenure-track faculty member, and has served—and continues to serve—as online adjunct faculty. Susan was Assistant Professor of English and Digital Art at LaSalle University from 1998 to 2000, before taking a job as an Instructional Analyst with the e-learning company Eduprise, Inc. (now SunGuard Collegis). She was hired by the Savannah College of Art and Design in 2002 to develop its distance education curricula and continues to serve as SCAD’s Director of Instructional Design. Susan holds several degrees in English Literature: a Ph.D. from Georgia State University, an M.A. from the University of British Columbia, and a B.A. from the University of Alaska.
Mona Meyer, CLO Mona holds a B.S. in Information and Computer Science from the University of California, Irvine and an M.A. in Educational Technology from San Diego State University. She has over twelve years experience designing and developing new media learning solutions for a variety of educational institutions and publishers, including: McGraw-Hill, Jostens Learning Corporation (now CompassLearning), Leapfrog, and the Savannah College of Art and Design. Mona specializes in object-oriented instructional design solutions that promote active collaboration. As instructional design manager for McGraw-Hill New Media, Mona led the development of hundreds of titles for the K-12 market in a wide variety of subject areas and played a crucial role in the design and development of the Codie-Award-winning McGraw-Hill Learning Network (www.mhln.com), a large-scale Internet education portal that offers interactive textbooks, multi-player educational games, and a suite of web-based classroom management tools.
Daniel Stanford, CCO Daniel holds a B.A. in Mass Communication and French from the University of Alabama and is currently completing his M.F.A. in Interactive Design at the Savannah College of Art and Design. An avid linguist and the recipient of a Capstone International Scholarship for study abroad, Daniel has spent semesters in France and Germany. He began his career in media design at the University of Alabama Center for Public Television, where he collaborated with producers to promote programs and distribute supplementary educational materials via the Web. He has since served as a media designer at the BLR Agency in Birmingham, Alabama, where he contributed significantly to the Birmingham Museum of Art’s Addy-award-winning website (www.artsbma.org). Five years of diverse media design experience led Daniel to SCAD, where he has put his combination of artistic and technical skills to use in learning object programming, graphic interface development, and project management.
Future Staffing As the client-base grows, the partners plan to hire a Technology Director who will work closely with the CLO and CCO to develop database-driven learning objects, as well as with the CEO to develop broader e-learning solutions, such as installation packages for open-source course management and learning management systems (CMS/LMS). In the first year, the partners will rely on outside consultants to provide information technology, instructional design, and media development support, as dictated by project load. As the client base grows and revenue is increasingly generated through content and technology re-licensure, the partners may add additional development staff to support project needs.
Financial Plan investor-ready personnel plan .">
Our financial plan is based on our assumption of achieving desired levels of sales. Our first-year revenues (projected at $360,000) will probably be insufficient to turn a profit in the first year. However, we plan to generate net profit starting in year two. Our initial cash reserve should be sufficient to keep us afloat during the first year. Subsequent years’ cash flows generate a cushion that will allow us to further develop our business.
8.1 Important Assumptions
Our main financial assumptions are summarized in the table below.
8.2 Break-even Analysis
The main development costs of the product will be our staff costs. Our variable costs are solely those related to packaging (5% of sales), since our staff costs are monthly payroll numbers, reflected in the P&L forecasts later in this document. Our Break-even Analysis is summarized in the table below.

8.3 Projected Profit and Loss
First-year revenue is generated primarily from curriculum and content development services. The first-year gross income goal is $360,000, which represents a development objective of at least three full MA programs or training programs (10 courses each) or a combination of comparable curricula. It is the intent of the partners that every development project will yield re-usable learning objects that can be subsequently re-packaged to meet the needs of additional clients. The partners also intend to solicit co-ownership agreements that allow Third Degree I.D. to re-license courses and curricula to institutions other than those for which they were first developed. The reusable learning objects and content re-licensure will provide a low-investment revenue stream that will contribute an increasingly large percentage of gross corporate revenue in subsequent years.
On the expense side, our staff costs are going to be our main cost. These are, technically, are our product development costs, as all three partners will be directly involved into the development of products for our clients. During the first year, we also plan to utilize services of outside consultants and contractors on the product development side. As stated earlier in this document, as our business grows, we plan to add additional staff. We also plan to utilize our CEO’s home office for the remaining part of 2004 and move into a new office space in January 2005.
Overall, we plan to end our first year of operations with a loss. Subsequent years wil show increasing profitability, as summarized in the table below.

8.4 Projected Cash Flow
Our cash plan is based on the assumption that we meet our sales objectives and collect receivables within 60 days. This will be especially critical during our first year of operations, during which our cash balance will also depend on the initial cash contributions of the three founding partners and a two-year $30,000 loan. The combination of the two should be sufficient to keep our cash balance positive during the most critical first year of operations.
The table below summarizes our cash flow forecasts.


8.5 Projected Balance Sheet
The table below summarizes our forecasted balance sheet. For the first two years of operations (i.e., until we generate a sufficient cash reserve), receivables represent our main current asset. Our fixed assets should be mostly limited to the computer equipment that we depreciate over 5 years. With manageable liabilities, our accounting net worth should steadily grow over the projected period.
8.6 Business Ratios
The table below summarizes our key business ratios, with comparisons to standard ratios for our industry, Educational Computer Software (SIC Code 7372.9903).

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
This website uses cookies to improve your browsing experience and help us with our marketing and analytics efforts. By continuing to use this website, you are giving your consent for us to set cookies.
How to Launch an EdTech Startup in 2024?

Key takeaways
Booming, promising, disruptive. It’s all about the market you’re going to enter. Find out how to start an EdTech startup in 2023 and what you can claim.
$7.3 trillion is a figure the global education market will reach by 2025. Explore the market trends to set out your niche.
The EdTech sector doesn’t differ: ups and downs are everywhere. Know more about successful startups that reached the stars and the top failures you can avoid.
Take a look at the monetization models and growth factors that are feasible in the education sector.
Clear up how to get funded and build relations with investors.
There’s something we can’t keep back from you: you’re the one who can disrupt the EdTech industry. You’re on the way to starting something new to deliver the new-founded society in the digital epoch. In the epoch, when teachers with a digital teaching experience are becoming ranked higher than orthodox, who are data-driven decision-makers in their pedagogical approach.
You’re at the point ready to go ahead.
Excitement is mixed with uncertainty about:
- Where to set out from?
- How do you plan steps when you want to start an education startup like Byju’s , the biggest unicorn in India, or Coursera is in a sweet spot regarding EdTech flourishing?
- What about money and how it be noticeable to investors?
We’ve got it. In this blog post, we’ll take you through each of those steps in a bit more detail. We will finish by clearing up how you can get what you need in one place with Aimprosoft. Let’s kick off things.
What is EdTech?
EdTech, short for Educational Technology, refers to using digital tools, platforms, and technologies to enhance learning and educational processes. It covers a wide range of applications, including online learning platforms, educational applications, virtual reality tools, gamified learning systems, and more. EdTech represents a significant business opportunity as it meets the growing demand for innovative and personalized learning solutions.
Later in the article, we assess the global EdTech market, which is proliferating due to the growing adoption of digital learning, the need for remote and flexible learning options, and the desire to improve learning outcomes.
Current vision about an EdTech concept

What is an EdTech company?
The roots of what we take as a core of elearning go back to computer-based training that emerged in the 1970s. EdTech is often synonymous with online education, but in fact, this very concept includes an entire set of digital tools aimed at improving the efficiency of the educational process.
If you have an entrepreneurial spirit and want to apply your gust to education, you will be named edupreneur, an EdTech entrepreneur.
In addition to online schools, interactive courses, and educational applications, there are vendors of electronic systems for educational institutions, training equipment, VR simulators, platforms for corporate training, and other products on the market.
Sorting out, EdTech refers to the usage of technological power to improve or manage the learning process while elearning is a way of internet-based learning as an alternative to a traditional classroom.
EdTech market is on a roll: why you should start an EdTech company in 2023
Education is one of the world’s largest industries, accounting for over 6% of GDP. Holon IQ analysts predict the total volume of the global education market will reach $7.3 trillion by 2025.
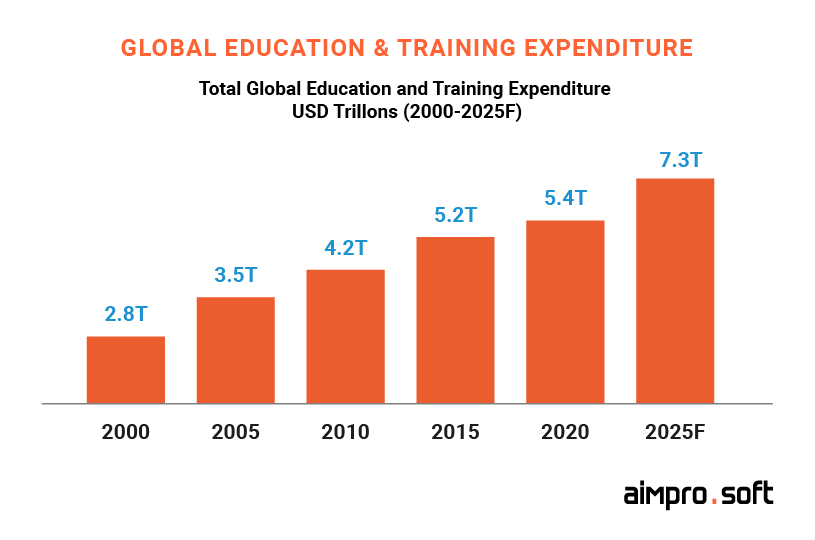
Getting used to the thought that education will be a $7 trillion industry in just three years, you are on the clock to start an educational technology company. Let’s go through the chief movers and shakers that set the pattern for change in the sector.
Education throughout life
People want that learning to be not a tedious, necessary measure but an entertaining process. It is possible to make education this way and at the same time attractive to investors with the help of technologies that are available in their variety on the market.
Lifelong learning brings grown-ups:
- Knowing a little bit about everything to be market adaptive
- Spotting new opportunities to fill knowledge gaps
- Widening career perspective with adjacent skills
Self-motivated acquisition of knowledge during life by interests or for the sake of a profession is what people want. For adults, the reasons can be deepening knowledge in the profession, gaining new experience in hobbies, experimentation, and an interest in discovering something new to be proud of their achievements. Children are interested in everything if this “everything” is playfully delivered and fascinating. One thing is clear, an agiotage around lifelong learning catalyzes EdTech startup ideas, and following one of them to create an elearning website is never a bad choice.
Picked academic demand for digital education
There were preconditions for the digitization of education long before schools closed their doors for in-person instruction and moved classes online in the spring of 2020.

During COVID-19, K-12 and higher education sectors experienced the most extensive growth because people had to master new technology tools to continue the educational process:
Teachers had to instruct students with proper engagement on a computer from their living rooms in a way unfamiliar to the majority.
Students were not wholly prepared to fully switch to the remote mode suffering from a lack of motivation despite being native to technology.
Parents wished to get a piece of relief by delegating efforts to technology to take control of the learning process.
Schools started hunting for tools to have a go at distance learning.
Portable device adoption in education was growing demonstrably, mostly due to new opportunities from the internet connection.
Even though digital adoption snails comparatively to other sectors globally, it is forecasted that education spending for digitization will reach $404 billion by 2025. The new technological landscape in K-12 and higher eds raises an ocean of new opportunities for startups to meet the needs of all stakeholders beyond creating a language learning app .
Investors adore EdTech
$10.76 billion is a figure for record-breaking venture capital investments that took off at an unprecedented clip by 2022.
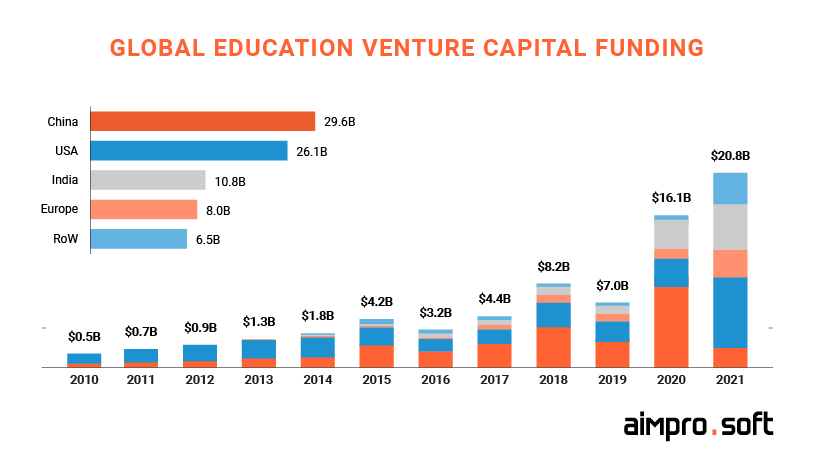
Yet on a pre-seed round, figures count $2.1 million to support Maqsad, a startup from Pakistan, aiming “to make education more accessible to 100 million Pakistani students.” It is a good ground for R&D and growth activities, isn’t it?
Leap, a two-year-old US-Indian startup focused on helping students with abroad education issues, raised $75 million in total in 2021 in Series B and C. Apart from intensive investors Sequoia Capital India and Jungle Ventures, Owl Ventures, and Harvard Management Company joined the forces to support the EdTech undertaking, finding it promising.
Another example, Panorama Education, serves 25% of American schools, having backed with $60 million in funding to provide an education software platform helping educational institutions to understand their K-12 students with surveys. In its turn, NoRedInk, a San Francisco-based startup, got a $50 million Series B support to help students get back on track with writing skills, which demonstrates the renewed interest of investors in the sector.
Zoomers are your trend-setters
“We should be the Zoomers” by the opinion of Megan Gerhardt , professor of leadership and management at the Farmer School of Business at Miami University. Named by Zoom and constrained by pandemic communication that was the most demand during forced home isolation in 2020, the Zoomers are ready to be educated in a native to their virtual life in a social network way where they are always on their chatting.
To back it up with supporting evidence, Screencast-O-Matic recognized that technology explosion happens with youth first bringing up field professionals in good time. With orientation on students’ lifestyles, a company started a platform enabling both teachers and students to get interactive communication via video streaming with screen sharing in their classrooms.
A platform where educators can adapt their orthodox approach to delivering exciting, immersive content instead of dull lectures provided in a native Zoomers format is worth considering if you want to launch an EdTech company.
People hunger for accessible and affordable education
While the prices for college tuition and fees increased with a pretty hefty rate of 32% for the period 2011-2019, according to the US Bureau of Labour Statistics , housing and textbooks, for instance, may claim for a significant budget share of the families.
Deliberating launching an EdTech startup, you can do a favor for millions of families. Be it a MOOC or digital tutorial hub, you can provide a less expensive offering combined with greater accessibility than a traditional one if you create a website like Udemy , for example. By betting on digital, you can attract the target audience with a quick update, revision, and distribution of educational materials as well as affordable course taking.
30 EdTech unicorns worldwide
Unicorns are young startups that were able to reach a capitalization of $1 billion in a short time. The term itself was coined by the founder of the American fund Cowboy Ventures Aileen Lee to underscore the rarity of the phenomenon in 2013.
Note: while this overview was being composed, the world got richer for one more unicorn.
Among over 800 unicorn companies, 30 are from the EdTech sector with a collective valuation of $89.6 billion, which shows the big time for the undertaking. The latest members of “the nine zeros club” are Emeritus with certified education from top-tier universities, upGrad global online higher ed to accelerate career, and GoGuardian for schools’ management.
Tutoring, language learning, corporate learning, test preparation, online post-secondary and curriculum, and career planning are impressive but far from the full list of clusters where you can find yourself hitting the unicorn list.
Book a consultation with our EdTech specialist to break free of the moment.
EdTech startups that took chances and succeeded
Outschool, Cambly, Labster, and other startup EdTech companies are growing as mushrooms after the rain. To stir you up, we’ve covered the three most inspirational startups from India, USA, and China.
Their path is a splashy story. Founded in 2011 by a married couple Byju Raveendran and Divya Gokulnath, a Bangalore-based educational platform, Byju’s provided learning programs for K-12 students. Its precise personalization and adaptation to the style and pace of every single student, paired with a strong leadership vision, allowed them to become a decacorn with a $16.7B valuation after the latest investment round with $150 million Series F in September 2021. Byju’s revenue from operations reached 82% in FY2020. The company continues attracting investments meanwhile acquiring tech companies to extend its portfolio.
Let’s start signing an NDA and proceed with a discussion.

While 2020 was a disastrous year for most companies, Chinese startup Yuanfudao hasn’t just grown and has become super successful. Its valuation reached $15.5 billion, experiencing a 200% year-over-year revenue increase, which made the project one of the most expensive in the world in online education. Starting with the idea of helping future civil servants prepare for exams, Fenbi (former name) has gradually grown into a multifunctional provider of preschool, adult, and K-12 online education services known throughout China and beyond. The last round brought them $300 million, and Yuanfudao announced sponsorship of the 2022 Beijing Winter Olympics. Selling live courses can be pretty profitable, right?
Articulate gave it another shot. Over 112,000 organizations, among which the Fortune 100 reps use the platform to create online courses for corporate training. The company initially took off with the life savings of CEO Adam Schwartz in 2002. The first outside investment came in July 2021 in a hefty amount of $1.5 billion, evaluating the company at $3.75 billion. A plug-in for PowerPoint turned into a software service with 119 million learners from 161 countries worldwide, proving any simple idea may have a big future. Articulate now dominates in course authoring apps building their business in the remote working model.
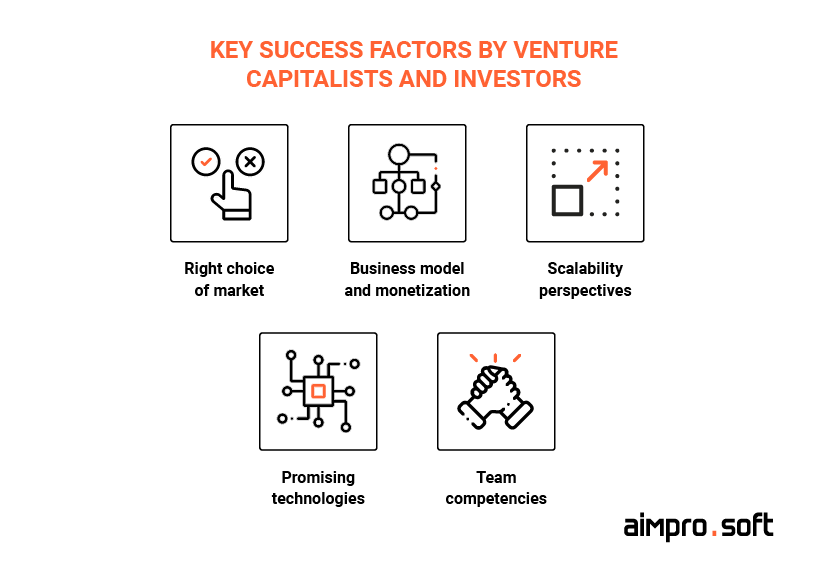
As you can see, the landscape of education startup ideas and their geo widespread are broad. There is a niche in any corner of the world for creating an educational technology company that can become a leader in its segment. Begs the question: how to launch an EdTech company and grow faster?
7 tips on how you may grow your startup faster (Infographic)
Getting into business throws down the gauntlet. You’re in. A series of decisions and overcoming challenges is here to stay. On the race of “uppy-righty” charts in your pitches, follow these feasible tips.

Expect big things for yourself
Plunge into your venture with the top of your head like you’re backed by the strictest coach forcing you to focus only on the win. There can be no failure in your mind.
Explore your market soundly
You should know the barriers and openings, the bottom and ceiling of your idea. Evaluating the market on time prevents a number of potential hindrances.
Sail in the same boat with your team
The first years of your child are the most crucial. So you, as the caring parent, should be ubiquitous and close at arm’s length to your team. At least you’re sailing in one vessel.
Keep this in mind, but better write it
Guidelines and manuals will do a favor in the routine delegation to your employees and help streamline the growing processes.
Be ready to pivot at any time
Starting from a single igniting idea so demanded now, you can come up to the broader portfolio or swerve forced by rapidly changing market conditions.
Treat your customers like your mom does
Assuming is great, but being in your customers’ shoes to experience what they exactly need is for what you are having a go at. Over-proud knights move to nowhere.
Turn your passion into a business
Doing hateful things kills. Even if they are profitable. You’re on another path. So separate the wheat from the chaff to unlock something really great for the world.
How to monetize your EdTech app?
Business is about money, right? How adorable, full of passion, and sprinkled with a starlight duster your business idea is, it may cost nothing without monetization. So stick with us here to know how to make money with your startup.
Coursera demonstrated the freemium model with a paid advanced plan being given a taste by many.
The paid subscription works well paired with a free trial when users can evaluate the service before turning to it for a long time. Peergrade, Mystery Science chose it.
If you want to create an EdTech company, consider a marketplace approach of Udemy that takes a 50% share of the creator’s revenue with a free course posting.
The product business model of Chegg allows making money by offering to rent digital and hard-copied textbooks.
Advertising is not new in a startup monetization, however, an ad-free subscription may bring an additional revenue stream.
The institutional approach focuses sales on school administrators if they are your target audience. Market reps are IntelliBoard and Schoolzilla .
The consumer approach of Scholastic uses schools as a lead generation channel allowing using an app for free in school and charging for home usage.
The partnership model demonstrated by GoNoodle allows getting financial assistance from sponsors promoting children’s health.
The B2B/B2C sales model of A Cloud Guru s oriented toward engineers and engineers-in-training who want to deepen their online cloud computing skill set.
Within the startup space, there are many more wide variants than wherever. We just opened the door slightly to clear up the opportunities. Probably, while we’re discussing the topic, some entrepreneur is inventing something significantly different right now. Be that one!
Where to take funding for your EdTech startup?
Angel investors.
In post-pandemic investors activated in funding EdTech startups seeing it as a global catalyst of eLearning solutions. You can reach out to someone in the space directly or pitch on AngelList , Gust , Angel Investment Network, or U.S. Angels Investors.
Venture capitalists (VCs)
A global EdTech venture capital was $16.1 billion in 2020. VC investors and firms are interested in growing unicorns, so they invest large amounts in startups to get enormous returns back. Apart from money, investors can mentor you on business and introduce you to their network, which is also a valuable gesture. You will give them a share in your company and a voice of influence in key decisions. Owl Ventures, Rethink Education, GSV Capital, and Reach Capital are high-profile EdTech backers.
Crowdfunding
Crowdfunding is a popular way to get your first money to create an EdTech company. It refers to small contributions from different people who expect a feasible bonus from you once the product or service is live. Appealing that control over the business is completely on your side, unlike with investors. Indiegogo , Kickstarter , and SeedInvest Technology are platforms where you can count on donations from individuals.
Bootstrapping
If you have some money and want to use it as an initial source of venture capital to build an EdTech startup, it refers to bootstrapping. Remember above we narrated about Articulate , an EdTech unicorn that bootstrapped on its own? Yes, you can take total control over your business, decide on your own and be independent of someone’s “making the rules.” Self-made entrepreneurs are a rare breed — a few resort to the use of individual capital, relying more on venture funding in startup booming times.
Corporate and government grants
Besides the most-talked-about investors, governments and corporations put education at the forefront. You are free to apply for grant funding to high-profile funds and programs. GrantWatch , GetEdFunding, Candid are databases with listed corporate grant funds to develop ed-tech innovations. As a case in point, Central Square Foundation currently supports Khan Academy and Nalanda Project in developing innovative products aimed at students. We believe that everybody can find something to start. Where there is a will, there is a way.
Accelerators and incubators
LearnLaunch, BoomStartup, and NYU Steinhardt Edtech Accelerator have EdTech-focused mentorship programs with up to three months duration for mostly early-stage startups. You have chances for $50k-170K funding to get your startup EdTech up and running. Normally, they take a small percentage of equity in your new company. Mentor support and intensive coaching with industry experts will immerse you into a business development atmosphere to reach your business goals professionally and swiftly.
5 failed EdTech startups
Lifespan: 2009-2013
Failure: Competition, ignored digital trends
Kno was focused on delivering mobile learning hardware and double-paneled e-textbooks. Even pivoting to digital textbooks, Kno couldn’t take the competition with the emerging iconic iPad anymore. The final straw was Apple’s entrance into the educational sector with textbooks.
SchoolGennie
Lifespan: 2013-2014
Failure: Lack of market experience, and incorrect budget distribution
SchoolGennie introduced an ERP for Indian schools to help make better decisions on schools. But they didn’t test their product-market fit. The lack of industry mentors led them to improper distribution of the budget and a number of failed pivots.
Lifespan: 2010-2013
Failure: Incomplete marketing and revenue model, risks ignorance
Tutorspree was conceived as an algorithm-based platform for students seeking tutors in the area. A Y Combinator-backed alumnus, it had to wind down because of high competition, charging 50% of tutor fees, and seasonal demand.
Lifespan: 2010-2014
Failure: Failed business model, no market demand
Readmill is a mobile app for reading that allows sharing highlighted extracts from ebooks and following books, users, and even authors. Pivoting from social reading to the book subscription model turned unviable for them.
Lernin Games
Lifespan: 2017-2019
Failure: Wrong monetization and growth strategy
Lernin Games introduced games for toddlers on a free basis shifting to a B2C subscription app with belated testing. It would have saved them to be leaner in office and team spending.
You see, there are as many as year-olds and five-year-olds experienced companies, funded well and fervid enough that closed at least, not managing to cope with challenges. Everybody does wrong things. We are all not perfect. But you can always lean on experienced partners like Aimprosoft.
Why EdTech startups fail
According to CB Insights , startups shut down mostly because of lack of capital for R&D, wrong market choice, red ocean of competitors, faulty business models, legal complexities. Sure, there the grey list of failures is much longer and so many challenges such as burnout, crashed pivot, discord among team members and investors can lie in the wait for startups as well.
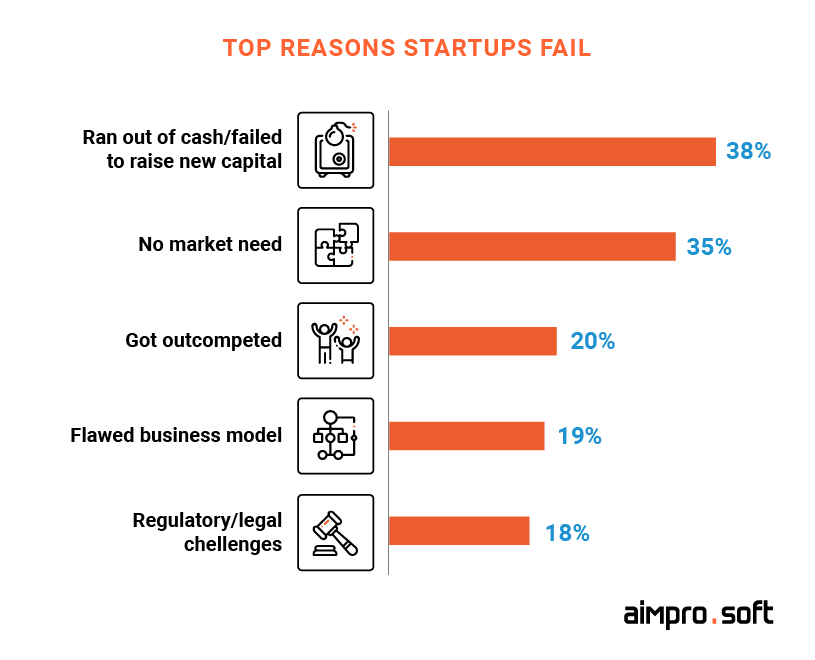
Forewarned is forearmed. Even if you have an awesome idea and see it pretty clear how to create an EdTech startup, you’d better check the following cases of failures of EdTech startups before kicking off.
Want to know more about creating an educational app?
Read article
Steps on how to start an EdTech startup
1. explore the edtech market: your niche might be the most problematic group of customers.
First and foremost, study the market, big players, and main competitors in your niche. Consider diving into a blue ocean of opportunities to create your own market. Define your solution statement addressing one niche to solve one exact problem. AI-based algorithms, ML for swift decision-making, immersive learning, and multi-layer management tools, to name a few, are examples of lines you can go with, be it a tool for parent-teacher communication or a tuition solution for disabled kids.
Recently, an edutainment platform, MasterClass, pivoted with a focus on employers to appeal to the motivation of star employees, enabling chat with a celebrity coach. A niche can be hidden in the niche.
The hottest EdTech trends in the industry you can find in our article.
2. Come with a time-relevant business strategy
Hyper-focus on building a profitable rather than fundable company. It’s never excessive to recall Articulate, whose founders were centered around their idea and market demand in place of bragging about the money raised, and after 20 years, attracted over $1,5B. Business models and value propositions are two interconnected things that have to be defined once you get down to business strategy development.
Changing the way of monetization is considered normal when entrepreneurs pivot to respond to market changes. So a cadence of timely actions with a couple of backup plans up your sleeve is what you need to start an EdTech business.
3. Pay attention to marketing across all stages
Edtech startups should pay attention to marketing for several reasons.
- Increase brand awareness;
- Reach your target audience;
- Differentiate yourself from your competitors;
- Stimulate user engagement and adoption;
- Establish thought leadership;
- Fundraising and partnerships support.
As for when to focus on marketing, it is recommended for EdTech startups to include marketing in the early stages of development. For example:
- At pre-launch, build anticipation and create hype before your product or EdTech platform officially launches.
- A product launch needs a strong marketing push through targeted advertising, content marketing, influencer partnerships, and media outreach.
- A product update or improvement is a great infomercial when marketing can grab the attention of existing users and new users who may have previously been hesitant.
- Expansion into new markets or consumer segments also requires marketing efforts that can be focused on introducing your solution to these new audiences.
- Remembering about yourself during seasonal or academic calendar events can help you increase visibility and attract attention.
4. Invaluable tech resources: find your development partner
There is nothing specific in EdTech at first sight. However, expertise in the domain of team members or your technology partner can extremely speed up involvement in the project, qualitative product delivery, and growth. Building an in-house team or outsourcing a piece of development scope to a vendor like Aimprosoft, qualified in the education domain, ensures that you are surrounded by like-minded, robust teammates. This mini checklist will help you define your vendor:
- EdTech expertise — professionalism is evident from the first communication, even if a company can’t disclose clients’ names.
- Seniority level of staff — at Aimprosoft, 90% of developers are of senior level.
- Readiness to get to work — look for experts in the domain and related technologies; the right vendor has both categories.
- Familiarity with a startup pace — essential to take the same lead.
- Master of the modern tech stack — pay attention to the vendor’s service offering and media presence, sharing an opinion on tech solutions.
5. Form a legal entity and register for taxes
Startups should create a legal entity as early in their business journey as possible once they have a clear vision, a viable business model, and the intention to operate as a separate legal entity.
- Liability protection: By operating as a separate legal entity (Limited Liability Company (LLC)), the business assumes its liabilities, reducing personal risk for the founders.
- Investor requirements: Investors generally prefer to invest in an established legal entity that provides a transparent ownership structure and protection for their investment.
- Tax considerations: Depending on the jurisdiction and the type of legal entity chosen, there may be advantages in tax planning, deductions, and exemptions available to the business.
- Long-term growth and scalability: Establishing a legal entity early on provides a solid foundation for hiring employees, contracts, partnerships, and other business activities.
6. Open a business bank account
Startups open bank accounts as soon as they are legally registered. Legal clearance includes registering the company, obtaining the necessary licenses and permits, and obtaining a tax identification number. With a dedicated bank account, you will be able to manage and track funds effectively. If you have received funding from investors or partners, having.
Consider factors such as account maintenance fees, transaction limits, online banking capabilities, customer support, and any specialized services that may be relevant to your business.
7. Think big, start small: progress over perfection with an MVP
Over a decade, the startup world has been worshiping a Lean Startup’s concept introduced by Eric Ries. You can build a minimal viable product (MVP), launch it to measure the feedback from first adopters, and go to the entrepreneurial learning of product progress with customers. In the circumstances of utmost uncertainty, which launching a startup is, this approach ensures against a mountain of mistakes related to customer needs, positioning, strategy, etc. Multiple iterations with improvements are way better for trying your unique EdTech business ideas than nailing a product that nobody has wanted to use for years.
8. Analyze your results to gain valuable insights
Edtech startups must analyze the results of their efforts to gain valuable insights, evaluate their performance, and make data-driven decisions. Here’s why and how EdTech startups should analyze results:
- Measure performance by key performance indicators (KPIs) such as website traffic, user engagement, conversion rate, and cost of customer engagement; you can assess the impact of your marketing efforts.
- Identifying areas for improvement will allow you to discover bottlenecks, gaps, or inefficiencies in your marketing processes and improve them.
- Refine your target audience and messages, evaluating the effectiveness of different marketing channels, message options, or audience segments.
- With an understanding of the return on investment (ROI) of various marketing activities, you can optimize your spending and focus resources on the strategies and channels that produce the best results.
- Analyzing the results gives you the data and insight to make strategic decisions.
How Aimprosoft can help start a survival EdTech business in 2023
Our clients come to the conversation with plenty of ideas that ignite both sides. That is the thing we love startups and are happy to help set out on a journey.
To make the first move right with a confident assistant is key to the successful delivery. There is a matrix of rules and regulations for protecting user data privacy, which we take into account elaborating on the EdTech app development strategy. Following the ‘language of education’ tone helps us deliver more intuitive user-centric experiences to create an educational app during the design stage. Swaying your MRR and ARR also starts here.
Backed by a trusted edtech software development vendor is a halfway win. We can help EdTech companies opt for the right technology, implement it, and maintain to stand customer influx and scale up on time. By delivering LMS and educational solutions for students, we’ve witnessed the very eyes of how a small idea was growing into an investor adorable product.
In pursuit of growth, Aimprosoft is next to you, ensuring the integrity of the delivery-growth space.
Let’s do it.
Experts and analysts around the world agree that online education and other EdTech segments will continue to grow exponentially over the next five years. Global challenges are pushing the industry towards change, and the pandemic is not the only one. Thus, it is known that by 2050 there will be two billion more graduates of schools , universities and other educational institutions in the world than today. The educational system must cope with the growing workload from year to year meanwhile. Write to us to find together how you can help the world with education.
STEAM (science, technology, engineering, the arts, and mathematics) forms the space of invention being one of the most demanded educational directions. Since they are quite complicated subjects, technology may help teach and learn in a more effective way.
There is a belief In Silicon Valley that a good entrepreneur is the one who failed more than once and got up off their knees to continue. There is always a chance for mergers and acquisitions if you decide to share the path and join your efforts in a partnership with other companies from the sector.
Uncertainty is the most typical thing when a business takes its first steps. We’d be lying if we said that you could avoid any risks. Natural disasters, an unexpected pandemic, a sharp turn in market demand to name a few, all can affect your business. However, implementing a risk management plan, at least, may protect the future, preventing you from various potential risks or events before they occur.
EdTech companies use a variety of revenue models to generate profits and sustain their operations. Here are a few common ways: subscription or license fees, the Freemium model, partnerships with educational institutions (B2B), content sales, advertising, and sponsorships, providing professional development and training for educators, data and analytics services, grants and funding from government agencies, foundations, venture capitalists or angel investors.
Creating an EdTech startup involves identifying a specific educational problem or need that your startup intends to solve, conducting thorough market research, developing a unique value proposition and creating a minimum viable product (MVP) to test and validate your idea, securing funding through investments, grants or bootstrapping, building a talented team with expertise in technology, education, and business.
There are several reasons why EdTech startups can fail. Here are some common factors that contribute to their failure:
- Lack of market fit;
- Lack of differentiation;
- Limited scalability;
- Inadequate monetization strategies;
- Ineffective user attraction and retention;
- Lack of funding or financial inefficiency;
- Regulatory and compliance issues;
- Limited partnerships and collaborations;
- Technological challenges;
- Lack of long-term vision and ability to adapt.
In just two years, education will be a $7 trillion industry. The global educational technology market is expected to grow from an estimated $74.2 billion in 2021 to $288.4 billion by 2031, representing a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 14.5%. So if you are planning to launch an ed-tech startup, now is a great time to do so.
Start by identifying key roles and necessary skills such as technology, education, marketing, and business expertise. Look for people with a passion for education and a desire to impact the industry positively. Hire candidates with relevant EdTech industry experience or a deep understanding of education needs. Use B2B platforms with reviews like Clutch, GoodFirms, The Manifest, and others to pick a development team from one vendor in one place. Conduct thorough interviews with vendor candidates, assess their alignment with your company’s values and vision, and make sure they have the proper knowledge and experience. Create a culture of collaboration and support to attract and retain top talent.
You can start with your resources or bootstrapping. Consider crowdfunding platforms and pitch competitions to raise funds from the broader community. More traditional traditional traditional funding sources include venture capital firms, angel investors, and government grants. Explore EdTech-focused funding opportunities such as incubators, gas pedals, and industry funds.
First and foremost, you should have a clear definition of your target market and an understanding of their needs and pain points. Create a compelling brand story that resonates with faculty, students, or administrators. Use social media, content marketing, and email campaigns to build awareness, engage audiences and drive conversions. Don’t neglect to collaborate with influencers, establish strategic partnerships and attend industry events to expand your reach. Developing an effective marketing strategy for your education technology company, once efforts are made, monitor and analyze marketing efforts, optimize campaigns based on the data, and continually refine strategy for maximum impact and sustainable growth.
Mariia takes marketing with a passion, being engaged in the occupation for several years. Flying up the ladder, she experienced sales, business development, and project management, ultimately favored marketing as a result. Having a strong understanding of the B2B partnership style, she is adroit with marketing best practices in handling challenging tasks.
Julia is a confident master of the writing craft. She combines a unique experience across marketing and sales, which enables her to convey the message. Julia is extremely knowledgeable and open-minded, so she has an extensive skill set that includes conducting thoughtful and effective research and gathering valuable information. It enables Julia to grasp the entire business picture and create content brilliantly for the high-tech sector and B2B needs. Julia also delivers Aimprosoft's PR activities, managing cooperation with media and developing the company communications system.
We are here to assist with your questions. Write us a message, and we will get back to you shortly.
The form was submitted successfully. We will contact you shortly. Meanwhile, we suggest checking out what our clients say about software development with Aimprosoft.
Featured in

You may also want to read

How to Hire JavaScript Programmers: Tips to Help You Find the Ideal Specialists for Your Project
Computer Vision in Healthcare: Revolutionizing Disease Identification to Human Doctor-Level in Medical Imaging

Real Estate Document Management Software: Which is the Best?
Business Plan Template for Education
- Great for beginners
- Ready-to-use, fully customizable Subcategory
- Get started in seconds
Starting or expanding an educational venture can be an exciting yet challenging endeavor. To ensure that your goals are clearly defined and your strategies are solid, you need a comprehensive business plan. That's where ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Education comes in!
This template is perfect for education institutions, entrepreneurs, or investors who want to outline their goals, strategies, and financial projections. With ClickUp's business plan template, you can create a roadmap for success and attract potential stakeholders to support your educational venture.
This template includes everything you need to:
- Define your educational goals and mission
- Develop strategies for growth and sustainability
- Create financial projections and budgets
- Outline marketing and outreach plans
- Identify potential risks and mitigation strategies
Don't miss out on the opportunity to bring your educational vision to life. Get started with ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Education today!
Business Plan Template for Education Benefits
A business plan template for education offers a multitude of benefits to education institutions, entrepreneurs, or investors looking to start or expand their educational ventures. Some of the key benefits include:
- Providing a clear roadmap for success by outlining goals, strategies, and financial projections
- Attracting potential stakeholders, such as investors or partners, by showcasing a well-thought-out plan
- Ensuring alignment and focus by defining the mission, vision, and values of the educational enterprise
- Analyzing market trends and competition to identify unique selling points and opportunities for growth
- Guiding resource allocation and budgeting decisions to optimize financial sustainability
- Facilitating communication and collaboration among team members and stakeholders
- Supporting decision-making processes by evaluating risks and creating contingency plans
- Enhancing credibility and professionalism for grant applications or funding proposals
- Monitoring progress and tracking key performance indicators to measure success and make adjustments as needed.
Main Elements of Education Business Plan Template
ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Education provides all the essential elements to help you create a comprehensive and strategic roadmap for your educational venture:
- Custom Statuses: Track the progress of your business plan with statuses such as Complete, In Progress, Needs Revision, and To Do.
- Custom Fields: Utilize custom fields like Reference, Approved, and Section to add important information and categorize different sections of your business plan.
- Custom Views: Access different views to organize and analyze your business plan, including Topics view to focus on specific topics, Status view to track the progress of each section, Timeline view to visualize milestones and deadlines, Business Plan view for a holistic overview, and the Getting Started Guide view to help you navigate through the template.
With ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Education, you can streamline your planning process, collaborate with stakeholders, and ensure a clear path to success for your educational venture.
How To Use Business Plan Template for Education
If you're in the education industry and need to create a business plan, our Business Plan Template for Education can help guide you through the process. Follow these four steps to effectively use the template and create a comprehensive and actionable plan for your educational institution:
1. Define your vision and mission
Start by clearly articulating your vision and mission for your educational institution. What is the long-term goal you want to achieve? What values and principles will guide your organization? By clearly defining your vision and mission, you'll have a solid foundation for your business plan.
Use a Doc in ClickUp to brainstorm and outline your vision and mission statements.
2. Conduct market research
To create a successful business plan, you need to have a deep understanding of the market and the competitive landscape. Research trends in the education industry, analyze your target audience, and identify your unique selling points. This information will help you position your institution effectively and develop strategies to attract and retain students.
Use the Table view in ClickUp to organize and analyze your market research data.
3. Develop your curriculum and programs
The curriculum and programs you offer are crucial to the success of your educational institution. Define the courses and programs you will offer, outline the learning objectives, and design a comprehensive curriculum that aligns with industry standards and meets the needs of your target audience.
Create tasks in ClickUp to outline each course and program, assign responsible team members, and set deadlines.
4. Create a financial plan
A solid financial plan is essential for the sustainability and growth of your educational institution. Determine your startup costs, projected revenue, and operating expenses. Additionally, consider funding options, such as grants or investments, and create a budget that aligns with your financial goals.
Use Dashboards in ClickUp to track your financial projections, expenses, and funding options in one centralized location.
By following these four steps and utilizing our Business Plan Template for Education in ClickUp, you'll be well on your way to creating a comprehensive and actionable business plan for your educational institution.
Get Started with ClickUp’s Business Plan Template for Education
Education institutions, entrepreneurs, or investors who are looking to start or expand educational ventures can use the ClickUp Business Plan Template for Education to create a comprehensive and organized business plan.
First, hit “Add Template” to sign up for ClickUp and add the template to your Workspace. Make sure you designate which Space or location in your Workspace you’d like this template applied.
Next, invite relevant members or guests to your Workspace to start collaborating.
Now you can take advantage of the full potential of this template to create a successful business plan:
- Use the Topics View to outline and organize the different sections of your business plan
- The Status View will help you track the progress of each section, with statuses like Complete, In Progress, Needs Revision, and To Do
- Utilize the Timeline View to set deadlines and milestones for each section, ensuring timely completion
- The Business Plan View provides a comprehensive overview of your entire plan, allowing you to review and make adjustments as needed
- Create a Getting Started Guide View to provide step-by-step instructions for team members or stakeholders involved in the implementation of the plan
- Customize the template by adding custom fields like Reference, Approved, and Section to provide additional information and categorization for each section
- Update statuses and custom fields as you progress through the plan to keep everyone informed and ensure accountability.
- Business Plan Template for Volunteer Organizations
- Business Plan Template for Kodak
- Business Plan Template for Staffing Agency
- Business Plan Template for Cleaning Technicians
- Business Plan Template for Warehouse Managers
Edtech Startup Business Model: Which One is Right for You?
Get the help you need.

A good product is just a part of success. You should have an edtech startup business model that’s actually sustainable. And this isn’t only about earning more than you spend.
As an e-Learning software development company , MindK has seen many startups over the past fifteen years that had an amazingly vague business plan without a good idea of how to earn money. Some of them ran out of cash before the product was ready. Others managed a valuable exit. But if you want to achieve success in the long term, think about something that people really want.
Then ask yourself: how can I create a sustainable business around this value?
Most of the edtech business models look pretty similar to what you can see in other niches. Yet, there are some specifics you should know. That’s why we detailed the top 7 types of business model for education startups to rock the market in 2024 and beyond.
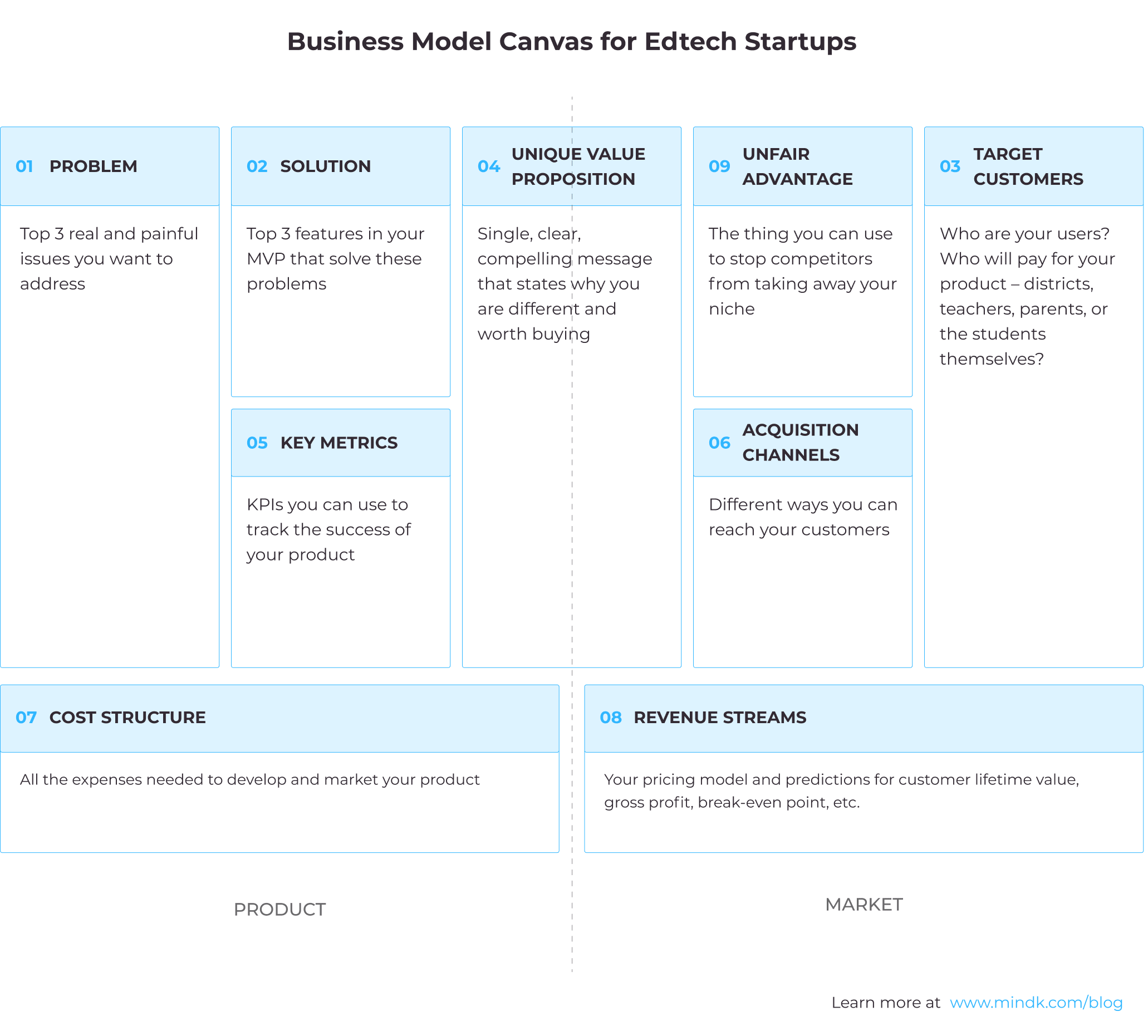
Edtech business model canvas
You can download a blank canvas template to quickly systematize your business model
Freemium (Coursera business model)
Give users a freebie and offer a more advanced plan as an upgrade. What could be easier?
It’s an attractive model for startups as it allows you to establish trust in your brand and quickly become a niche leader.
Initially, Coursera offered free courses on a variety of topics with an option to pay for a certificate. Powered by $210+ million of investments, the company quickly became an edtech powerhouse.
In 2023, Coursera gained 24 million new users.
Introducing a free enterprise tier brought $58.3 million in revenue and attracted thousands of institutions. Yet, Coursera still reported a net loss of $(116.6) million in 2023.
And this leads us to the the two main challenges with the freemium model:
- You will burn through lots of cash acquiring and supporting a large number of free users – marketing alone accounts for 36.5% of Coursera’s revenue.
- You’ll need to somehow convert these free users (and this can be harder than it seems ).
So, is there anything you can do to improve your chances of success?
For starters, you can charge a small one-time payment for your basic plan (aka Cheapium ) to filter out freeloaders and convert users with subscription fatigue.
Or you could go the free trial route (which I’ll explain next, so read on;)
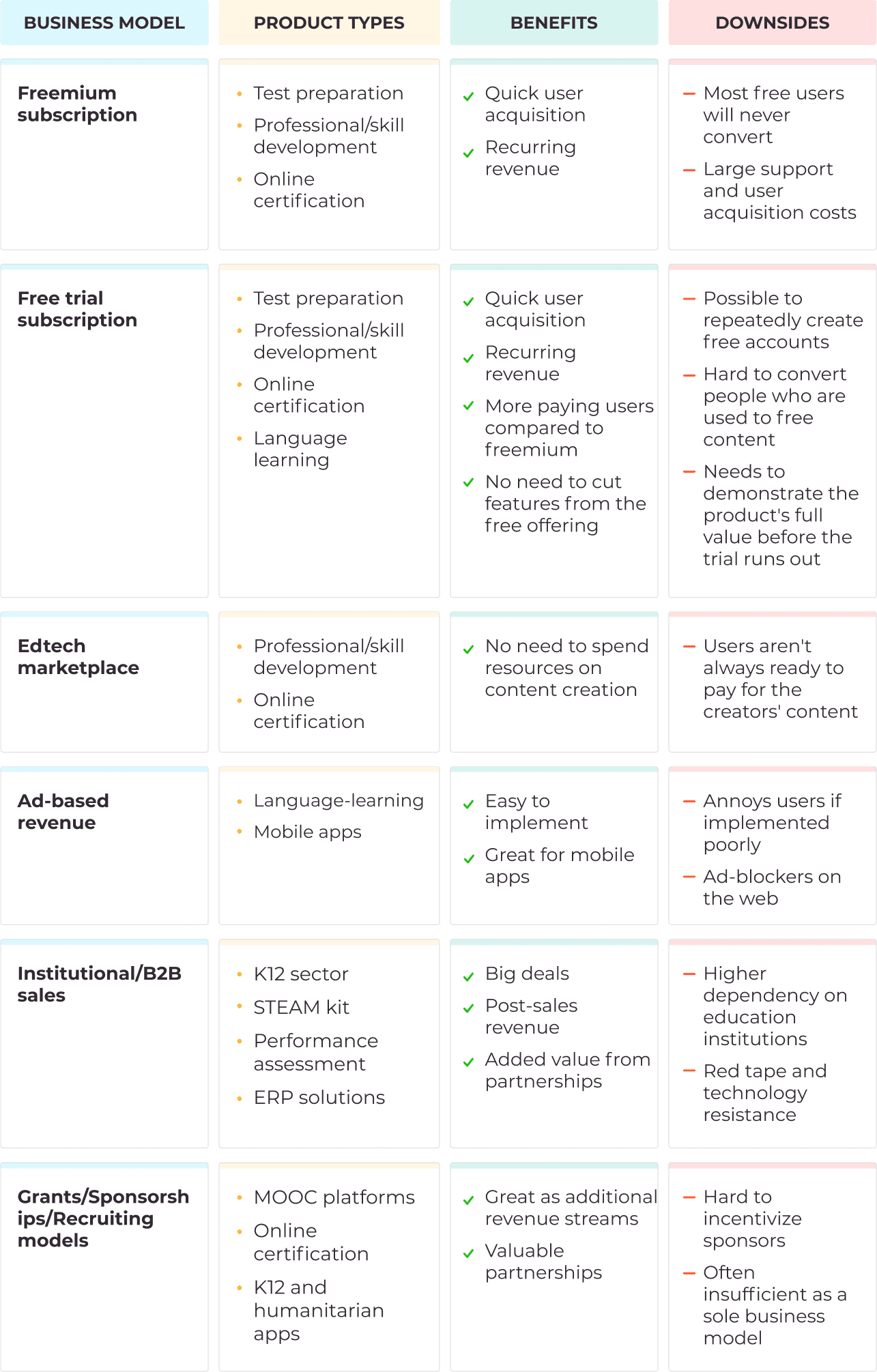
Free trial + paid subscription
This approach is similar to freemium. The only difference is that you offer a complete package right off the bat, but for a short period of time.
After the trial runs out, people either stop using your app or purchase an upgrade. This means that at any point in time, most users will be paying customers generating early revenue, especially, if the trial automatically changes to a paid subscription.
Some users may simply forget to unsubscribe, others will be too lazy. But if you offer a valuable service, most will stay as your loyal customers.
For example, Mystery Science is successfully using the free trial model to help kids fall in love with science. They offer a ton of free lessons on a variety of STEM-related topics.
The company uses a somewhat unusual spin on the free-trial model. Most teachers learn about Mister Science from a friend or a colleague. They can use the product free of charge. At the end of a school year, their school or a district buys a membership for all the teachers.
Read more: 7 edtech market trends to keep an eye on in 2024
Edtech marketplace
Few startups have enough resources to produce educational content at scale. This is one of the reasons why edtech marketplace is such a popular business model.
The idea is simple – build a platform where creators can make money from their educational content and take a share of their revenue.
Udemy is one of the world’s most valuable edtech companies, worth $3.3 billion.
The platform hosts thousands of 3rd-party courses from businesses and individuals offering a full set of tools to produce, market, and monetize learning materials.
Posting a course is free but Udemy takes 50% of the creator’s revenue. There are other edtech revenue models you can use, like charging an upfront fee for hosting a course or taking the first $50,000 earned on the platform like edX.
But the marketplace model isn’t only suitable for the edtech giants.

Tyoch Learning is a Luxembourg-based platform that unites coaches, enterprises, and professionals. As a self-funded startup, it couldn’t afford a massive custom platform. Using our experience with existing Learning Management Solutions, our engineers built an MVP that allowed Tyoch to take off.
The platform now hosts a variety of courses in leadership, time management, communication, and professional skills. It has both B2C and B2B models with one-time purchases and enterprise coaching programs.
Read more: how to build a Learning Management System using a combination of AI, integrations, custom, and readymade modules.
Advertising + ads-free subscription
Duolingo started back in 2009, when language learning software cost hundreds of dollars apiece.
But the app went with a very different business model. Duolingo planned to provide the service 100% free and charge businesses for user-translated texts.
The company spent its early years growing the user base. They tested every little detail, measured user behavior, experimented with gamification, and iterated to make the app as engaging as possible.
Usage grew at a steady pace, but the startup wasn’t making any money.
In 2013, the company partnered with CNN and BuzzFeed, translating 600+ articles a day.
Over the next few years, Duolingo built a flashcard app called TinyCards and introduced paid language testing which accounts for about 20% of the company’s bottom line.
Yet, these revenue streams were insufficient to make the app profitable. Instead of focusing on the B2B service that was bringing money, the founders went back to the core idea – provide the best way to learn a language, free of charge.
They started showing ads at the end of a lesson with an option to pay for the ads-free experience. Combined, this earned the company $16.6 million of net profit in 2023.
The key to succeeding with an ad-based model is to make it your ads as unobtrusive as possible. User experience is still the king!
Whatever model you choose, Duolingo proves it’s essential to test all your assumptions with real users, experiment in quick iterations, and pivot if necessary.
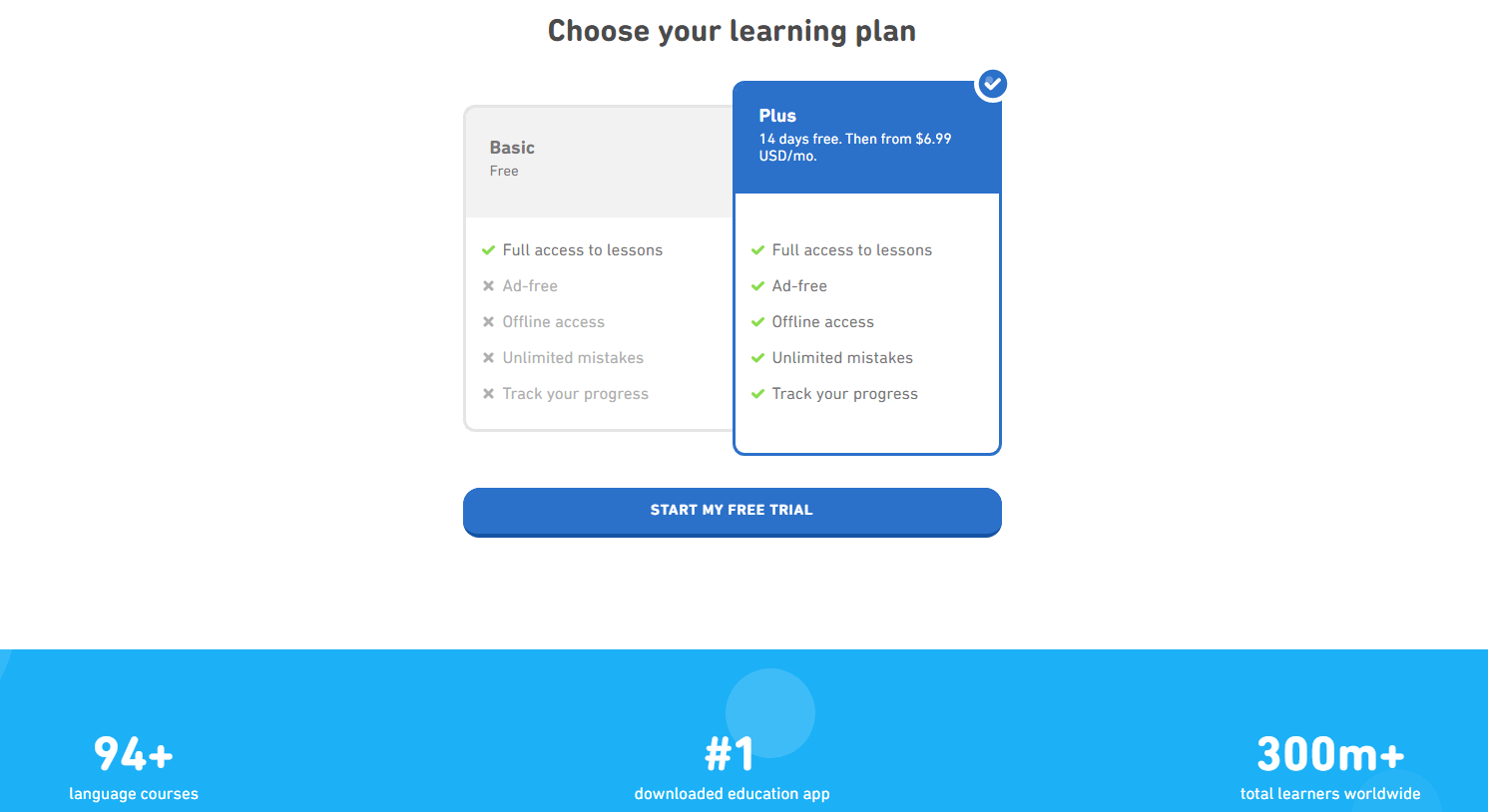
Duolingo Plus combines freemium and free trial models
Institutional model
This is a traditional model for the K12 sector.
The concept is simple – pitch your product to school districts, university administrations, and other decision-makers.
This model can be a winning choice if your product benefits organizations more than individuals. Or if it needs to be integrated into data systems at the district level.
Schoolzilla offers interactive dashboards to 140+ school districts across the US. Its main benefit is better decision-making, which appeals to principals and district admins. So the top-down approach was a natural extension of the product.
However, it’s not a one-fits-all solution.
There are over 16,000 districts in the US alone. Some of them big, some small and there can be large differences in the procurement process.
You can, of course, sell to individual schools instead of districts. According to Y Combinator’s CEO Geoff Ralston, schools now have bigger IT budgets and often employ directors of technology to help with purchasing decisions. Getting to know people those might be the key to your success.
However, to scale effectively, this model might require a large number of people doing the groundwork across the country.
Another challenge is that your end-users (teachers and schoolchildren) are often not your customers (people who pay for your product).
SharpScholar founders had to reboot their product because it had too many approval layers. The buy-in process involved both teachers, admins, and students. This resulted in a lack of focus and muddied positioning.
Their advice is to reduce the layers of approval and maintain a direct relationship with your customers, whoever they may be.
Enterprise/B2B sales
A similar top-down approach works if you work in B2B and association management niches.
Enterprise models involve pitching your product to decision-makers within large organizations. The contracts usually have a fixed duration, designated value, and come with a renewal at the end of the term.
Benefits are two-fold – large deals for some early revenue and long-term partnerships you can use to produce high-value content for the B2C sector.
Udacity is a $1.1 billion unicorn that sells educational courses both to businesses and users. These so-called nano degrees are created in partnership with companies like Google and Amazon. This makes them more attractive for the students and helps the company stand out from the crowd.
The company also has a successful B2B model with on-site training for corporate clients.
By combining different B2C and B2B models, Udacity managed to increase its revenue by 260% in 2020, reaching $100M three years later.
AlreadyOn is a niche player targeting Norwegian communities and associations. They evolved from a pure enterprise model (sell the product to organization leaders as a single transaction) to a more traditional SaaS business.
A self-service portal we built for them can be easily customized for any organization, be it a professional association, a political party, or a business entity.
The subscription is based on the selected modules and the number of members in your system.

Learn how MindK can help you build a successful edtech business as a custom application development company .
Subscribe to MindK Blog
React Native or Ionic, PhoneGap and Cordova: find the best tech for a cross-platform app

Digital Transformation in Education: Redefining the Experience of Everyone Involved

How to Import Existing Resources In Terraform for HIPAA Compliance
This website uses cookies to improve your user experience. Check our privacy policy here .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
But there's still a need to develop educational software to support these new online initiatives, providing an opportunity for education technology businesses to make their mark. If you want to start your own education tech business but aren't sure where to start, check out our assortment of sample business plans for inspiration.
Explore our library of Education Business Plan Templates and find inspiration for your own business. Business Planning. What is a business plan? ... Education Technology Business Plans. Computer Software Business Plan; Educational Software Business Plan; Educational Software K-12 Business Plan;
1. Develop A Technology Business Plan - The first step in starting a business is to create a detailed technology business plan that outlines all aspects of the venture. This should include potential market size and target customers, the services or products you will offer, pricing strategies and a detailed financial forecast.
Explore a real-world educational software business plan example and download a free template with this information to start writing your own business plan. Don't bother with copy and paste. ... Irvine and an M.A. in Educational Technology from San Diego State University. She has over twelve years experience designing and developing new media ...
ClickUp's Business Plan Template for Educational Technology provides all the essential elements for EdTech startups and entrepreneurs to create a comprehensive and strategic business plan. Custom Statuses: Track the progress of each section of your business plan with statuses like Complete, In Progress, Needs Revision, and To Do, ensuring ...
Lots of well-known education technology companies used this option to get off the ground or get additional funding. XuetangX, for example, was supported by Tsinghua University and the China Ministry of Education Research while FutureLearn has over 210+ partners. #9 Grow your edtech business
Start by identifying key roles and necessary skills such as technology, education, marketing, and business expertise. Look for people with a passion for education and a desire to impact the industry positively. Hire candidates with relevant EdTech industry experience or a deep understanding of education needs.
A business plan template for education offers a multitude of benefits to education institutions, entrepreneurs, or investors looking to start or expand their educational ventures. Some of the key benefits include: Providing a clear roadmap for success by outlining goals, strategies, and financial projections ...
As an e-Learning software development company, MindK has seen many startups over the past fifteen years that had an amazingly vague business plan without a good idea of how to earn money. Some of them ran out of cash before the product was ready. Others managed a valuable exit. But if you want to achieve success in the long term, think about something that people really want.
Teachers Pay Teachers, a marketplace for educational resources, allows educators to sell lesson plans, worksheets, and other educational materials to other teachers. 5. Partnership Model. Partnership is a business model where a company forms a strategic partnership with another company to provide a product or service.