
Reading & Math for K-5
- Kindergarten
- Learning numbers
- Comparing numbers
- Place Value
- Roman numerals
- Subtraction
- Multiplication
- Order of operations
- Drills & practice
- Measurement
- Factoring & prime factors
- Proportions
- Shape & geometry
- Data & graphing
- Word problems
- Children's stories
- Leveled stories
- Sight words
- Sentences & passages
- Context clues
- Cause & effect
- Compare & contrast
- Fact vs. fiction
- Fact vs. opinion
- Main idea & details
- Story elements
- Conclusions & inferences
- Sounds & phonics
- Words & vocabulary
- Reading comprehension
- Early writing
- Numbers & counting
- Simple math
- Social skills
- Other activities
- Dolch sight words
- Fry sight words
- Multiple meaning words
- Prefixes & suffixes
- Vocabulary cards
- Other parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Capitalization
- Narrative writing
- Opinion writing
- Informative writing
- Cursive alphabet
- Cursive letters
- Cursive letter joins
- Cursive words
- Cursive sentences
- Cursive passages
- Grammar & Writing
Breadcrumbs
- Word Problems

Download & Print From only $3.60

1st Grade Math Word Problems Worksheets
Grade 1 word problems.
These grade 1 word problem worksheets relate first grade math concepts to the real world. The word problems cover addition, subtraction, time, money, fractions and lengths.
We encourage students to think about the problems carefully by:
- providing a number of mixed word problem worksheets;
- sometimes including irrelevant data within word problems.
Addition word problems
Single digit addition
Addition with sums 50 or less
3 or more numbers added together
Subtraction word problems
Subtracting single digit numbers
Subtracting numbers under 50
Mixed addition and subtraction word problems
Add / subtract word problems with mostly single digit numbers
Add / subtract word problems with numbers under 50
Time word problems
Time and elapsed time problems (whole hours)
Money word problems
Counting money (coins only)
Measurement word problems
Combining and comparing lengths (inches)
Combining and comparing lengths (cm)
Fraction word problems
Write the fraction from the story (parts of whole, parts of group)
Mixed word problems
Addition, subtraction, money, time, fractions and length word problems mixed

Sample Grade 1 Word Problem Worksheet
More word problem worksheets
Explore all of our math word problem worksheets , from kindergarten through grade 5.
What is K5?
K5 Learning offers free worksheets , flashcards and inexpensive workbooks for kids in kindergarten to grade 5. Become a member to access additional content and skip ads.

Our members helped us give away millions of worksheets last year.
We provide free educational materials to parents and teachers in over 100 countries. If you can, please consider purchasing a membership ($24/year) to support our efforts.
Members skip ads and access exclusive features.
Learn about member benefits
This content is available to members only.
Join K5 to save time, skip ads and access more content. Learn More
High Impact Tutoring Built By Math Experts
Personalized standards-aligned one-on-one math tutoring for schools and districts
Free ready-to-use math resources
Hundreds of free math resources created by experienced math teachers to save time, build engagement and accelerate growth
36 Math Problems For 1st Graders With Answers & Teaching Ideas
Melanie Doppler
Math problems for 1st graders connect kindergarten math skills to 2nd grade math skills and beyond. 1st grade math problems focus on building an understanding of addition and subtraction and learning a variety of strategies for efficient problem-solving.
This blog post covers the key areas for 1st grade math problems including addition and subtraction, place value, measurement, fractions, telling time, representing data and shapes. It includes ready-to-use math problems with solutions and strategies for teaching 1st grade math.
What are math problems for 1st graders?
Math problems for 1st graders are math problems for 6-7-year-olds. These first grade math problems are specific to 1st grade math skills and are designed for 1st grade students.
They build on kindergarten math concepts such as counting and simple addition by transitioning to more complex problems such as addition and subtraction up to 20.
1st grade math problems also set the foundation for 2nd grade math and beyond.

14 Fun Math Games and Activities Pack for 1st Grade
14 fun math games and activities for 1st grade students to complete independently or with a partner. All activities are ready to go and suitable to a range of abilities.
Math curriculum for 1st graders
1st grade math problems cover a range of skills across four domains of Common Core Math Standards including:
- Operations and Algebraic Thinking
- Numbers and Operations in Base Ten
- Measurement and Data
By first grade, students are expected to connect counting and cardinality skills to addition and subtraction and be fluent in their addition and subtraction facts within 5.
The first grade math year is important in the K-5 math progression; it introduces addition and subtraction with numbers up to 20 and addition with numbers up to 100. It also covers the idea of decomposing a number into tens and ones (by place value), a necessary skill for 2nd grade, 3rd grade, 4th grade and 5th grade math.
This foundational year focuses on hands-on math manipulatives and visual models to build the conceptual understanding needed for more advanced math in later years.
In first grade, students learn new skills such as:
- Simple addition and subtraction (with numbers up to 20)
- Addition and subtraction word problems
- Place value with 2-digit numbers
- Addition within 100 (adding a 2-digit number and a 1-digit number and/or a 2-digit number and multiples of ten)
- Sequences and missing numbers
- Basic fraction concepts and partitioning shapes
- Telling time (analog and digital)
- Measurement (measuring and comparing objects using basic measurement units)
- Representing data
First graders are expected to be fluent in addition and subtraction math facts within 10 by the end of the grade. These addition and subtraction skills are integrated into the other math content throughout 1st grade to solidify skills and apply them to real world math situations.
All 1st grade math skills set the foundation for second grade and third grade skills such as adding and subtracting larger numbers, multiplication and division concepts and more.
36 math problems for 1st graders and answers
The following is a collection of 1st grade math problems, organized by domain and skill.
Each problem includes an answer key and explanation of how to answer the math question.
Math problems for 1st graders: Operations & Algebraic thinking
Operations & Algebraic thinking focus on addition and subtraction skills within 20. At the first grade level, students learn efficient strategies for adding and subtracting and develop fluency with addition and subtraction within 10.
First graders also use the properties of operations to add and subtract, relate addition to subtraction and develop an understanding of the meaning of the equal sign.
Simple addition and subtraction within 20
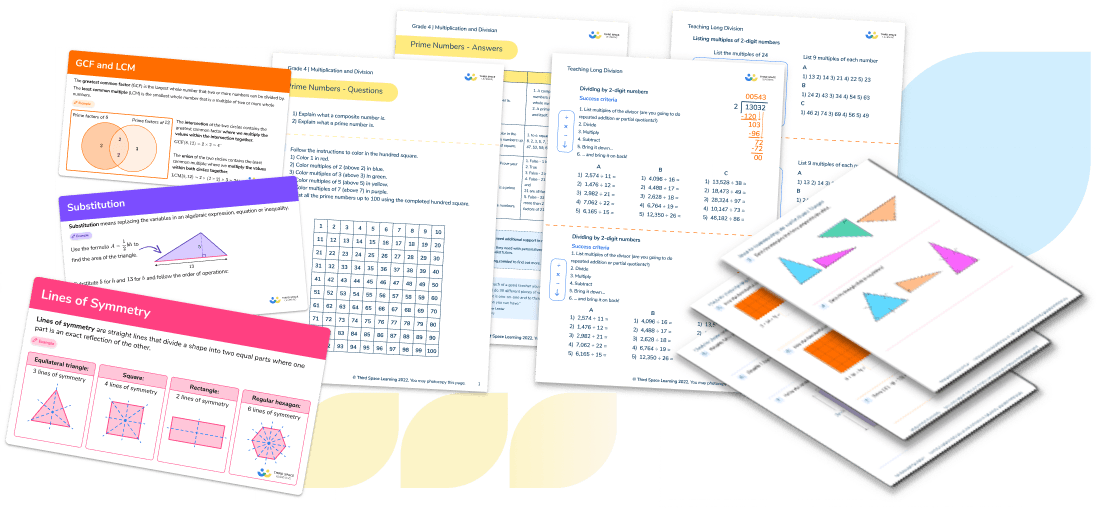
5 + 7 = ___
Answer: 12
There are a variety of strategies students can use to solve this problem. They can count on/add on 7 from 5. But, to solve the problem more efficiently they can use the commutative property to switch the order of the addends so the larger addend is first.
The problem becomes 7 + 5 which means they can more easily count on 5 from 7. Students can use a visual model such as counters in a double ten frame to support their thinking.
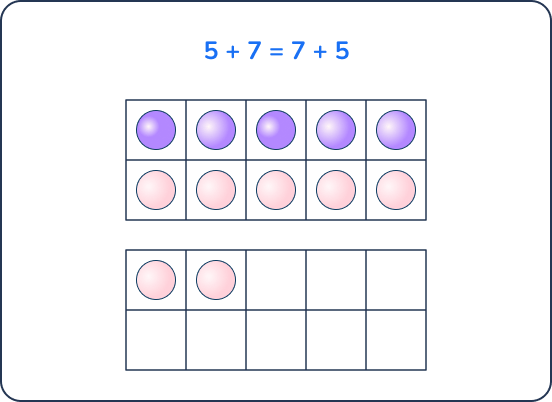
7 + 6 = ___
Answer: 13
This problem has the larger addend first. An efficient way to add is to break apart the second addend.
Using this strategy allows students to focus on ways to make ten. For example, 6 can decompose into 3 + 3. Then students can add in parts:
- 7 + 3 = 10
- 10 + 3 = 13
Anchoring to 10 is an efficient strategy that bridges larger problems and allows students to use their knowledge to solve larger problems.
Teachers can support student understanding by encouraging them to use a double 10 frame.
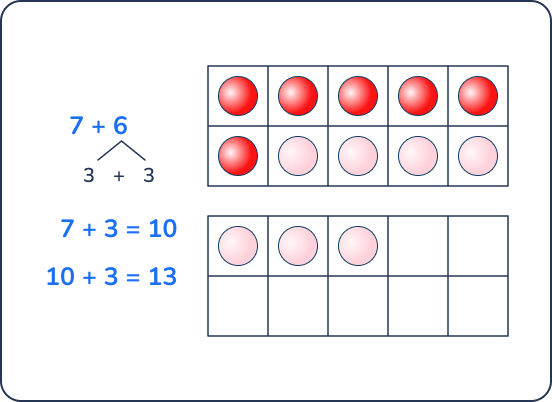
8 + ___ = 15
Answer: 7
This problem is framed as a missing addend problem, which connects addition strategies to subtraction.
To find the missing value, students would subtract 15 – 8. However, students can use an addition strategy to support their subtraction problem solving. Students could add on from 8 to 15, adding in parts by anchoring to a 10.
Using a number line is a helpful strategy to find the difference between 8 and 15. Students can find the difference by adding on or subtracting back.
9 – 5 = ___
Students can solve this problem by subtracting 5 from 9. They can model this on a number line or a ten frame.
Knowing fact families within 10 will help students solve this problem more efficiently. If a student knows that 5 + 4 = 9, they know that 9 – 5 = 4 and 9 – 4 = 5.
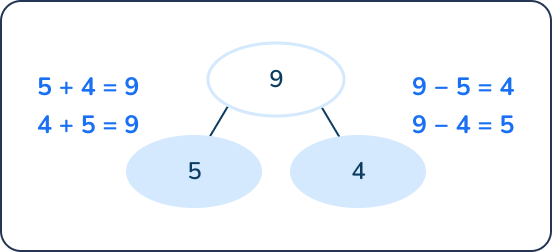
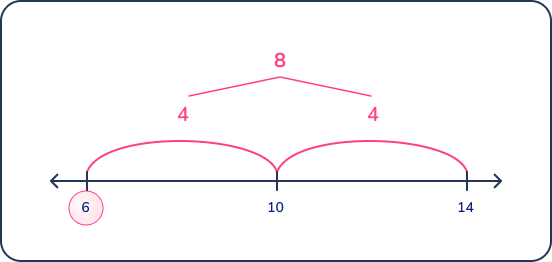
14 – 8 = ___
Answer: 6
This problem appears more difficult than the previous subtraction problem because the minuend (first number in the equation) is a two-digit number.
If solving this problem using the standard algorithm/’place value’ subtraction, regroup/rename 4 ones for 14 ones.
However, in first grade, students do not use the standard algorithm for subtraction. First grade math focuses on building conceptual understanding and efficient mental math strategies.
Teachers should emphasize that anchoring to ten is a helpful strategy. First graders should learn to decompose the 8 into 4 + 4. Then they can subtract on a number line or double ten frame:
- 14 – 4 = 10
- 10 – 4 = 6
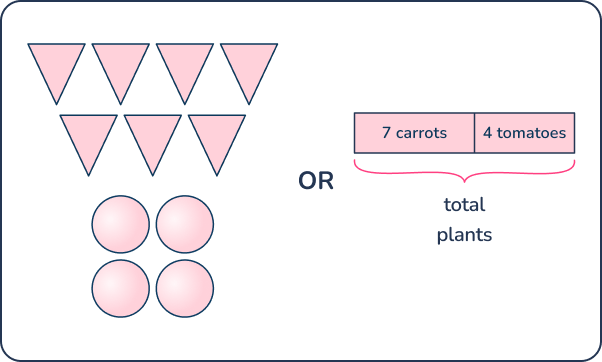
Addition word problems
There were 7 carrot plants and 4 tomato plants growing in the garden. How many total plants were growing in the garden?
Answer: 11 plants
First graders will become familiar with the structure of word problems like this. It is a simple part-part-whole problem.
Drawing a picture of the plants or a bar model helps children see the parts of the problem and the whole.
Using a double ten frame helps students anchor making a 10 to help them solve this problem. Students should label their work as they solve problems to make sense of the problem.
9 friends were playing on the playground. 5 more friends joined. How many friends were playing on the playground all together?
Answer: 14 friends
This ‘join result unknown’ problem is great for visualizing the meaning of addition. Students can draw or act out 9 people and 5 more people joining. They can use counters or act it out with their peers.
A number line to anchor to 10 is a helpful visual model for solving this problem.
Jesse has 5 stickers in his collection. Ben has 6 more stickers than Jesse in his collection. How many stickers does Ben have in his collection?
Answer: 11 stickers
Drawing a bar model helps students understand this comparison problem. This problem is a ‘doubles plus one’ problem.
Students can use the basic fact of 5 + 5 = 10, to see that this is 5 + 5 + 1. They can also anchor to 10 and break apart 6 into 5 + 1 to solve the problem.
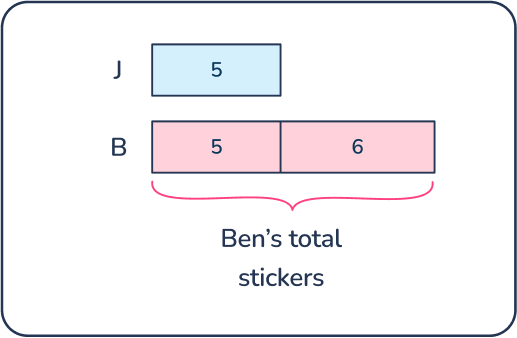
Question 10
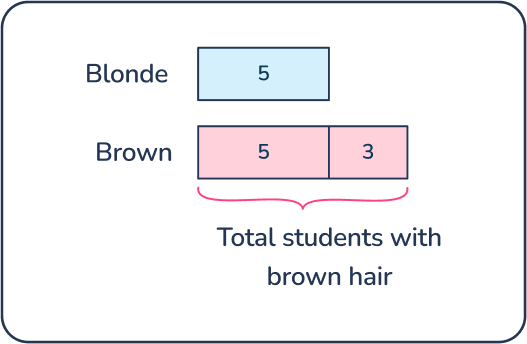
There are 3 more students with brown hair in Mr. Archer’s class than students with blonde hair. If there are 5 students with blonde hair in Mr. Archer’s class, how many students in class have brown hair?
Answer: 8 students have brown hair
A bar model /tape diagram is a visual model students will become familiar with as they begin problem solving with math word problem structures in 1st grade.
Bar models help students recognize that they need to add 5 + 3. They can add on 3 from 5 to get to 8.
By the end of the year, students should be fluent in math facts within 10 so they should know that 5 + 3 = 8 using mental math or with little think time.
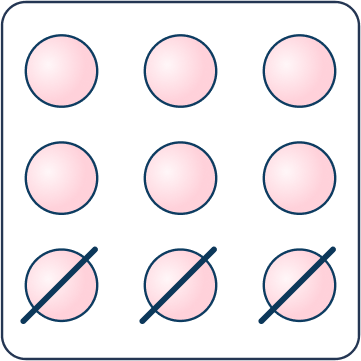
Subtraction word problems
Question 11.
There were 9 blueberries on my plate. I ate 3 blueberries. How many blueberries are left on my plate?
Answer: 6 blueberries
Drawing a traditional subtraction picture where students draw 9 circles for blueberries and then cross off 3 is a great problem solving strategy for basic separate result unknown problems.
Additionally, using counters and physically moving them helps students build a conceptual understanding of subtraction.
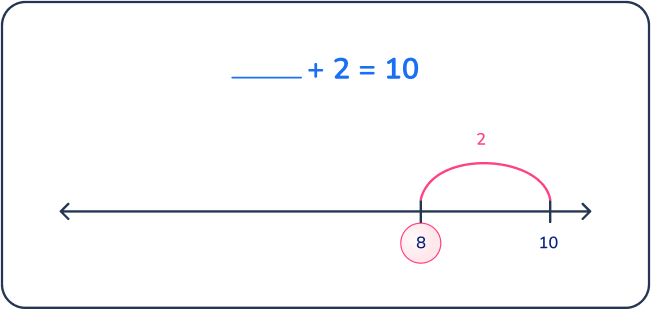
Question 12
Some birds were in an oak tree. 2 more birds joined. Now there are 10 birds in the oak tree. How many birds started in the oak tree?
Answer: 8 birds
This ‘join, start unknown’ problem is particularly challenging for first graders because they do not know the starting number.
Drawing a picture or using hands-on math manipulatives can help students see that the problem they are trying to solve is ___+ 2 = 10.
Then they can use their fact fluency within 10 or add on from 2 to 10.
Question 13
14 dogs were playing at the dog park. 9 dogs had long tails and the rest had short tails. How many dogs at the dog park had short tails?
Answer: 5 dogs
Teachers should encourage students to use a bar model for this part-part-whole problem. Students can see that if there are 14 total dogs and 9 have long tails they would need to subtract 14 – 9 to find the number of dogs with short tails.
To solve, students can add on from 9 to 14 or subtract from 14 to 9 on a number line.
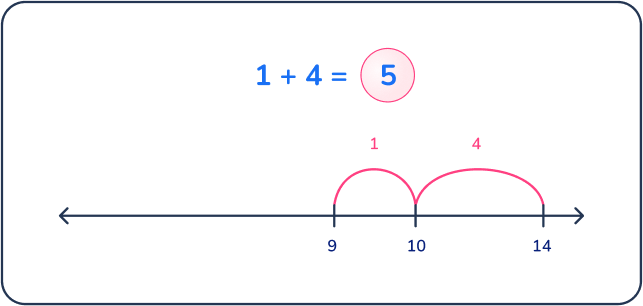
Question 14
Julie bought a pack of 16 thank you cards. After her party, she mailed 8 of the cards. How many thank you cards did Julie have left?
Answer: 8 cards
Students can look for a way to make 10:
- 10 + 6 more is 16
- All together the difference is 6 + 2 which is 8
Alternatively, they could subtract:
- 16 – 6 to get to 10
- Then subtract 2 more to get to 8
By the end of 1st grade, students will be familiar with their doubles facts and will recognize more quickly that 8 + 8 = 16.
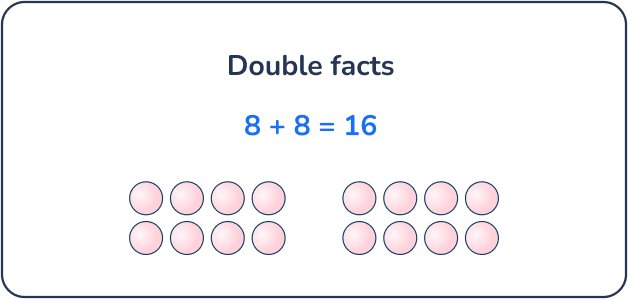
Math problems for 1st graders: Numbers & Operations in Base Ten
The numbers and operations in base ten for first grade focus on two-digit numbers. First graders learn to decompose or break apart 2-digit numbers using place value. They understand the meaning of tens and ones in each number and learn to compare 2-digit numbers.
This domain also focuses on transitioning from single-digit addition to double-digit addition. Students learn to add 2-digit numbers to 1-digit numbers within 100 and add and subtract multiples of 10 from 2-digit numbers.
Students also use base ten blocks for actual problem solving, as opposed to kindergarten where blocks are used for modelling numbers. It is an important year for developing conceptual understanding of place value .
Place value
Question 15.
Compare the following two numbers using the greater than, less than or equal to symbols (>, <, =).
Answer: 35 < 52
Students can build both numbers using base ten blocks or a quick picture to see that 52 has 5 tens and 35 only has 3 tens so 52 is greater than 35.
A common misconception is that because there is a larger number in the one’s place then the number itself is larger, so students might think that 35 is greater than 52. Teachers must teach 1st graders to compare starting with the largest place value.
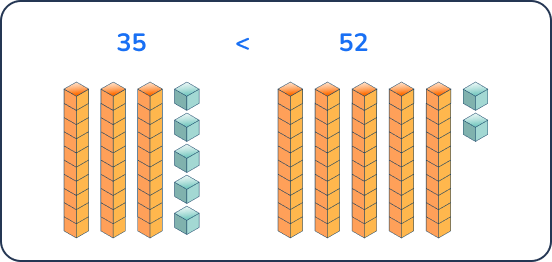
Question 16
Which number has a greater value: 48 or 84? Explain.
Answer: 84 has the greater value because 8 tens is more than 4 tens.
In first grade, students should always build and model numbers when comparing them by place value. This builds the foundation of conceptual understanding when they begin problem solving with larger numbers.
Using the vocabulary of ‘greater value’ is key.
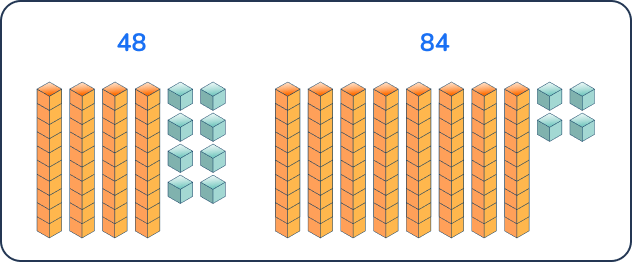
Question 17
How many tens are in the number 73? Draw a picture to show your thinking.
Answer: 7 tens
Using base ten blocks helps children organize their thinking when decomposing numbers by place value.
Students can also use a place value chart to organize their work. Place value charts are increasingly important in the later grades so this is a good time to introduce that tool.
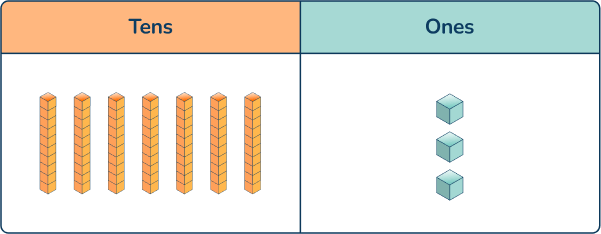
Question 18
There were 28 red cars and 32 black cars parked in the lot. Were there more red cars or black cars parked in the lot? How do you know?
Answer: There were more black cars because 28 < 32 (or 32 > 28)
Students could solve this problem by drawing pictures of cars but this is inefficient. Teachers can show students how it is much more efficient to use base ten blocks or a quick picture to model both numbers and compare the tens and ones.
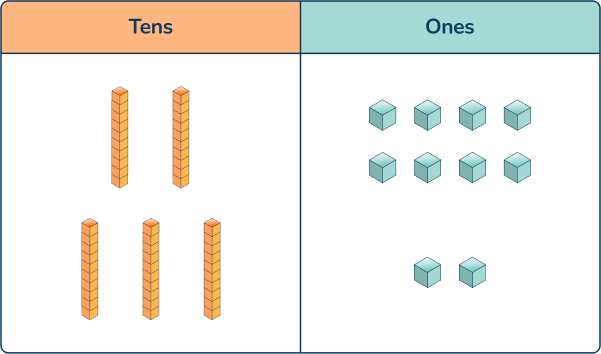
Adding and subtracting using place value
Question 19.
18 + 6 = ____
To solve addition and subtraction problems within 100, first graders learn to use place value blocks for problem solving.
In this problem, they can model the number 18 with 1 ten and 8 ones and physically count on 6 more ones. They can replace 10 of the ones for one ten to see that they have the number 24.
Anchoring to smaller facts is helpful. If students know 8 + 6 = 14, it can help them solve 18 + 6.
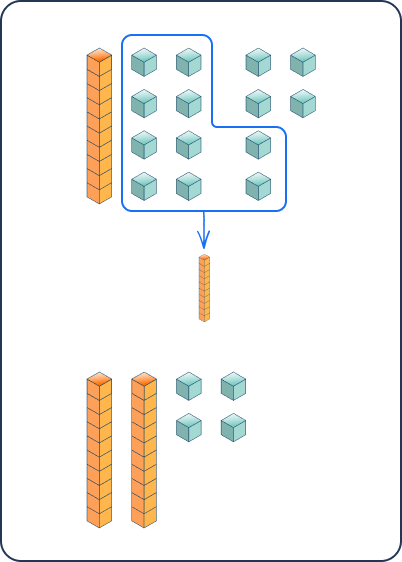
Question 20
____ = 33 + 7
In this problem, the unknown value is on the left side of the equal sign. This is intentional. In first grade, students learn that the equal sign means ‘the same value’ so one side should be the same value as the other side of the equal sign.
This is particularly challenging for students because they are used to the traditional format of a + b = c. Practicing balancing equations helps children understand this concept.
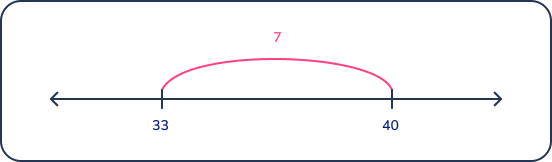
To solve, students can use their knowledge of making ten (3 + 7 = 10) to add 33 + 7 to get to the next multiple of ten which is 40.
A number line is a helpful strategy for visualizing this problem.
Question 21
40 – 10 = ____
Using a hundreds chart is beneficial for first graders to subtract multiples of ten. It allows students to see how when adding or subtracting ten from a number, the digit in the one’s place remains the same but the digit in the tens place changes.
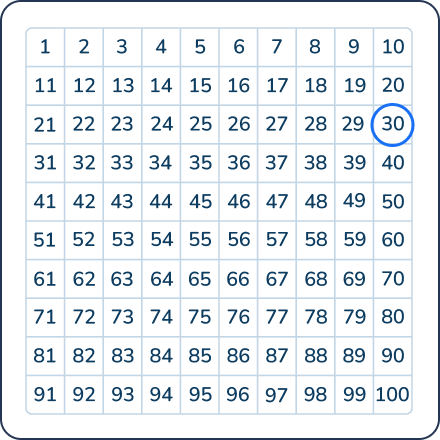
Question 22
____ = 62 + 10
Answer: 72
By the end of first grade, students should be able to add ten to a given two-digit number using mental math.
However, for fluency, a hundreds chart or base ten blocks are a helpful visual for seeing these large numbers.
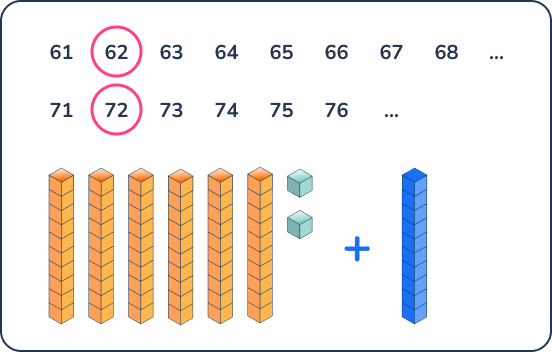
Sequencing and missing numbers
Question 23.
Look at the sequence of numbers below. What is the next number in the sequence?
90, 80, 70, 60, 50, 40, ____
Answer: 30
Students can solve this problem using base ten blocks and taking one block away to model each step of the sequence.
They can also move a transparent counter across the hundreds chart to see that the next number is 30.
Missing number problems are challenging for students but teachers can help first graders understand these problems by showing them that by finding the difference between each number in the sequence, they can solve for the next number.

Question 24
Find the missing number in the sequence:
25, 35, 45, 55, ____, 75, 85
Answer: 65
Using the same strategies as the previous problem, students can find the difference between each number in the sequence. Once they see that the difference is ten, they can use a number line, base ten or hundreds chart to add 10 to 55 or subtract 10 from 75 to find the missing number.

Math problems for 1st graders: Measurement & Data
Students learn the basics of linear measurement in first grade. They learn to use other objects as units and basic measurement units to measure objects.
First graders do not use standard units of measure such as inches or centimeters for most measuring situations. Instead, they compare objects to determine the length. For example, they might measure the length of a desk using pencils as the unit to see how many pencils long the desk is. This prepares students for learning standard measurement units in 2nd grade.
1st graders learn the foundation of time reading a clock to the nearest half hour, and basic data organization, such as tally marks to record data.
Measurement
Question 25.
Which of the following objects is about the same length as a new pencil?
Answer: D TV Remote
Students need to use estimation skills to determine a reasonable answer. A TV remote may not be exactly the size of a pencil, but it is close to the length of a pencil. A bicycle and desk are much bigger and a fingernail is much smaller.
Estimating lengths is an important skill for first graders so they can use non-standard units to measure and compare objects. For example, determining how many pencils long a desk is, or how many pencils tall they are.
Question 26
Put the following people in order from tallest to shortest:
Quinn: 3 desks tall
Ivy: 2 desks tall
Jordan: 4 desks tall
Answer: Jordan, Quinn, Ivy
Emphasize that the desks are all the same size, so the unit is the same for each person and that all measurement units should be used with no gaps or overlaps.
Question 27
Use a standard piece of paper as a measurement unit. How many pieces of paper long is your desk?
Answer: Answers will vary based on desk and paper size.
First graders must get practice with hands-on measuring. Students must be able to use tools to measure lengths.
In this case, the piece of paper is the measurement unit. Teachers should instruct students to check their answers to ensure they are reasonable.
Telling time
Question 28.
I have a dentist appointment at 5:00. Which clock below shows 5:00?
Answer: A
In first grade, students are introduced to reading digital and analog clocks. They must learn the meaning of the minute hand and the hour hand.
For this problem, students need to identify that the hour hand should point to 5 and the minute hand should point to 12 because it is the beginning of the hour.
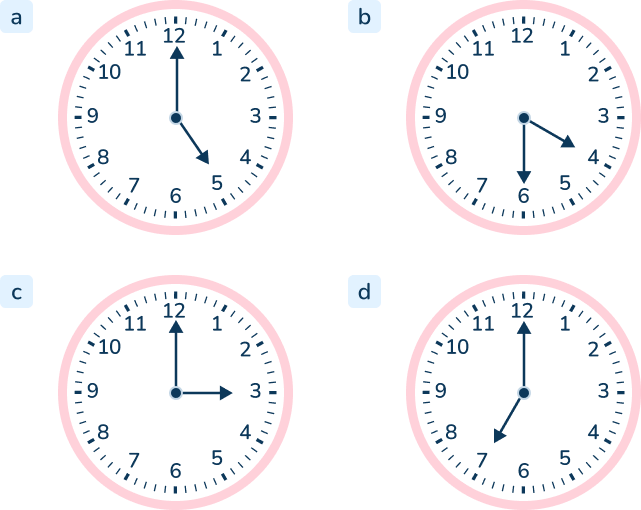

Question 29
Choose the clock(s) that shows 6:30. What is something that you might do at 6:30? How does that differ from 6:30 in the morning and 6:30 at night?
Answer: B & C
This time word problem helps teachers identify misconceptions about digital and analog clocks when teaching time . If a student chooses option D, they do not understand how time is represented on a digital clock.
6:30 is a challenging time to show on a clock so students must recognize that the hour hand is halfway past the 6 and the minute hand is pointing towards the 6.

Question 30
Match the three digital clock times to the corresponding time on the analog clocks.
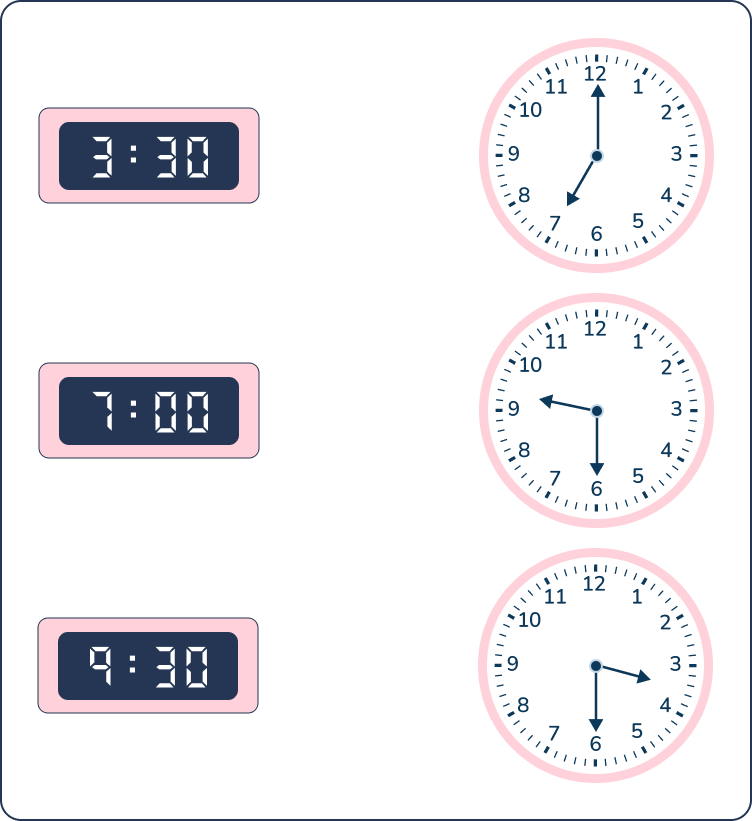
Organizing data
Question 31.
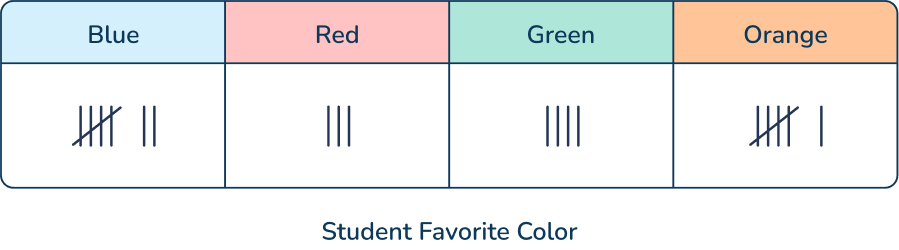
The students in Mr. Jensen’s class voted for their favorite color. The data was collected in the chart shown below. How many more students voted for blue than voted for green?
Answer: 3 more students
Tally marks are more organized than drawing dots or making unorganized lines because students can go back and more easily see the numbers because of the bundles of 5.
For example, for blue, they can see a group of 5 and 2 more. If they compare that to the 4 tally marks for green, they know they just have to find the difference between 7 and 4 to find the answer.
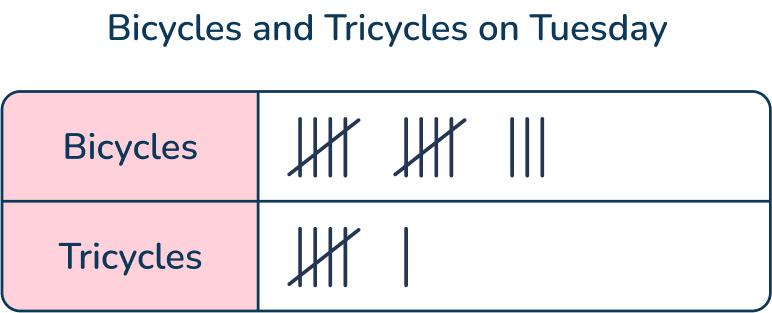
Question 32
Oliver kept track of the number of bicycles and tricycles he saw ride past his house on Tuesday. He used tally marks to organize his data. How many total bicycles and tricycles did Oliver see ride past his house on Tuesday?
1st graders learn the basics of data organization, including:
- Structure (in this case, a t-chart)
This sets the foundation of organization for more advanced data representation models such as bar graphs and line plots in later years.
Students must read and understand all the parts of a graph or chart and interpret the data.
Math problems for 1st graders: Geometry
First grade geometry teaches students the defining attributes of shapes such as the number of sides and angles and non-defining attributes such as color and size.
1st graders also learn the basics of how to:
- Compose two-dimensional and three-dimensional
- Partition circles and rectangles into equal shares, setting the foundation for fractions
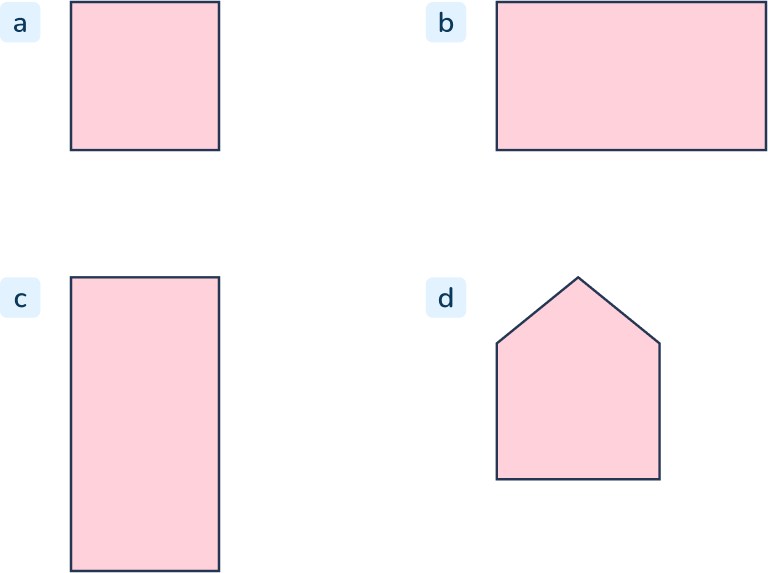
Question 33
Which of the shapes below is not a rectangle? How do you know?
Answer: D
For this problem, students should identify that the defining attributes of a rectangle are that it has 4 sides and 4 angles and that the angles are all the same size, or right angles. D has 5 sides and 5 angles so it is not a rectangle.
Question 34
Two triangles were put together to make this shape. What is the name of the new shape?
Answer: Square
The two right triangles compose a square with sides the same length. Students might also answer rectangle if they are not sure that all sides are the same length. Students should see that together two three-sided shapes can create a four-sided shape.

Basic fractions
Question 35.
If you wanted to share a pizza equally between two people, which pizza should you choose? Why?
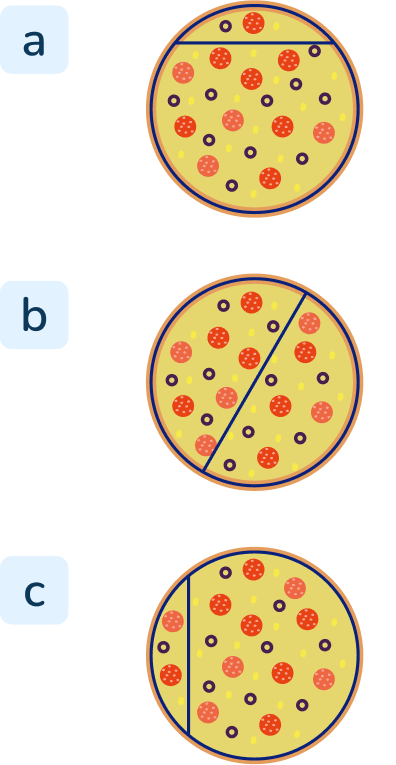
Answer: B
To share a pizza equally partition the pizza into two equal-sized pieces. In A and C, the pizza is cut into two pieces but the pieces are equal.
In first grade, teachers should emphasize that partitioning shapes equally means making equal-sized shares.
Question 36
Partition the picture of a chocolate bar into fourths. How many people can share the chocolate bar equally?
First graders should practice folding paper and partitioning hands-on models into equal shares, drawing these models on paper, and identifying models shared equally.
Attending to precision and ensuring all the parts are equal is an important step at this level. This helps students build a foundation of understanding that they can build on as they learn about fractions in later grades.
3 top tips for teaching 1st grade math problems
First grade is an important transition year for children to connect their counting and basic addition/subtraction skills from kindergarten to adding and subtracting with larger numbers.
Here are three tips for elementary math teaching to support 1st grade students build an understanding of new math concepts:
- Follow the CRA progression and transition from concrete, to representational, to abstract models.
- Use purposeful visual models such as ten frames, double ten frames and number lines to help children understand addition and subtraction.
- Build fluency with addition and subtraction math facts within 10 by anchoring to facts students know within 5. Similarly, encourage students to find ways to make ten to support them with solving larger problems within 20 and beyond.
1st grade math worksheets and resources
Looking for more resources? Check out our math games and our selection of first grade printable math worksheets, posters and digital activities covering 1st grade key math topics and more:
- 14 Fun Math Games And Activities Pack For 1st Grade
- Summer Math Activities For 1st and 2nd Grade
- 2D Shapes Math Posters Kindergarten – Grade 1
READ MORE :
- 2nd grade math problems
- 3rd grade math problems
- 4th grade math problems
- 5th grade math problems
- 6th Grade Math Problems
- 7th grade math problems
- 8th grade math problems
Frequently asked questions
What math should a 1st grader know?
By the end of 1st grade, students should: Add and subtract numbers up to 20 Be fluent in addition and subtraction math facts within 10 Understand the base ten number system and compare 2-digit numbers by place value Add 2-digit numbers to 1-digit numbers Subtract multiples of 10 from any 2-digit number Tell time to the nearest half-hour Organize data Measure and compare the lengths of various objects Identify defining attributes of shapes Partition shapes into two and four equal shares
What are the mathematical concepts for 1st grade?
1st graders learn math in 4 different domains or content areas. The main focus of these domains is: Addition and subtraction of numbers up to 20 with fluency in adding and subtracting to 10 Place value up to 2-digit numbers 1-digit addition and basic 2-digit addition Telling time Basic measurement concepts Early fraction concepts Organizing data and geometry
What are good questions to ask a 1st grader?
First grade is a pivotal year for students to make connections between adding and subtracting smaller numbers and larger numbers. Students should develop their identity as mathematicians, focusing on a growth mindset. Ask questions such as: What makes you feel confident in math? Is there an area of math you need more support in? Explain. Which hands-on tools do you like to use for solving math problems? Which picture or visual model could help you solve that problem? When solving, for example, the problem 7 + 8, you might say, ‘Do you see a way to make 10 in this problem?’ When solving a problem such as 27 + 8, you might say ‘Can you use 7 + 8 to help you solve this problem?’ Try solving this problem in two different ways. Which strategy was most efficient for this problem?
Do you have students who need extra support in math? Give your students more opportunities to consolidate learning and practice skills through personalized math tutoring with their own dedicated online math tutor. Each student receives differentiated instruction designed to close their individual learning gaps, and scaffolded learning ensures every student learns at the right pace. Lessons are aligned with your state’s standards and assessments, plus you’ll receive regular reports every step of the way. Personalized one-on-one math tutoring programs are available for: – 2nd grade tutoring – 3rd grade tutoring – 4th grade tutoring – 5th grade tutoring – 6th grade tutoring – 7th grade tutoring – 8th grade tutoring Why not learn more about how it works ?
Related articles

30 8th Grade Math Problems: Answers With Worked Examples

28 Math Problems For 2nd Graders With Answers & Teaching Ideas

37 Math Problems For 3rd Graders: Answers With Worked Examples
34 6th Grade Math Problems: Answers With Worked Examples
3rd to 8th Grade Practice Tests
Get ready for your state math test with our 3rd to 8th grade practice assessments. These 6 multiple-choice tests, created by US math experts, cover essential topics and include detailed answers for effective test prep. Aligned with Common Core Standards, they’re the perfect tool to build student confidence.
Privacy Overview
1st Grade Math Worksheets

Free 1st Grade Math Worksheets
All of the first grade math worksheets below are samples from the 1st Grade Math Worksheet Library on our Infinite K-8 Math Worksheet Portal .
Click any of the links below to download the corresponding 1st grade math worksheets and answer key.
▶️: Sample Worksheet Download | 🔒: Worksheet Only Available to Members | 🔽 Jump to a Topic:
Numbers and Counting
Comparing Numbers
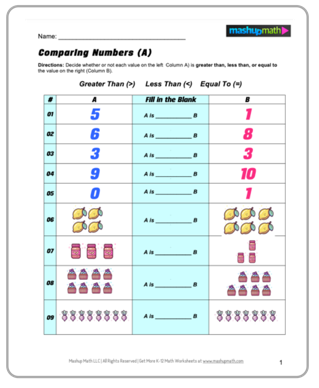
Subtraction

Place Value and Base-10

Data/Graphing

Lengths and Measurement

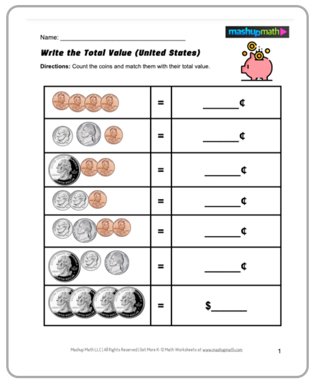
Working with Money
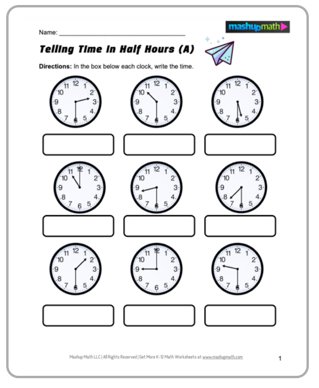
Learning How to Tell Time
Word Problems

This collection of 1st Grade Math Worksheets are organized by topic and overall skill level. Each worksheet is designed with the needs of 1st grade students in mind, as they are created to be engaging, colorful, and appropriately challenging for a typical first grade student. The math skills and topics below are all key foundational mathematics and problem-solving skills that students will need in order to be successful in higher levels of math in science when they eventually enter middle school and high school, so getting first grade students interested in mathematics early on is incredibly important.
The free sample first grade math worksheets below are unique in that they are not overloaded with repetitive and monotonous practice problems. Instead, they are considerate of a first graders attention span, and they are designed to allow 1st grade students to practice and learn math in ways that are exploratory, engaging, and fun!
If you want to gain access our complete library of 1st grade math worksheets and answer keys, you can sign-up for access to our K-8 math worksheet portal , where you can download ALL of our grade and topic-specific math worksheets.
🛑 Wait! Would you like getting FREE K-8 math activities, lesson resources, worksheets, and puzzles in your inbox every week? 💁♀️
⇥ Click here to join our mailing list and get a free pdf math workbook as a bonus!

▶️ Writing Numbers: 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10
▶️ Writing Numbers: 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20
▶️ Number Tracing 1-10
🔒 Number Tracing 6-10
▶️ Number Reference Sheet (0-10)
▶️ Finger Counting Reference Sheet (1-10)
▶️ Practice Finger Counting
▶️ Practice writing numbers 0-7
🔒 Practice writing numbers 8 and 9
🔒 Practice writing numbers 10-13
▶️ Focus on 0-3
▶️ Focus on 4
▶️ Focus on 5
🔒 Focus on 6 and 7
🔒 Focus on 8, 9, and 10
🔒 Focus on 11
▶️ Matching numbers with words (up to 10)
🔒 Matching numbers with words (up to 20)
▶️ (A) Counting numbers 1-10
▶️ (B) Counting numbers 1-10
🔒 (C) Counting numbers 1-10
🔒 (D) Counting numbers 1-10
▶️ Simple skip counting by 2s
🔒 Skip counting by 2
▶️ Skip Counting by 2s (Start at 2)
🔒 Skip Counting by 2s (Start at 8)
🔒 Skip Counting by 2s (Start at 11)
🔒 Skip Counting by 2s (Start at 100)
▶️ Skip counting by 3
🔒 Skip counting by 4
🔒 Skip counting by 5
▶️ Skip Counting by 5s (Start at 5)
🔒 Skip Counting by 5s (Start at 25)
🔒 Skip Counting by 5s (Start at 21)
▶️ Skip counting by 10
🔒 Skip Counting by 10s (Start at 10)
▶️ Skip Counting by 10s (Start at 40)
🔒 Skip Counting by 10s (Start at 27)
🔒 Skip Counting by 10s (Start at 75)
▶️ Counting backwards 10-1 A
▶️ Counting backwards 10-1 B
🔒 Counting backwards 20-1 A
🔒 Counting backwards 20-1 B
▶️ Counting grouped objects up to 10
▶️ Counting grouped objects up to 20
▶️ Practice writing numbers 1-25
▶️ Practice writing numbers 26-50
🔒 Practice writing numbers 51-75
🔒 Practice writing numbers 76-100
▶️ Writing numbers as words 1-10
▶️ Writing numbers as words 11-20
▶️ Writing numbers as words 21-30
🔒 Writing numbers as words 31-40
🔒 Writing numbers as words 41-50
🔒 Writing numbers as words 51-60
▶️ Writing numbers as words 61-70
▶️ Writing numbers as words 71-80
🔒 Writing numbers as words 81-90
🔒 Writing numbers as words 91-100
▶️ Matching numbers with words 1-20
▶️ Matching numbers with words 1-80
🔒 Matching numbers with words 1-150
▶️ Circle a number of objects (to 10)
🔒 Circle a number of objects (to 20)
▶️ Count to 100 Chart
▶️ 101 Bananas! (Count to 101)
▶️ Make 5 through 10 using number bonds
🔒 Practice with number bonds (mixed)
▶️ Identifying number patterns (up: 1,2,or 5)
▶️ Identifying number patterns (up/down: 1, 2, 5, or 10)
🔒 Identifying number patterns (up/down: 1-5, 10)
▶️ Input and output charts (A)
🔒 Input and output charts (B)
🔒 Input and output charts (C)
▶️ Reading number lines (A)
🔒 Reading number lines (B)
🔒 Reading number lines (C)

▶️ Which number/group is larger?
🔒 Which number/group is smaller?
▶️ Comparing numbers A
🔒 Comparing numbers B
🔒 Comparing numbers C
▶️ Comparing numbers using < or > (up to 25)
🔒 Comparing numbers using < or > (up to 50)
🔒 Comparing numbers using < or > (up to 100)
▶️ Even or odd? (up to 25)
▶️ Even or odd? (up to 50)
🔒 Even or odd? (up to 100)
▶️ Writing ordinal numbers A
🔒 Writing ordinal numbers B
🔒 Matching ordinal numbers
▶️ Order numbers from greatest to least (up to 10)
▶️ Order numbers from greatest to least (up to 50)
🔒 Order numbers from greatest to least (up to 100)
🔒 Order numbers from least to greatest (up to 10)
🔒 Order numbers from least to greatest (up to 50)
🔒 Order numbers from least to greatest (up to 100)

▶️ Base 10 blocks-regrouping (A)
🔒 Base 10 blocks-regrouping (B)
▶️ Counting with base 10 blocks (A)
🔒 Counting with base 10 blocks (B)
🔒 Counting with base 10 blocks (C)
▶️ Express numbers as 10’s and 1’s (A)
🔒 Express numbers as 10’s and 1’s (B)
🔒 Express numbers as 10’s and 1’s (C)
▶️ Adding using base 10 blocks (A)
🔒 Adding using base 10 blocks (B)
🔒 Adding using base 10 blocks (C)
▶️ Place value: identify tens and ones (A)
🔒 Place value: identify tens and ones (B)
🔒 Place value: identify tens and ones (C)
▶️ Combine tens and ones (A)
▶️ Combine tens and ones (B)
🔒 Combine tens and ones (C)
▶️ Identifying place value: tens and ones (A)
🔒 Identifying place value: tens and ones (B)
🔒 Identifying place value: tens and ones (C)
▶️ Adding tens and ones (A)
🔒 Adding tens and ones (B)
▶️ Adding tens and ones - advanced (A)
🔒 Adding tens and ones - advanced (B)
▶️ Rounding to the nearest 10 (A)
🔒 Rounding to the nearest 10 (B)
🔒 Rounding to the nearest 10 (C)

▶️ Longer or shorter?
▶️ Measuring lengths in inches (A)
▶️ Measuring lengths in inches (B)
🔒 Measuring lengths in inches (C)
🔒 Measuring lengths in inches (D)
🔒 Measuring lengths in inches (E)
🔒 Measuring lengths in inches (F)
▶️ Measure the object in centimeters (A)
▶️ Measure the object in centimeters (B)
🔒 Measure the object in centimeters (C)
▶️ Which object weighs more?
🔒 Which object weighs less?

▶️ Matching coins with names (USD)
▶️ Matching coins with names (CAD)
🔒 Matching coins with values (USD)
🔒 Matching coins with values (CAD)
▶️ Coin Chart (USD)
▶️ Coin Chart (CAD)
▶️ Coin Focus: Penny (USD)
▶️ Coin Focus: Nickel (USD)
🔒 Coin Focus: Dime (USD)
🔒 Coin Focus: Quarter (USD)
▶️ Match the total value of coins (USD)
▶️ Match the total value of coins (CAD)
▶️ Write the total value of coins (USD)
▶️ Write the total value of coins (CAD)
🔒 Piggy bank: count the coins (USD)
▶️ How much does it cost? (USD) (A)
🔒 How much does it cost? (USD) (B)

▶️ Practice with Number Bonds: 5
▶️ Practice with Number Bonds: 6
▶️ Practice with Number Bonds: 7
▶️ Practice with Number Bonds: 8
▶️ Practice with Number Bonds: 9
🔒 Practice with Number Bonds: 10
🔒 Practice with Number Bonds: 11-19
🔒 Practice with Number Bonds: 20
▶️ Adding using pictures
▶️ Add one (single-digit)
▶️ Add two (single-digit)
🔒 Add three (single-digit)
▶️ Adding using your fingers
🔒 Add using dice
▶️ Simple addition: single-digit (large font) (A)
🔒 Simple addition: single-digit (large font) (B)
▶️ Addition: make 10 (A)
▶️ Addition: make 10 (B)
▶️ Vertical addition to 10 (A)
🔒 Vertical addition to 10 (B)
▶️ Vertical addition to 20 (A)
🔒 Vertical addition to 20 (B)
🔒 Vertical addition to 50 (A)
🔒 Vertical addition to 50 (B)
🔒 Vertical addition to 100 (A)
🔒 Vertical addition to 100 (B)
▶️ Adding Doubles
▶️ Practice adding 7
▶️ Practice adding 8
🔒 Practice adding 9
🔒 Practice adding 10
▶️ Addition practice: add to the next ten
▶️ Addition practice: adding whole tens
▶️ Addition: fill in the missing number (up to 10)
🔒 Addition: fill in the missing number (up to 20)
🔒 Addition: fill in the missing number (up to 100)
▶️ Adding single-digit numbers
▶️ Adding double-digit numbers (A)
🔒 Adding double-digit numbers (B)
🔒 Adding triple-digit numbers
▶️ Mixed addition and subtraction (single-digit)
▶️ Mixed addition and subtraction (2-digit) A
🔒 Mixed addition and subtraction (2-digit) B
🔒 Mixed addition and subtraction (3-digit)

▶️ Subtracting using pictures
▶️ Subtract one (single-digit)
▶️ Subtract two (single-digit)
🔒 Subtract three (single-digit)
▶️ Subtract from 10 (A)
🔒 Subtract from 10 (B)
▶️ Simple subtraction: single-digit (large font) (A)
🔒 Simple subtraction: single-digit (large font) (B)
▶️ Vertical subtraction (to 10)
▶️ Vertical subtraction (to 20)
🔒 Vertical subtraction (to 50)
🔒 Vertical subtraction (to 100)
▶️ Subtraction: fill in the missing number (up to 10)
🔒 Subtraction: fill in the missing number (up to 20)
🔒 Subtraction: fill in the missing number (up to 100)
▶️ Subtracting single-digit numbers
▶️ Subtracting double-digit numbers (A)
🔒 Subtracting double-digit numbers (B)
🔒 Subtracting triple-digit numbers
▶️ Subtracting doubles
▶️ Practice subtracting 7
▶️ Practice subtracting 8
🔒 Practice subtracting 9
🔒 Practice subtracting 10
▶️ Subtraction practice: subtract to the next ten
🔒 Subtraction practice: subtracting whole tens
🔒 Mixed addition and subtraction (2-digit) A

▶️ Counting tally marks (A)
🔒 Counting tally marks (B)
▶️ Drawing tally marks (A)
🔒 Drawing tally marks (B)
▶️ Completing tally charts (A)
🔒 Completing tally charts (B)
▶️ Completing tally charts (C)
▶️ Reading bar graphs (A)
🔒 Reading bar graphs (B)
🔒 Reading bar graphs (C)
▶️ Making bar graphs (A)
🔒 Making bar graphs (B)
🔒 Making bar graphs (C)
▶️ Analyzing bar graphs (A)
🔒 Analyzing bar graphs (B)
🔒 Analyzing bar graphs (C)

▶️ Identifying equal parts (shapes)
🔒 Dividing shapes into equal parts
▶️ Matching fractions with pictures
▶️ Matching fractions with words A
🔒 Matching fractions with words B
🔒 Matching fractions with words C
▶️ Writing Fractions A
🔒 Writing Fractions B

▶️ Patterns of letters
🔒 Patterns of objects
🔒 Patterns of shapes
▶️ Common shapes reference sheet
🔒 Matching shapes and their names
▶️ Matching Shapes to Real-World Objects (A)
▶️ Matching Shapes to Real-World Objects (B)
🔒 Matching Shapes to Real-World Objects (C)
🔒 Matching Shapes to Real-World Objects (D)
🔒 Matching Shapes to Real-World Objects (E)
▶️ Matching Shapes to Their Names (A)
🔒 Matching Shapes to Their Names (B)
▶️ Matching similar shapes
▶️ Drawing shapes: circles
🔒 Drawing shapes: ovals
🔒 Drawing shapes: squares
▶️ Drawing shapes: rectangles
▶️ Drawing shapes: triangles
🔒 Drawing shapes: diamonds
▶️ Naming Three-Dimensional Shapes

▶️ Addition word problems (single-digit)
▶️ Addition word problems (2-digit) A
🔒 Addition word problems (2-digit) B
🔒 Addition word problems (3-digit)
▶️ Subtraction word problems (single-digit)
🔒 Subtraction word problems (2-digit) A
🔒 Subtraction word problems (2-digit) B
🔒 Subtraction word problems (2-digit)
▶️ Mixed addition and subtraction word problems
▶️ Length word problems (in inches) (A)
🔒 Length word problems (in inches) (B)
▶️ Length word problems (in centimeters) (A)
🔒 Length word problems (in centimeters) (B)

▶️ Units of time (minutes)
🔒 Units of time (hours)
🔒 Units of time (days)
▶️ Reading the clock (hours) (large font) (A)
🔒 Reading the clock (hours) (large font) (B)
🔒 Units of time: minutes, hours, or days?
▶️ Telling time in whole hours (A)
🔒 Telling time in whole hours (B)
▶️ Telling time in half hours (A)
🔒 Telling time in half hours (B)
▶️ Telling time in quarter hours (A)
🔒 Telling time in quarter hours (B)
▶️ Draw the time on the clock (hours)
🔒 Draw the time on the clock using a digital clock (hours)
🔒 Draw the time on the clock (hours, half hours)
▶️ Draw the time on the clock (hours, half hours, quarter hours)
▶️ Elapsed time (A)
🔒 Elapsed time (B)
🔒 Elapsed time (C)
🛑 WAIT! Are you looking to unlock ALL of our 1st Grade Math Worksheets?
When you sign up for the Mashup Math Infinite K-8 Worksheet Portal, you will gain access to all of our first grade math worksheets and answer keys all in one convenient place.
▶️ Click here to gain on-demand access to all of our 1st Grade math worksheets
Why Are Our 1st Grade Math Worksheets a Great Fit for Your Students?
The first grade math worksheets shared above were carefully designed to give your 1st grade students a fun and engaging experience with exploring, practicing, and developing key foundational math skills including counting, number sense, working with money, adding and subtracting, telling time, and solving word problems. Each of our first grade math worksheets are designed to make practicing and learning math a challenging, yet fun and enjoyable experience for kids and they are meant to help students become interested in mathematics at a very early age. By helping students to master foundational math skills, they will be better prepared to succeed in mathematics when they enter higher levels of education.
So, what makes Mashup Math’s 1st grade math worksheets different from all of the other practice worksheets out there? For starters, our worksheets are appropriately challenging for 1st grade students as they do not include excessive amounts of practice problems. This focus on only including 10-20 practice problems is intentional as it prevents students from getting bored and believing that learning math is a repetitive and monotonous activity. Our first grade math worksheets are also colorful and visually appealing, which makes them both fun and approachable for first graders. The first grade math worksheets included in the collection above are also designed to allow students to work at their own pace and they are not meant to have time restrictions. Every first grade student learns at his or her own pace, so it is crucial to allow them to practice and learn math without feeling rushed. After all, learning math is not a race, which is why many teachers use our worksheets as homework assignments and why many parents use our worksheets with their kids at home—because they can engage with mathematics at their own pace.

Our 1st Grade math worksheets give students opportunities to practice and learn math at their own pace. (Image: Mashup Math MJ)
Whether you are considering using our first grade math worksheets with your students in a classroom setting or with your kids at home, they are exactly the resource that you need for promoting self-paced learning, exploration, and deep mathematical thinking. By giving your kids a math learning experience that is both engaging and appropriately challenging, you are helping them to develop positive beliefs about the subject during a crucial formative period in their lives. Why is this so important? Because far too many students lose interest in math at a young age, which often ends up limiting their opportunities later in life.
We should also note that our 1st grade math worksheets can be utilized in essentially any curriculum or math course. Since our worksheets are organized by topic and level of difficulty, they can be used in a variety of ways including primary practice activities, warm-up and/or cool-down activities, spiral reviews, extra practice or extra credit assignments, and as homework assignments.
On a final note, we believe that interacting with math via exploration is the key for students to develop deep and meaningful understanding. If you work with 1st graders in any capacity, then you know that they approach learning with a natural curiosity and that they have a wonderful desire to make sense of and understand their world. To the curious young mind, exploring and learning math can be an incredible experience that sparks lifelong learning, which is why our worksheets are designed to give first graders structured opportunities to explore math and develop understandings of topics that make sense to them individually.
Not all math worksheets are the same and not all math worksheets are effective, but when they are designed and utilized correctly (appropriately challenging, engaging, exploratory, etc.), they can be a key contributor to a first grade student’s math development. It’s no secret that worksheets are a useful and practical tool for teaching math, giving students opportunities to practice and apply their skills, and for exploring math topics in general. When you can give your students a math learning experience that is enjoyable and engaging, you are putting them on a path of loving math and being interested in pursuing it as they progress through higher grade levels, which will make many desirable opportunities and careers available to them later in life.
Looking for more awesome First Grade Math Worksheets? Click here to gain access to our complete library of worksheets and answer keys , where you can gain access to ALL of our 1st Grade math resources.

1st Grade Math Worksheets
This dynamic math worksheet generator for grade 1 students provides customizable word problem worksheets covering essential math skills. With options to generate 5 to 40 questions, it supports students' growth through practice in various key topics, ensuring a comprehensive approach to foundational math learning.
Grade 1 Addition Workshets
Practicing addition word problems helps grade 1 students strengthen their math skills and gain confidence in problem-solving.
Grade 1 Subtraction Workshets
Subtraction word problems teach students to identify situations where quantities decrease or need removal. This skill is essential for everyday activities, such as making changes or comparing amounts. By practicing subtraction, students improve their ability to solve practical problems confidently.
Grade 1 Comparison Workshets
Comparison word problems help students learn to analyze differences and similarities between quantities. This foundational skill supports mathematical reasoning, assisting young learners to make connections between numbers, sizes, or amounts, which is critical for developing logical thinking abilities.
Grade 1 True or False Equations Workshets
Practicing true or false equations encourages students to evaluate mathematical statements and determine their accuracy. This skill promotes a deeper understanding of equality and arithmetic principles, enhancing logical reasoning as students identify correct and incorrect expressions.
Grade 1 Place Value (Tens and Ones) Workshets
Place value word problems emphasize understanding tens and ones, a crucial skill for early numeracy. This practice strengthens students' ability to decompose numbers, recognize their values, and solve problems involving multi-digit numbers, laying a strong foundation for future math concepts.
Grade 1 Measurement Workshets
Measurement word problems introduce students to comparing lengths, weights, and capacities in practical situations. By working through these problems, children grasp the significance of measurement units and develop skills in estimating, comparing, and solving real-life measurement tasks.
Grade 1 Time Workshets
Time word problems help students learn to tell time and understand daily schedules. By solving these problems, students gain familiarity with clocks, time intervals, and concepts such as hours and minutes, fostering time-management skills and awareness of daily routines.
Grade 1 Days, Months, and Seasons Workshets
Solving word problems related to days, months, and seasons introduces students to the calendar and the passage of time. This practice strengthens their understanding of natural sequences and patterns, helping them recognize time-related concepts that structure everyday life.
Grade 1 Money Workshets
Money word problems teach students the value of coins and bills and the basics of financial literacy. This skill is vital for practical decision-making, such as counting money, making purchases, and understanding change, equipping children for real-world transactions.
Grade 1 Data and Graphs Workshets
Data and graphs word problems introduce young learners to interpreting visual information. This skill develops their ability to collect, organize, and analyze data, enhancing critical thinking by teaching them how to extract meaningful insights from charts and tables.
Grade 1 Patterns Workshets
Pattern word problems encourage students to identify and predict sequences. This skill is key for mathematical reasoning, as recognizing patterns lays the groundwork for algebraic thinking and helps students make sense of recurring structures in numbers and shapes.
Grade 1 Two-dimensional Shapes Workshets
Practicing with two-dimensional shape word problems helps students recognize, describe, and classify shapes like circles, squares, and triangles. This foundational geometry skill enhances spatial awareness and supports an understanding of shape properties and their relationships.
Grade 1 Three-dimensional Shapes Workshets
Three-dimensional shape word problems introduce students to solids such as cubes, spheres, and cylinders. By exploring the properties of these shapes, children develop spatial reasoning skills essential for understanding volume, surface area, and other geometric concepts.
Grade 1 Venn Diagrams Workshets
Venn diagram word problems teach students to compare and classify objects based on shared characteristics. This practice enhances logical thinking and problem-solving skills by showing children how to organize information visually and identify relationships between different sets.
Grade 1 Fractions Workshets
Fractions word problems familiarize students with the concept of parts of a whole. This skill is fundamental for understanding division and proportional reasoning, helping children recognize fractional quantities in everyday contexts, such as sharing or dividing objects.
Math and Logic Problems
to develop logical reasoning and problem solving skills
A+Click helps students become problem solvers without any ads and without signing-up. More than 16,000 challenging questions with answers for students in grades 1 through 12, starting from the very simple to the extremely difficult. The problems concentrate on understanding, usefulness, and problem solving.

Problem of the Day


IMAGES
COMMENTS
Free 1st grade word problem worksheets. Includes word problems for addition, subtraction, fractions, lengths, time and money, as well as mixed problem worksheets. Also number charts, addition, subtraction, telling time, counting money and much more. No login required.
Sep 23, 2024 · Math problems for 1st graders connect kindergarten math skills to 2nd grade math skills and beyond. 1st grade math problems focus on building an understanding of addition and subtraction and learning a variety of strategies for efficient problem-solving.
Each worksheet is designed with the needs of 1st grade students in mind, as they are created to be engaging, colorful, and appropriately challenging for a typical first grade student. The math skills and topics below are all key foundational mathematics and problem-solving skills that students will need in order to be successful in higher ...
Grade 1 Venn Diagrams Workshets. Venn diagram word problems teach students to compare and classify objects based on shared characteristics. This practice enhances logical thinking and problem-solving skills by showing children how to organize information visually and identify relationships between different sets.
to develop logical reasoning and problem solving skills. A+Click helps students become problem solvers without any ads and without signing-up. More than 16,000 challenging questions with answers for students in grades 1 through 12, starting from the very simple to the extremely difficult. The problems concentrate on understanding, usefulness ...
MHID: 0-02-111965-1 Homework Practice and Problem-Solving Practice Workbook Contents Include: • 117 Homework Practice worksheets- one for each lesson • 117 Problem-Solving Practice worksheets- one for each lesson to apply lesson concepts in a real-world situation Homework Practice and Problem-Solving Practice Workbook