

Case Study Questions Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
- Post author: studyrate
- Post published:
- Post category: class 10th
- Post comments: 0 Comments
CBSE Board Exam is on the way, so you must practice some good Case Studies and Passage Based Questions of Class 10 Science to boost your preparation to score 95+% on Boards. In this post, you will get Case Study and Passage Based Questions that will come in CBSE Class 10 Science Board Exams. These Case Study Questions Class 10 Science are written by experts.
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.

In CBSE Class 10 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason . There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Chemical Reactions and Equations Case Study Questions With Answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Question 1:
A chemical reaction is a representation of chemical change in terms of symbols and formulae of reactants and products. There are various types of chemical reactions like combination, decomposition, displacement, double displacement, oxidation, and reduction reactions. Reactions in which heat is released along with the formation of products are called exothermic chemical reactions. All combustion reactions are exothermic reactions.
(i) The chemical reaction in which a single substance breaks down into two or simpler substances upon heating is known as (a) thermal decomposition reaction (b) photodecomposition reaction (c) electric decomposition reaction (d) both (a) and (c)
Answer: (a) The chemical reaction in which a single substance breaks down into two or more simpler substances upon heating is known as thermal decomposition reaction.
(ii) The massive force that pushes the rocket forward through space is generated due to the (a) combination reaction (b) decomposition reaction (c) displacement reaction (d) double displacement reaction
Answer: (b) The massive force that pushes the rocket forward through space is generated due to the decomposition reaction. Hydrogen peroxide decomposes and provides it with a considerable reaction force thrust.
(iii) A white salt on heating decomposes to give brown fumes and the yellow residue is left behind. The yellow residue left is of (a) lead nitrate (b) nitrogen oxide (c) lead oxide (d) oxygen gas
Answer: (c) Lead nitrate decomposes to give brown fumes of nitrogen dioxide gas and yellow residue of lead oxide is left behind.
(iv) Which of the following reactions represents a combination reaction? (a) CaO (s) + H 2 O (l) → Ca(OH) 2 (aq) (b) CaCO 3 (s) → CaO (s) + CO 2 (g) (c) Zn(s) + CuSO 4 (aq) → ZnSO 4 (aq) + Cu(s) (d) 2FeSO 4 (s) → Fe 2 O 3 (s) +SO 2 (g) + SO 3 (g)
Answer: (a) A reaction in which two or more reactants combine to form a single product is known as a combination reaction.
(v) Complete the following statements by choosing correct type of reaction for X and Y. Statement 1: The heating of lead nitrate is an example of ‘X’ reaction. Statement 2: The burning of magnesium is an example of ‘Y’ reaction. (a) X- Combination, Y- Decomposition (b) X- Decomposition, Y-Combination (c) X- Combination, Y-Displacement (d) X- Displacement, Y-Decomposition
Answer: (b) Heating of lead nitrate to form nitrogen dioxide and lead oxide is an example of thermal decomposition reaction and the burning of magnesium ribbon in the air to form magnesium oxide is an example of combination reaction.
Question 2:
In a chemical reaction, reactants are converted into products. The conversion of reactants into products in a chemical reaction is often accompanied by some features which can be observed easily. These easily observed features which take place as a result of chemical reactions are known as characteristics of chemical reactions. Some important characteristics of chemical reactions are: (I) Evolution of heat (II) Formation of a precipitate (III) Change in color (IV) Change in temperature (V) Change in state
Anyone of these general characteristics can tell us whether a chemical reaction has taken place or not.
(i) Reaction of magnesium with air is a/an
Answer: (a) exothermic reaction
(ii) In the following reaction Ca 2+ (aq)+2OH−(aq)⟶Ca(OH) 2 (s)Ca(aq) 2 ++2OH(aq)−⟶Ca(OH) 2 (s) precipitate of calcium hydroxide will be of
Answer: (d) white colour
(iii) In the given reaction, S(s)+O 2 (g)⟶SO 2 S(s)+O 2 (g)⟶SO 2 the physical state of SO 2 is
Answer: (c) gaseous
(iv) Which one of the following processes involves chemical reactions?
Answer: (d) Heating copper wire in the presence of air at high temperature.
(v) In which of the following reactions, high amount of heat energy will be evolved?
Answer: (c) Burning of L.P.G.
Case Study 3: Chemical reactions and equations are fundamental concepts in chemistry that help us understand the transformation of substances. A chemical reaction involves the rearrangement of atoms to form new substances with different properties. In a chemical equation, the reactants are written on the left side, and the products are written on the right side, separated by an arrow. The number of atoms of each element must be balanced on both sides of the equation. This is achieved by using coefficients to adjust the number of molecules involved in the reaction. Chemical reactions can be classified into various types, such as combination reactions, decomposition reactions, displacement reactions, and redox reactions. Understanding and balancing chemical equations is crucial for studying chemical reactions, predicting the products formed, and analyzing the stoichiometry of reactions.
What do chemical reactions involve? a) Formation of new substances with different properties b) Rearrangement of atoms c) Balancing of equations d) All of the above Answer: d) All of the above
How are reactants and products represented in a chemical equation? a) Reactants on the left side, products on the right side b) Reactants on the right side, products on the left side c) Reactants and products mixed together d) Reactants and products in different equations Answer: a) Reactants on the left side, products on the right side
What must be balanced in a chemical equation? a) Number of molecules b) Number of atoms of each element c) Physical properties of substances d) Coefficients Answer: b) Number of atoms of each element
Which type of chemical reaction involves the breakdown of a compound into simpler substances? a) Combination reaction b) Decomposition reaction c) Displacement reaction d) Redox reaction Answer: b) Decomposition reaction
Why is balancing chemical equations important? a) To predict the products formed in a reaction b) To analyze the stoichiometry of reactions c) To study chemical reactions d) All of the above Answer: d) All of the above
Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries about CBSE Class 10 Science Chemical Reactions and Equations Case Study and Passage Based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible. By Team Study Rate
You Might Also Like

CBSE Class 10 Maths Chapter 5 –Arithmetic Progression MCQ Quiz
Case study questions class 10 economics money and credit, case study questions class 10 science chapter 12 electricity, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Chemical Reactions and Equations Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 1

Last Updated on August 26, 2024 by XAM CONTENT
Hello students, we are providing case study questions for class 10 science. Case study questions are the new question format that is introduced in CBSE board. The resources for case study questions are very less. So, to help students we have created chapterwise case study questions for class 10 science. In this article, you will find case study questions for cbse class 10 science chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations.

Table of Contents
Case Study Questions on Chemical Reactions and Equations
Question 1:
Rahul is a skilled painter. He mixed a white coloured powder, compound X with water. The compound X reacted vigorously with water to produce a compound Y and a large amount of heat. Then, Rahul used the compound Y for white washing the walls. Customer was not satisfied with the work of Rahul as walls were not shining. But Rahul guaranteed him that the walls would shine after 2-3 days and after 3 days of whitewash, the walls became shiny.
Read the above passage carefully and give the answer to the following questions:
Q 1. Name the compound X, that Rahul mixed with water.
Difficulty Level: Medium
Ans. The compound X is calcium oxide (CaO).
Q 2. Name the compound Y, that Rahul got after mixing X with water.
Ans. Compound Y is calcium hydroxide.
Q 3. What type of reaction has occurred here?
Difficulty Level: Easy
Ans. Combination reaction
Q 4. Write the chemical reaction responsible for shiny finish of the walls.
Ans. Ca (OH) 2 (aq) + CO 2 (g) → CaCO 3 (s) + H 2 O (l)
Q 5. Write the common name of X and Y.
Ans. Common name of CaO (X) is quick lime and that of Ca(OH) 2 is slaked lime.
- Electricity Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 12
- The Human Eye and the Colourful World Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 11
- Metals and Non-metals Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 3
- Light – Reflection and Refraction Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 10
Life Processes Class 10 Case Study Questions Science Chapter 6
Acids bases and salts class 10 case study questions science chapter 2, you may also like.
- Assertion Reason Questions for Class 10 Science
- Physics Numerical Problems for Class 10 Science
Topics from which case study questions may be asked
- Understand the concept of chemical reactions and their importance in daily life.
- Learn to write chemical equations for different types of chemical reactions.
- Master the skill of balancing chemical equations.
- Identify and classify different types of chemical reactions, such as combination, decomposition, displacement, double displacement, and redox reactions.
- Explore the concepts of oxidation and reduction in chemical reactions.
- Understand the phenomena of corrosion and rancidity and their prevention methods.
- Recognize the applications of chemical reactions in various industries and everyday scenarios.
- Develop critical thinking skills by analyzing and predicting the outcomes of chemical reactions.
- Appreciate the role of chemical reactions in environmental processes and human activities.
This chapter deals with introducing students to the fundamental concepts of chemical reactions, equations, and their implications.
Important Links for CBSE Class 10 Science Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
- Download 59 Important Questions for Chemical Reactions and Equations
- Download Chapter Test for Chemical Reactions and Equations
Helpful Links for CBSE Class 10 Science Preparation
- Download 125 Important Case Study Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science
- Download 220 Important Assertion Reason Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science
- Download 225 Practical Based Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science
- Download 65 Important Numerical Problems for CBSE Class 10 Physics
- Download 60 Important Diagram Based Questions for CBSE Class 10 Physics
- Download 150 Most Repeated Questions for CBSE Class 10 Science
- Download Chapter Test for CBSE Class 10 Science
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on Chemical Reactions and Equations Case Study Questions
Q1: what are case study questions for cbse examinations.
A1: Case study questions in CBSE examinations typically involve scenarios or real-life examples, requiring students to apply their understanding of concepts to solve problems or analyze situations.
Q2: Why are case study questions important for understanding class 10 science chapters?
A2: Case study questions provide a practical context for students to apply theoretical knowledge to real-world situations, fostering deeper understanding and critical thinking skills.
Q3: How should students approach answering case study questions for CBSE?
A3: Students should carefully read the case study, identify the key issues or problems presented, analyze the information provided, apply relevant concepts and principles of chemical reactions and equations, and formulate well-supported solutions or responses.

Q4: Are there any resources available online for students to practice case study questions on class 10 science chapters for CBSE exams?
A4: Yes, several educational websites offer case study questions for CBSE students preparing for science examinations. We also offer a collection of case study questions for all classes and subject on our website. Visit our website to access these questions and enhance your learning experience. If you need more case study questions for your preparation, then you visit Physics Gurukul website.
Q5: How can students effectively prepare for case study questions on chemical reactions and equations for CBSE exams?
A5: Effective preparation strategies include regular revision of concepts, solving practice questions, analyzing case studies from previous exams, seeking clarification on doubts, and consulting with teachers or peers for guidance and support.
Q6: How can teachers incorporate case study questions on chemical reactions and equations class 10 science into classroom teaching?
A6: Teachers can integrate case studies into lesson plans, group discussions, or interactive activities to engage students in active learning, promote problem-solving skills, and facilitate a deeper understanding of chemical reactions and equations.
Q7: Name the law based on which chemical equations must be balanced.
A7: Law of conservation of mass. Mass can neither be created nor can it be destroyed during a chemical reaction.
Q8: List any two observations when ferrous sulphate is heated in a dry test tube.
A8: (i) Initial light green colour changes to reddish brown colour. (ii) Colourless gas is evolved. (iii) Gas with choking smell is evolved
Q9: Why do silver articles become black after some time, when exposed to air?
A9: They get tarnished by reacting with atmospheric air to form silver sulphide.
Q10: Give reason why do chips manufacturers usually flush bags of chips with gas such as nitrogen?
A10: To prevent the oil and fats of the chips from being oxidized or become rancid.

Related Posts

- RS Aggarwal
- ML Aggarwal
- Merchant of Venice
- NCERT Books
- Questions and Answers
- NCERT Notes
- Important Questions
- Chemical Reactions and Equations
Case Based Questions for Ch 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations Class 10 Science
(i) The massive force that pushes the rocket forward through space is generated due to the
(a) combination reaction
(b) decomposition reaction
(c) displacement reaction
(d) double displacement reaction
(ii) A white salt on heating decomposes to give brown fumes and yellow residue is left behind. The yellow residue left is of
(a) lead nitrate
(b) nitrogen oxide
(c) lead oxide
(d) oxygen gas
(iii) Which of the following reactions represents a combination reaction?
(a) CaO (s) + H 2 O (l) ⟶ Ca(OH) 2 (aq)
(b) CaCO 3 (s) ⟶ CaO (s) + CO 2 (g)
(c) Zn(s) + CuSO 4 (aq) ⟶ ZnSO 4 (aq) + Cu(s)
(d) 2FeSO 4 (s) ⟶ Fe 2 O 3 (s) + SO 2 (g) + SO 3 (g)
(iv) Complete the following statements by choosing correct type of reaction for X and Y.
Statement 1: The heating of lead nitrate is an example of ‘X’ reaction.
Statement 2: The burning of magnesium is an example of ‘Y’ reaction.
(a) X-Combination, Y-Decomposition
(b) X-Decomposition, Y-Combination
(c) X-Combination, Y-Displacement
(d) X- Displacement, Y-Decomposition
Lead nitrate decomposes to give lead oxide and nitrogen oxide. Thus, X is a decomposition reaction.
2Pb(NO 3 ) 2 (s) ⟶ 2PbO(s) + 4NO 2 (g)
Magnesium burns in the presence of oxygen gas to magnesium oxide. Thus, Y is a combination reaction.
2Mg + O 2 ⟶ 2MgO
(b) combustion
(c) decomposition reaction
(d) photosynthesis
(ii) Which of the following is essential for photosynthesis?
(a) Sunlight
(b) Chlorophyll
(c) Glucose
(d) Both 'a' and 'b’
(iii) When a chemical compound decomposes on absorbing light and energy, then the reaction which takes place is known as:
(a) photosynthesis
(b) photodecomposition
(c) combination
(d) thermal decomposition
(iv) Which of the following reactions is an example of combustion reaction?
(a) C(s) + O 2 (g) ⟶ CO 2 (g)
(b) Zn(s) + H 2 SO 4 (aq) ⟶ ZnSO 4 + H 2 (g)
(c) Zn(s) +2HCl(aq) ⟶ ZnCl 2 (aq) + H 2 (g)
(d) 3Mg(s) + N 2 (g) ⟶ Mg 3 N 2 (s)
(v) Which of the following is an example of combination reaction?
(a) H 2 + Cl 2 ⟶ 2HCl
(b) Fe + S ⟶ FeS
(c) 2H 2 + O 2 ⟶ 2H 2 O
(d) All of them
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants and some other organisms use sunlight to synthesis nutrients from carbon dioxide and water.
(iii) (b) photodecomposition
A combustion reaction is a reaction in which a substance reacts with oxygen gas, releasing energy in the form of light and heat.
(v) (d) All of them
The values of x and y are:
(a) 3 and 5
(b) 8 and 6
(c) 4 and 2
(d) 7 and 1
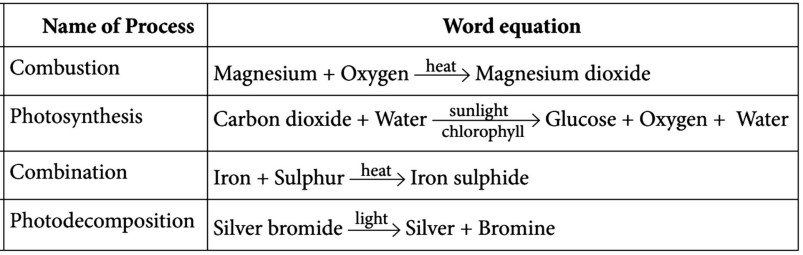
(ii) What happens when copper rod is dipped in iron sulphate solution:
(a) Copper displaces iron
(b) Blue colour of copper sulphate solution is obtained
(c) No reaction takes place
(d) Reaction is exothermic
(iii) A substance which oxidised itself and reduces other is known as:
(a) Oxidising agent
(b) Reducing agent
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
(iv) Fe 2 O 3 + 2Al ⟶ Al 2 O 3 + 2Fe
The above reaction is an example of a:
(a) Combination reaction
(b) Double displacement reaction
(c) Decomposition reaction
(d) Displacement reaction
(v) Name the products formed when iron filings are heated with dilute hydrochloric acid.
(a) Fe (III) chloride and water
(b) Fe (II) chloride and water
(c) Fe (II) chloride and hydrogen gas
(d) Fe (III) chloride and hydrogen gas
After balancing the equation, we get
Cu + 4HNO 3 ⟶ Cu(NO 3 ) 2 + 2NO 2 + 2H 2 O
(ii) (c) No reaction takes place.
(iii) (b) Reducing agent
Reducing agents reduce the other substance and in turn, get oxidized.
(iv) (d) Displacement reaction
(v) (c) Fe (II) chloride and hydrogen gas
When dilute Hydrochloric acid is added to iron filings, iron chloride & hydrogen gas is produced.
Fe + 2HCl ⟶ FeCl 2 + H 2
The iron displaces hydrogen from hydrochloric acid to form iron (II) chloride & hydrogen gas. This is a single displacement reaction.
(a) bleaching agent in the textile, paper and jute industry
(b) disinfectant for water to make water free of germs
(c) oxidising agent in many industries
(d) all of these
(ii) Bleaching powder is also known as:
(a) calcium oxychloride
(b) calcium hypochlorite
(c) chloride of lime
(iii) Bleaching powder gives smell of chlorine because it:
(a) is unstable
(b) gives chlorine on exposure to atmosphere
(c) is a mixture of chlorine and slaked lime
(d) contains excess of chlorine.
(iv) Select the correct statement(s) regarding bleaching powder.
(a) It is pale yellow powder having smell of chlorine.
(b) It is sparingly soluble in water and gives milky suspension when dissolved in water.
(c) As bleaching powder gives nascent oxygen, it shows bleaching property.
(d) All of these.
(v) Identify the product ‘X’ in the given reaction.
Ca(OH) 2 + Cl 2 ⟶ X + H 2 O
(a) CaOCl 2
(c) Ca(ClO 3 ) 2
Bleaching powder gives chlorine on exposure to air by reacting with CO 2 .
CaOCl 2 + CO 2 ⟶ CaCO 3 + Cl 2
Ca(OH) 2 + Cl 2 ⟶ CaOCl 2 + H 2 O
CaOCl 2 : calcium oxychloride (bleaching powder)
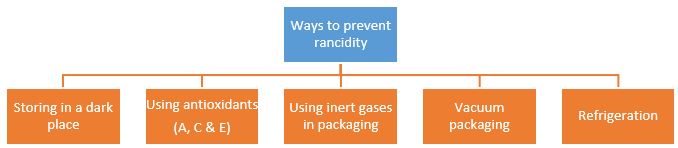
(i) Rancidity can be prevented by:
(a) adding antioxidants
(b) packaging oily food in nitrogen gas
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) none of these.
(ii) Combination of phosphorus and oxygen is an example of:
(a) oxidation
(b) reduction
(c) rancidity
(d) none of these
(iii) A science teacher wrote the following statements about rancidity:
(I) When fats and oils are reduced, they become rancid.
(II) In chips packet, rancidity is prevented by oxygen.
(III) Rancidity is prevented by adding antioxidants.
Select the correct option
(a) (I) only
(b) (II) and (III) only
(c) (III) only
(d) (I), (II) and (III)
(iv) Two statements are given below regarding rusting of iron.
(I) The rusting of iron is a redox reaction and reaction occurs as,
4Fe + 3O 2 ⟶ 4Fe 3+ + 6O 2–
(II) The metallic iron is oxidised to Fe 2+ and O 2 is reduced to O 2– .
Select the correct statement(s).
(b) II only
(c) Both I and II
(v) Which of the following measures can be adopted to prevent or slow down rancidity?
(I) Food materials should be packed in air tight container.
(II) Food should be refrigerated.
(III)Food materials and cooked food should be kept away from direct sunlight.
(a) Only II and III
(b) Only I and III
(c) Only II and III
(d) I, II and III
Antioxidants and nitrogen gas prevent oxidation of food.
(ii) (a) oxidation
4P + 3O 2 ⟶ 2P 2 O 3 ,
4P + 5O 2 ⟶ 2P 2 O 5
(iii) (III) only
The oils and fats are slowly oxidised to certain bad smelling compounds, which release foul smell. This is known as rancidity. Rancidity is prevented by filling nitrogen gas in chips packets.
(iv) (a) I only
(v) (d) I, II and III
(i) Consider the following reaction:
pMg 3 N 2 + qH 2 O ⟶ rMg(OH) 2 + sNH 3
When the equation is balanced, the coefficients p, q, r, s respectively are:
(a) 1, 3, 3, 2
(b) 1, 6, 3, 2
(c) 1, 2, 3, 2
(d) 2, 3, 6, 2
(ii) Which of the following information is not conveyed by a balanced chemical equation?
(a) Physical states of reactants and products
(b) Symbols and formulae of all the substances involved in a particular reaction
(c) Number of atoms/molecules of the reactants and products formed
(d) Whether a particular reaction is actually feasible or not
(iii) The balancing of chemical equations is in accordance with
(a) law of combining volumes
(b) law of constant proportions
(c) law of conservation of mass
(d) both (b) and (c)
(iv) Which of the following chemical equations is an unbalanced one?
(a) 2NaHCO 3 ⟶ Na 2 CO 3 + H 2 O + CO 2
(b) 2C 4 H 10 + 12O 2 ⟶ 8CO 2 + 10H 2 O
(c) 2Al + 6H 2 O ⟶ 2Al(OH) 3 + 3H 2
(d) 4NH 3 + 5O 2 ⟶ 4NO + 6H 2 O
(v) Which of the following statements is/are correct?
(a) A chemical equation tells us about the substances involved in a reaction.
(b) A chemical equation informs us about the symbols and formulae of the substances involved in a reaction.
(c) A chemical equation tells us about the atoms or molecules of the reactants and products involved in a reaction.
(d) All the above.
(i) (b) 1, 6, 3, 2
Mg 3 N 2 + 6H 2 O ⟶ 3Mg(OH) 2 + 2NH 3
(ii) (d) Whether a particular reaction is actually feasible or not
(iii) (c) law of conservation of mass
In a balanced chemical equation, total mass of reactants must be equal to the total mass of products. This is the statement of law of conservation of mass.
(iv) (b) 2C 4 H 10 + 12O 2 ⟶ 8CO 2 + 10H 2 O
(v) (d) All the above.
(i) Which of the following is a redox reaction?
(a) CaCO 3 ⟶ CaO + CO 2
(b) H 2 + Cl 2 ⟶ 2HCl
(c) CaO + 2HCl ⟶ CaCl 2 + H 2 O
(d) NaOH + HCl ⟶ NaCl + H 2 O
(ii) Identify the reaction in which H2O2 is acting as a reducing agent.
(a) H 2 SO 3 + H 2 O 2 ⟶ H 2 SO 4 + H 2 O
(b) 2HI + H 2 O 2 ⟶ 2H 2 O + I 2
(c) Cl 2 + H 2 O 2 ⟶ 2HCl + O 2
(d) 2FeCl 2 + 2HCl + H 2 O 2 ⟶ 2FeCl 3 + 2H 2 O
(iii) For the following reactions, identify the one in which H2S acts as a reducing agent.
(a) CuSO 4 + H 2 S ⟶ CuS + H 2 SO 4
(b) Cd(NO 3 ) 2 + H 2 S ⟶ CdS + 2HNO 3
(c) 2FeCl 3 + H 2 S ⟶ 2FeCl 2 + 2HCl + S
(iv) For the following reaction, identify the correct statement.
ZnO + CO ⟶ Zn + CO 2
(a) ZnO is being reduced.
(b) CO 2 is being oxidised.
(c) CO is being reduced.
(d) ZnO is being oxidised.
(v) In the following reaction, which substance is reduced?
Pbs + 4H 2 O 2 ⟶ PbSO 4 + 4H 2 O
(b) H 2 O 2
(i) (b) H 2 + Cl 2 ⟶ 2HCl
H 2 is oxidised to HCl while Cl 2 is reduced to HCl.
(ii) (c) Cl 2 + H 2 O 2 ⟶ 2HCl + O 2
(iii) (c) 2FeCl 3 + H 2 S ⟶ 2FeCl 2 + 2HCl + S
H 2 S itself gets oxidised to S and reduces FeCl 3 to FeCl 2 .
(iv) (a) ZnO is being reduced. ZnO is reduced to Zn and CO is oxidised to CO 2 .
(v) (b) H 2 O 2 is reduced to water by removal of oxygen.
In a chemical reaction, reactants are converted into products. The conversion of reactants into products in a chemical reaction is often accompanied by some features which can be observed easily. These easily observed features which take place as a result of chemical reaction are known as characteristics of chemicals reactions. Some important characteristics of chemical reactions are:
(I) Evolution of heat
(II) Formation of precipitate
(III) Change in colour
(IV) Change in temperature
(V) Change in state
Any one of these general characteristics can tell us whether a chemical reaction has taken place or not.
(i) Reaction of magnesium with air is a/an:
(a) exothermic reaction
(b) endothermic reaction
(c) reversible reaction
(d) substitution reaction
(ii) In the following reaction,
Ca 2+ (aq) + 2OH - (aq) ⟶ Ca(OH) 2 (s)
precipitate of calcium hydroxide will be of:
(a) green colour
(b) blue colour
(c) brown colour
(d) white colour.
(iii) In the given reaction,
S(s) + O 2 (g) ⟶ SO 2
the physical state of SO 2 is
(c) gaseous
(d) all three.
(iv) Which one of the following processes involve chemical reactions?
(a) Storing of oxygen gas under pressure in a gas cylinder.
(b) Keeping petrol in a china dish in the open.
(c) Liquefaction of air.
(d) Heating copper wire in the presence of air at high temperature.
(v) In which of the following reactions, high amount of heat energy will be evolved?
(a) Electrolysis of water
(b) Dissolution of NH 4 Cl in water
(c) Burning of L.P.G.
(d) Decomposition of AgBr in the presence of light.
(i) (a) exothermic reaction
(ii) (d) white colour.
Calcium hydroxide is a white colour solid.
(iii) (c) gaseous
SO 2 is gaseous in nature.
(iv) (d) Heating copper wire in the presence of air at high temperature.
When copper is heated in the presence of air in a very high temperature, a chemical reaction takes place. Copper reacts with oxygen of the air to form a thin layer of copper oxide on the surface of metallic copper.
(v) (c) Burning of L.P.G.
On burning of L.P.G., heat is evolved.
(i) Copper displaces which of the following metals from its salt solution?
(ii) When zinc reacts with dilute sulphuric acid, the gas evolved is
(a) red in colour and have a sweet smelling.
(b) green in colour and have a foul smell.
(c) colourless, odourless and burns with a pop sound.
(d) colourless, pungent smelling and burns with a pop sound.
(iii) When dry hydrogen is passed over a heated oxide of metal X using the apparatus shown below, a reddish-brown residue is obtained.
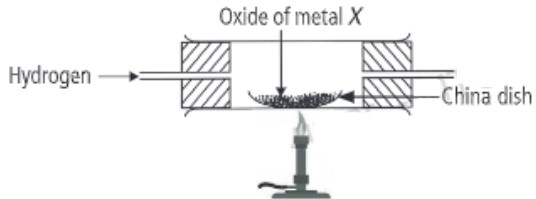
The reddish-brown residue could be
(iv) Which of the following reactions is a displacement reaction?
(a) CaO + H 2 O ⟶ Ca(OH) 2
(c) Mg + CuSO 4 ⟶ MgSO 4 + Cu
(b) MgCO 3 ⟶ Mg + CO 2
(d) H 2 + Cl 2 ⟶ 2HCl
(v) When dilute hydrochloric acid is added to granulated zinc placed in a test tube, the observation made is
(a) the surface of the metal turns shining
(b) the reaction mixture turns milky
(c) greenish yellow gas is evolved
(d) the colourless and odourless gas evolves burns with a pop sound.
(i) (c) AgNO 3
Cu + 2AgNO 3 ⟶ Cu(NO 3 ) 2 + 2Ag
Copper can displace silver from its salt solution since, copper is more reactive than silver.
(ii) (c) colourless, odourless and burns with a pop sound.
Zn + H 2 SO 4 (dil.) ⟶ ZnSO 4 + H 2 ↑
H 2 is a colourless, odourless gas and burns with a pop sound.
(iii) (a) Copper is the reddish-brown residue as shown in below reaction.
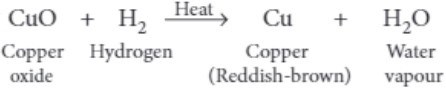
(iv) (c) Mg + CuSO 4 ⟶ MgSO 4 + Cu
It is a single displacement reaction.
(v) (d) the colourless and odourless gas evolves burns with a pop sound.
Hydrogen gas is evolved in this reaction as shown in the reaction.
Zn + 2HCl ⟶ ZnCl 2 + H 2 ↑
Hydrogen gas is colourless and odourless which burns with a pop sound.
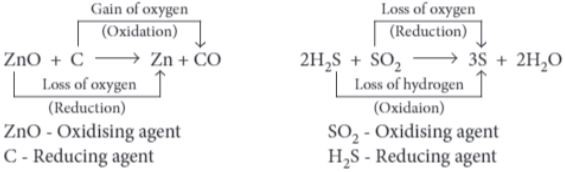
Those reactions in which two compounds react by an exchange of ions to form two new compounds are called double displacement reactions. A double displacement reaction usually occurs in solution and one of the products, being insoluble, precipitate out (separates as a solid). Any reaction in which an insoluble solid (called precipitate) is formed that separates from the solution is called a precipitation reaction. The reaction in which acid or acidic oxide reacts with base or basic oxide to form salt and water is called neutralisation reaction.
For example, 2NaOH + H 2 SO 4 ⟶ Na 2 SO 4 + H 2 O
(i) When hydrogen sulphide gas is passed through a blue solution of copper sulphate, a black precipitate of copper sulphide is obtained and the sulphuric acid so formed remains in the solution. The reaction is an example of a:
(b) displacement reaction
(ii) Which of the following is not a double displacement reaction?
(a) AgNO 3 (aq) + NaCl(aq) ⟶ AgCl(s) + NaNO 3 (aq)
(b) Zn(s) + H 2 SO 4 (aq) ⟶ ZnSO 4 (aq) + H 2 (g)
(c) CuSO 4 (aq) + H 2 S (aq) ⟶ CuS(s) + H 2 SO 4 (aq)
(d) Pb(NO 3 ) 2 (aq) + 2KI (aq) ⟶ PbI 2 (s) + 2KNO 3 (aq)
(iii) Barium chloride on reaction with ammonium sulphate forms barium sulphate and ammonium chloride. Which of the following correctly represents the type of the reaction involved?
(I) Displacement reaction
(II) Precipitation reaction
(III) Combination reaction
(IV) Double displacement reaction
(b) (II) only
(c) (III) and (IV) only
(d) (II) and (IV) only
(iv) Identify A in the following reaction.
AlCl 3 (aq) + 3NH 4 OH(aq) ⟶ A + 3NH 4 Cl(aq)
(a) Al(OH) 3
(b) Al 2 O 3
(v) Consider the following reaction,
BaCl 2 + Na 2 SO 4 ⟶ BaSO 4 + 2NaCl
Identify the precipitate in the reaction.
(c) Na 2 SO 4
(i) (d) double displacement reaction
CuSO 4 + H 2 S ⟶ CuS + H 2 SO 4
Both CuSO 4 and H 2 S exchange their ions to give new compounds- CuS and H 2 SO 4 . Hence, this is a double displacement reaction.
(ii) (b) Zn(s) + H 2 SO 4 (aq) ⟶ ZnSO 4 (aq) + H 2 (g)
It is an example of single displacement reaction.
(iii) (d) (II) and (IV) only
BaCl 2 + (NH 4 ) 2 SO 4 ⟶ BaSO 4 ↓ + 2NH 4 Cl
(BaSO 4 : white ppt.)
It is a precipitation reaction as well as double displacement reaction.
(iv) (a) Al(OH) 3
AlCl 3 + 3NH 4 OH ⟶ Al(OH) 3 + 3NH 4 Cl
(v) (b) BaSO 4
BaCl 2 (aq) + Na 2 SO 4 (aq) ⟶ BaSO 4 (s) ↓ + 2NaCl(aq)
(i) A redox reaction is one in which:
(a) both the substances are reduced
(b) both the substances are oxidized
(c) an acid is neutralised by the base
(d) one substance is oxidised while the other is reduced.
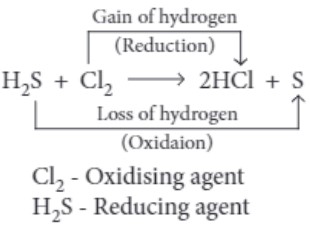
(ii) In the reaction, H 2 S + Cl 2 ⟶ S + 2HCI
(a) H 2 S is the reducing agent.
(c) H 2 S is the oxidising agent.
(b) HCl is the oxidising agent.
(d) Cl 2 is the reducing agent.
(iii) Which of the following processes does not involve either oxidation or reduction?
(a) Formation of slaked lime from quick lime.
(b) Heating mercuric oxide.
(c) Formation of manganese chloride from manganese oxide (MnO 2 ).
(d) Formation of zinc from zinc blend.
(iv) Mg + CuO ⟶ MgO + Cu
Which of the following is wrong relating to the above reaction?
(a) CuO gets reduced.
(b) Mg gets oxidised.
(c) CuO gets oxidised.
(d) It is a redox reaction.
(v) Identify the correct oxidising agent and reducing agent in the following reaction.
Fe 2 O 3 + 2AI ⟶ 2Fe + Al 2 O 3
(a) Al - Oxidising agent, Fe 2 O 3 - Reducing agent
(b) Fe 2 O 3 - Oxidising agent, Al - Reducing agent
(c) Fe - Oxidising agent, Al 2 O 3 - Reducing agent
(b) Fe 2 O 3 - Oxidising agent, Al 2 O 3 - Reducing agent
(i) (d) one substance is oxidised while the other is reduced.
In a redox reaction, one reactant is reduced while other reactant is oxidised.
(ii) (a) H 2 S is the reducing agent.
(iii) (a) Formation of slaked lime from quick lime

It is a decomposition reaction.
(iv) (c) CuO gets oxidised.
Addition of oxygen is called oxidation while the removal of oxygen is called reduction.
Thus, Mg gets oxidised and CuO gets reduced and it is a redox reaction.
NCERT Solutions for Chapter 4 The Age of Industrialisation Class 10 History
Related chapters.
- Acids, Bases and Salts
- Metals and Non-metals
- Carbon and its Compounds
- Periodic Classification of Elements (Not in Syllabus)
Related Questions
- NCERT Solutions for Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations Class 10 Science
- NCERT Revision Notes for Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations Class 10 Science
- VSAQ for Ch 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations Class 10 Science NCERT
- Assertion and Reason for Ch 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations Class 10 Science
Report a problem
- Question is incorrect
- Answer is Incorrect
- Spelling Mistakes
- Not explained in detail
