How to Do an ISO 27001 Risk Assessment
When you boil it down, the purpose of ISO 27001 is pretty straightforward. Identify the security incidents that could affect your business. Then find the best ways to either keep those incidents from happening or lessen their impact.
Risk assessments are essential to that purpose. Without one, you won’t have the knowledge you need to build a secure information security management system in the first place, let alone get ISO 27001 certified.
In this post, we’ll lay out the step-by-step process of completing an ISO 27001 risk assessment.
And we’ll share some tips, templates, and resources to help simplify and streamline things along the way.

What is an ISO 27001 risk assessment?
A risk assessment is a requirement for the ISO 27001 standard. If you want to be ISO 27001 certified , you’ll need to:
- Identify the risks your organization faces
- Determine the probability of each risk actually occurring
- Estimate the potential impact on your business
A risk treatment plan involves deciding how you will respond to each risk to keep your business secure.
Together, your risk assessment and your risk treatment plan make up your overall ISO 27001 risk management process.
ISO 27001 risk assessment requirements include:
- Establishing set criteria for evaluating information security risk
- Identifying risks for all of the information assets within scope of the ISMS
- Assigning owners for each risk
- Creating a repeatable, consistent risk assessment process
Recommended Reading

ISO 27001 Certification Costs
How to do a risk assessment for iso 27001 .
To meet ISO 27001 certification requirements , your ISO 27001 risk assessment procedure should follow these steps:
Choose your risk management approach
How will you identify and respond to information security risk? How will you estimate likelihood and impact? What is your company’s acceptable level of risk?
In general, there are two approaches to risk assessment: qualitative and quantitative.
With a qualitative approach, you’ll go through different scenarios and answer “what if” questions to identify risks. A quantitative approach uses data and numbers to define levels of risk.
Some common risk management frameworks include ISO 27005:2018 , OCTAVE , and NIST SP 800-30 Revision 1 . Whichever approach or methodology you choose, company management should be closely involved in this process. They’ll be instrumental in determining your organization’s baseline security criteria and level of acceptable risk.
And by establishing your risk management methodology at the company level, every department will be able to follow the same cohesive process.
Identify risks
Start with a list of information assets and then identify risks that could impact data confidentiality, integrity, and availability for each one. You’ll need to consider your hardware (including mobile devices), software, information databases, and intellectual property.
Analyze risks
Once you’ve identified a set of risks, determine the potential likelihood of each one occurring and its business impact. Remember that impact isn’t always monetary — it could be an impact on your brand’s reputation and customer relationships, a legal or contractual issue, or a threat to your compliance.
Assign each risk a likelihood and impact score. On a scale from 1-10, how probable is it that the incident will occur? How significant would its impact be? These scores will help you prioritize risks in the next step.
Evaluate and prioritize risks
No business has unlimited resources. You’ll need to decide which risks you should spend time, money, and effort to address and which fall within your acceptable level of risk.
Now that you’ve analyzed the likelihood and impact of each risk, you can use those scores to prioritize your risk management efforts. A risk matrix can be a helpful tool in visualizing these priorities.
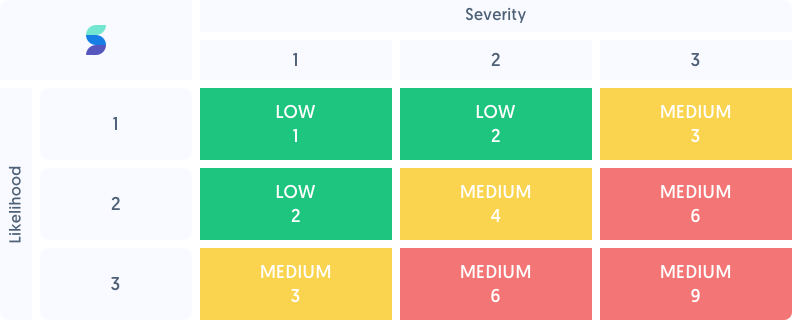
Complete a risk treatment plan
The risk treatment plan is an essential document for ISO 27001 certification, and it’s one your certification auditor will want to review. It records how your organization has decided to respond to the threats you identified in your risk assessment.
The ISO 27001 standard outlines four possible actions:
- Treat the risk with security controls that reduce the likelihood it will occur
- Avoid the risk by preventing the circumstances where it could occur
- Transfer the risk with a third party (i.e., outsource security efforts to another company, purchase insurance, etc.)
- Accept the risk because the cost of addressing it is greater than the potential damage
ISO 27001 also requires that each risk have an established owner. The owner will be responsible for approving your treatment plan for that risk and accepting any residual risk.
Produce a risk report
Your certification auditor will likely want to review evidence that you’ve completed your risk management process. These documents may include a risk assessment report and a risk summary report.
The ISO 27001 risk assessment report provides an overview of your risk assessment process, including which information assets you evaluated, which risk treatment option you selected for each identified risk, and the probability and impact scores for each.
The risk summary details the risks that your organization is choosing to address after completing the risk treatment process.
Review and monitor risks to improve the ISMS
Continuous improvement is one of the central ideas of the ISO 27001 standard. You’ll need to make conducting these risk assessments an ongoing process.
Monitoring and assessing risk should be incorporated into the day-to-day habits of your team. That said, the recommended formal ISO 27001 risk assessment frequency is once a year, ideally when you conduct your internal audit.
Internal auditors should consider any new risks that have emerged and evaluate how well your current risk management program is working to safeguard your ISMS.
ISO 27001 risk assessment template
Get your copy of our ISO 27001 risk assessment template .
This editable spreadsheet will guide you through the process of creating an asset register, assigning asset and risk owners, identifying and scoring risks, and selecting your risk treatment. It includes a built-in risk matrix to help you quickly visualize high-priority risks and build out your remediation plan.

Simplify risk assessments with Secureframe
Want to skip the spreadsheets?
Our compliance automation platform guides you through the risk assessment process and automatically generates an ISO 27001 readiness report. You’ll be able to see exactly how close you are to achieving certification and get actionable advice for closing any gaps.
Request a demo with one of our product experts today.
ISO 27001 Overview
What is iso 27001 certification, why is iso 27001 important benefits of compliance, the history of iso 27001, iso 27001 vs soc 2, iso 27001 vs nist csf: what’s the difference & how to choose, iso 27001 requirements, an introduction to the iso 27001 isms, the core requirements of clauses 4-10, iso 27001 controls explained: a guide to annex a, iso 27001 vs iso 27002: what’s the difference, iso 27001 certification process, the iso 27001 certification process: a step-by-step guide, how long does iso 27001 certification take, iso 27001 certification validity, how to prepare for an iso 27001 audit, iso 27001 documentation: what’s required for compliance, iso 27001 evidence collection list for your certification audit, how to conduct an iso 27001 internal audit, automating iso 27001 compliance, manual vs. automated: streamline your iso 27001 compliance, the cost benefits of iso 27001 compliance automation, why iso 27001 compliance automation unveils better security insights, maintaining iso 27001 compliance, iso 27001 resources and tools, iso 27001 compliance checklists, iso 27001 policy templates, trusted iso 27001 audit firms, iso 27001 penetration testing firms.

ISO 27001 Risk Assessment for your ISMS: 7 Examples to get you Started

In today’s digital age, businesses are constantly faced with potential risks and threats to their information security – hazards that could have dire financial consequences. In fact, according to a report by IBM the average cost of a data breach in 2022, in the USA, was $9.44. million. To ensure that sensitive information is protected, it’s essential to have an effective Information Security Management System (ISMS) in place. One of the crucial components of an ISMS is an ISO 27001 risk assessment. Let’s look at what an ISO 27001 risk assessment is, why it’s important for your ISMS, and examine some practical examples to get you started.
What is an ISO 27001 Risk Assessment and why is it important for ISMS?
An ISO 27001 risk assessment is a process that involves identifying, analysing, and evaluating potential risks to an organisation’s information security. This assessment helps organisations understand their current information security posture and identify areas that need improvement. By conducting a risk assessment, organisations can develop strategies to avoid and manage risks effectively.
7 Examples of ISO Risk Assessments
Let’s look at some practical examples of ISO 27001 risk assessments:
1. Information Security Risk Assessment (ISRA)
2. Security Continuity Assessment
3. Disaster Recovery Plan Assessment
4. Supplier Assessment
5. GDPR Assessment
6. Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA)
7. Internal Audit
Understanding ISO 27001 Risk Assessments
ISO 27001, clause 6.1.2 requires you to:
- Define how to identify the risks that could cause the loss of confidentiality, integrity, and/or availability of your information.
- Define how to identify the risk owners.
- Define the criteria for assessing consequences and assessing the likelihood of the risk.
- Define how the risk will be calculated.
- Define the criteria for accepting risks.
So, an ISO 27001 risk assessment is the process of identifying potential risks to an organisation’s information security and evaluating their likelihood and impact. The assessment helps organisations understand their current information security posture and develop strategies to avoid and manage risks effectively.
Benefits of ISO 27001 Risk Assessment
1. Helps identify potential risks to sensitive information;
2. Provides a baseline for measuring and improving the effectiveness of security controls;
3. Enables organisations to prioritise security initiatives and allocate resources effectively;
4. Helps organisations comply with relevant regulations and standards;
5. Improves stakeholder confidence in the organisation’s ability to manage sensitive information.
Steps in ISO 27001 Risk Assessment
The ISO 27001 risk assessment process usually involves the following steps:
1. Identify the information assets to be assessed
2. Identify potential threats and vulnerabilities
3. Determine the likelihood and impact of each risk
4. Evaluate the risks and prioritise them based on their likelihood and impact
5. Develop strategies to mitigate and manage the identified risks.
ISO 27001 Risk Assessment Methodologies
An organisation needs to choose a suitable risk assessment methodology based on its size, complexity, and resources. Commonly used qualitative and quantitative methodologies include:
- Asset-based risk assessment: identify and assess the risks associated with each asset of an organisation.
- Scenario-based risk assessment: create hypothetical scenarios and evaluate the potential impact of those scenarios.
- Threat-based risk assessment: assess the risks based on the identified threats.
- Control-based risk assessment: evaluate the effectiveness of existing controls and identify gaps in control implementation.
- Vulnerability-based risk assessment: focus on identifying vulnerabilities in the organisation’s IT infrastructure and assess the associated risks.
Choosing the Right Methodology
To choose the right methodology for your organisation, consider the following factors:
- The methodology should align with the organisation’s business objectives.
- The availability of resources, including financial resources, expertise, and time.
- The methodology should align with the organisation’s culture and values.
- Consider the regulatory requirements that apply to your organisation.
The Role of Risk Assessment in ISMS
Risk assessment helps organisations to:
1. Identify and evaluate potential security risks to their sensitive information.
2. Develop strategies to mitigate risks and ensure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of their information.
3. Ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
Risk Management Strategies in ISMS
An ISMS requires organisations to adopt a risk management strategy that includes the following steps:
1. Identify the potential security risks to the organisation’s sensitive information.
2. Evaluate the potential impact and likelihood of each risk.
3. Develop strategies to mitigate the identified risks.
4. Implement the strategies to mitigate the risks.
5. Regularly monitor and review the effectiveness of the implemented strategies and update them if necessary.
7 Practical Examples of ISO 27001 Risk Assessment
Here are seven practical examples of ISO 27001 risk assessment:
- Information Security Risk Assessment (ISRA)
- Security Continuity Assessment (former BCP Assessment)
- Disaster Recovery Plan (DRP)
- Supplier Assessment
- GDPR Assessment
- Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA)
- Internal Audit
How Each Example Can Be Applied to Different Types of Organisations
Each risk assessment example can be applied to different types of organisations based on their specific requirements. Depending on the business profile, certain risk assessments will be weighted more than others. For example, the disaster recovery process will be more important if the business processes or computes large amounts of data. However, if a company processes sensitive personal data, more attention should be paid to assessing the compliance with GDPR. So, all of the assessments are applicable, but the results and importance may vary depending on how the company operates or what services they provide.
Best Practices for Conducting an ISO 27001 Risk Assessment
Performing a successful ISO 27001 risk assessment requires careful planning, attention to detail, and a comprehensive understanding of the organisation’s information security risks. Here are some tips on how to perform a successful ISO 27001 risk assessment:
- Just as you would when defining your ISO 27001 scope statement , when performing a successful risk assessment, you’ll need to define the scope of the assessment: identify the systems, applications, processes, and data that are in scope for the assessment.
- Identify and assess risks and evaluate the likelihood and impact of those risks by conducting interviews with stakeholders, reviewing existing documentation, and conducting technical assessments.
- Evaluate the likelihood and impact of each risk and assign it a risk level. This can help prioritise the risks and determine which ones require immediate attention.
- Develop risk treatment plans that outline the actions that will be taken to mitigate or eliminate the risks, including assigning responsibilities, timelines, and budgets.
- Implement risk treatment plans, monitor progress, and adjust the plans as necessary.
- Regularly monitor and review the risk assessment process to ensure that it remains effective and up-to-date. This involves reviewing risk treatment plans, assessing the effectiveness of controls, and updating the risk assessment as necessary.
- Finally, engage stakeholders throughout the risk assessment process to ensure that the assessment is comprehensive and that all risks are identified and addressed. It can also help build support for the risk assessment process and ensure that the organisation’s information security program is aligned with business objectives.
Common mistakes to avoid
Risk assessment isn’t a one-person job, and it requires clear objectives and methodologies. Finding a balance between simplicity and complexity is vital in order to avoid the following common mistakes when implementing your assessment strategy:
- Not involving all stakeholders: Risk assessment requires the involvement of all stakeholders who have knowledge of the organisation’s assets, threats, and vulnerabilities. Involve all relevant departments such as IT, legal, finance, and management.
- Focusing too much on technology: While technology plays a significant role in data protection, focusing too much on technology may result in overlooking other essential aspects such as policies, procedures, and people. Take a holistic approach that considers all aspects of your organisation’s operations.
- Not using a structured methodology: Without a structured methodology, your risk assessment process may lack coherence, making it difficult to achieve reliable results.
- Not setting clear objectives: Setting clear objectives is crucial to ensure that the risk assessment process remains focused. Set specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART) information security objectives that guide the entire process.
- Failing to document the process: Documentation provides a reference point for future audits or reviews. Document the entire process, including the methodology used, the results obtained, and the decisions made.
- Relying too much on assumptions: Assumptions can can lead to inaccurate results. Use factual information and data to support your risk assessment process.
- Not revisiting the assessment regularly: Risk is a dynamic process that changes over time. Failing to revisit the assessment regularly can result in an inaccurate risk profile.
By implementing ISO 27001 Risk Assessments you can identify potential risks to sensitive information and improve the effectiveness of your security controls while prioritising security initiatives, complying with relevant regulations and standards and, perhaps most importantly, ensuring stakeholder confidence in your organisation’s ability to manage sensitive information.
According to the annual ISO survey , last conducted in 2021, the number of valid certificates for ISO 27001 increased by 13%, from 2020 to 2021, showing that more and more organisations are become aware of the need to implement a solid ISMS. So, don’t waste another minute, get started on your ISO 27001 Risk Assessment plan and strengthen your ISMS.
Table of Contents

Compliance Platform for Tech Companies
All-in-One DIY Compliance Platform to help tech businesses towards their ISO 27001, ISO 9001, or SOC-2 certification and stronger performance on privacy and security. Ready?

Kattenburgerstraat 5 Building 027E 1018 JA Amsterdam The Netherlands [email protected] linkedin.com/company/c-board
Compliance Information
Privacy Policy
Cookies Notice
Terms & Conditions
Terms of Use
Compleye has Compliance Cookies!
Privacy overview.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
ISO 27001 Risk Assessment & Management: Complete Blueprint
Srividhya Karthik
Jan 29, 2024.
- Share on WhatsApp
- Email this Page
- Share on LinkedIn
- Share on Facebook

Risk assessment and management is a critical step in your ISO 27001 certification journey. An organization-wide risk assessment, in fact, is the central focus of ISO 27001. The information security standard helps to protect an organization’s information assets by identifying the risks and protecting them by deploying relevant security controls and measures.
In this article, we highlight the main steps to an effective ISO 27001 risk assessment and discuss the best practices involved in going about this critical step. And don’t miss our ‘quick and dirty’ cheat sheet on risk assessment at the end of the article.
- The ISO 27001 risk assessment process helps organizations identify various types and levels of risks relevant to a business and score them based on severity and likelihood of occurrence.
- Under ISO 27001, risk management guidelines entail implementing preventive controls, establishing an incident response plan, enabling response reporting, and continuously monitoring control effectiveness.
- The risk treatment plan under ISO 27001 guidelines necessitates a detailed action plan to mitigate the impact of control failures or breached safeguards.
What is ISO 27001 risk assessment?
The ISO 27001 risk assessment is a systematic process by which an organization identifies its information security risks, their likelihood, and their impact, so as to implement plans to mitigate them. It follows the setting up of a robust and cost-effective Information Security Management System (ISMS).
The entire process is complex and requires a detailed and integrated approach to risk management – from risk identification to risk assessment, and eventually executing a risk treatment plan to mitigate the risks .
Why do organizations need to perform ISO 27001 risk assessment?
ISO 27001 advocates for robust information security policies and procedures and risk assessment is a crucial part of this process. The purpose of ISO 27001 risk assessment is to help organizations identify the threats and vulnerabilities along with their severity and likelihood of occurrence so adequate measures can be taken against each of those threats.
ISO 27001 risk assessment is a proactive security measure that enables the organization to make well-informed decisions. It minimizes the costs of sudden security incidents and reduces the chances of business operations disruption. It is additionally a strategic imperative to expedite the certification process and shorten the sales cycle.
As we jump into the article, here’s an interesting take on risk management by the industry veteran and Co-Founder of Sprinto, Girish Redekar:
“Risk is something which is common sense and we do it every day. It is also core to frameworks like ISO. If you find a good system that helps you translate that risk into the way your business runs, then you can do well as a risk function.”
Girish Redekar, Co-Founder at Sprinto
Read how Equalture increased its sales velocity after getting ISO 27001 certified with Sprinto.
5 ISO 27001 security areas you need to know to assess and manage risks
1) company security policy.
A company security policy is typically a document outlining an organization’s procedures and approach to identifying, treating, and managing risks. Functioning as a foundation, it helps scope out key objectives, roles and responsibilities, and timelines of the activities.
2) Asset management
You can’t protect what you can’t see or don’t know about. Asset management involves identifying all assets that need protection, maintaining an updated inventory, and establishing safeguards to protect them against known threats.
3) Physical and environmental security
Even though the number of digital threats greatly outpaces physical and environmental threats, physical security breaches can cause serious repercussions for any organization, necessitating certain mechanisms of resilience against such instances.
This section of ISO 27001 risk management covers the necessary controls to mitigate such risks, for example, authenticated entry, physical barriers, and backup power generators to protect your valuable resources and ensure operational resilience in the face of potential threats.
4) Access control
Access controls define the levels of information access within an organization, ensuring that people can access what they are authorized to. These controls typically use authentication workflows to verify users’ identities and grant access according to their authorization level.
For example, biometric authentication along with role-based access controls offer baseline resilience against phishing attacks and internal vulnerabilities within an organization.
5) Incident management
To put it simply, Incident management is your response plan for handling security incidents effectively. It includes immediate actions to contain failures, assigns responsibility for managing risks, outlines procedures and timelines for reporting incidents, and assembles a response team. Each action is classified by priority and severity to ensure appropriate and timely responses.
How to perform ISO 27001 risk assessment
ISO risk assessment is subjective; no two organizations can have identical risks and assessments. It is therefore crucial to identify information security risks applicable to the organization and determine corrective actions based on risk profile.
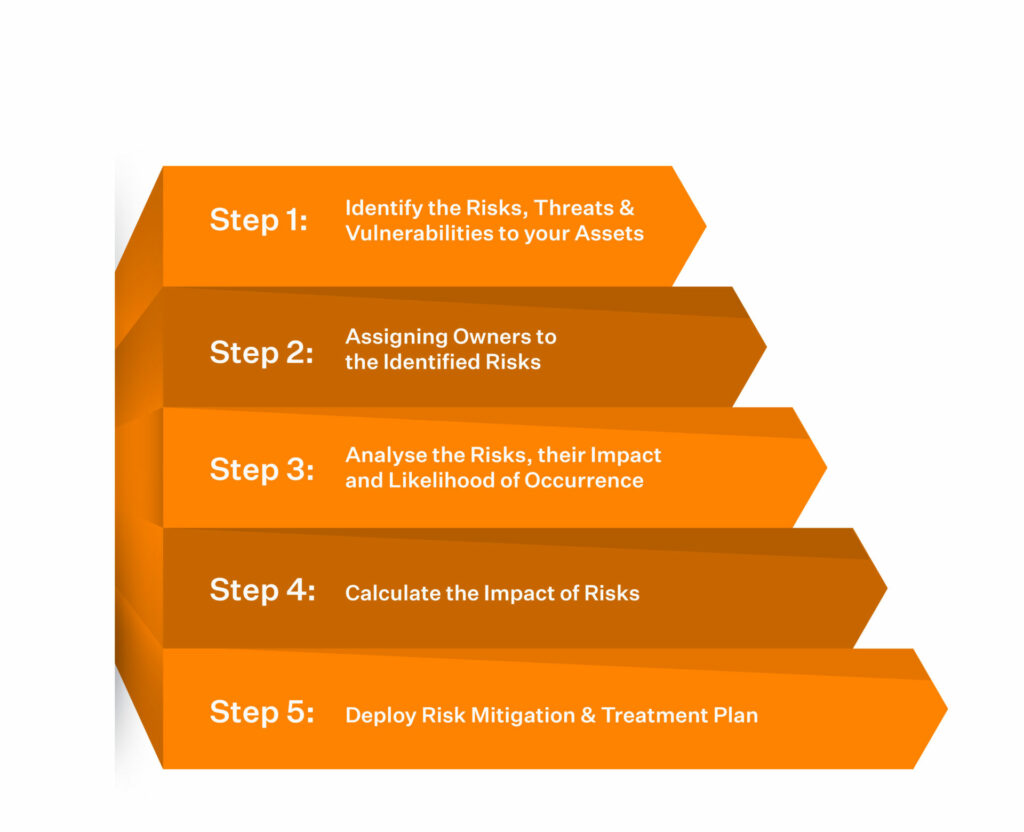
Here is the five step procedure to perform ISO 27001 risk assessment for your organization:
1. Identify the risks, threats, and vulnerabilities
Identification of assets: Make a list of the information assets across your organization. These would include your software, hardware, databases, and intellectual property, to name a few.
Assessing the risks attached: Once you have a comprehensive asset list, identify the risks attached to each asset – risks that could impact the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of each listed information asset. Your threats and vulnerabilities could range from unauthorized access to your database to embezzlement and espionage to inadequate data backup, and password management, to name a few.
How can Sprinto help?
Integrate Sprinto with your cloud stack, select your framework, and start scoping out risks with Sprinto’s comprehensive risk library. Score risks for their likelihood of occurrence and impact using trusted industry benchmark that come right out of the box with Sprinto.
Save time by automating the ISO risk assessment process
Sprinto lets you assign risk owners and sends automatic alerts for remediation actions to the right individuals.
2. Assigning owners to the identified risks
Often overlooked, this is an essential step in determining the success of your organization’s risk assessment exercise. For every risk, assign risk owners who would be in charge of monitoring the risk, and eventually implementing the risk treatment plans.
3. Analyze the risks, their severity, and the likelihood of occurrence
ISO 27001 doesn’t define any specific way to analyze and score the risks. It is, therefore, essential to determine an organization-wide standardized approach for the same. Remember, you will base your risk analysis on this pre-defined approach.
Once you have identified and defined your risk universe, the next step is to analyze the identified risks by assigning a likelihood of occurrence and ranking its potential impact on a scale of 1-10 (10 being the highest impact). You could also rank them Low-Medium-High.
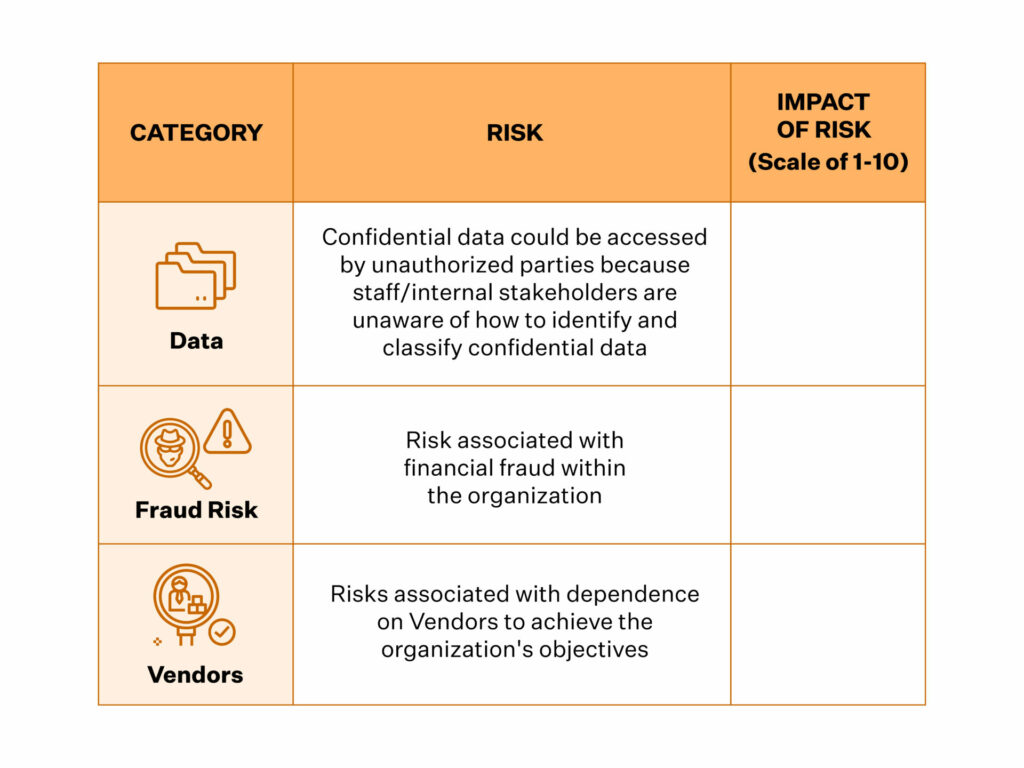
4. Calculate the impact of risks
To calculate the impact of the risks, it is a good step to categorize them first. Depending on the nature of your business, your risk categories could be financial, legal, regulatory, and your reputation, to name a few. While rating the impact, you must also consider factors such as how fast the impact will be felt and the likelihood of its occurrence.
The scores you assign (from 1-10 or low-medium-high) will help you design and prioritize your risk treatment process.
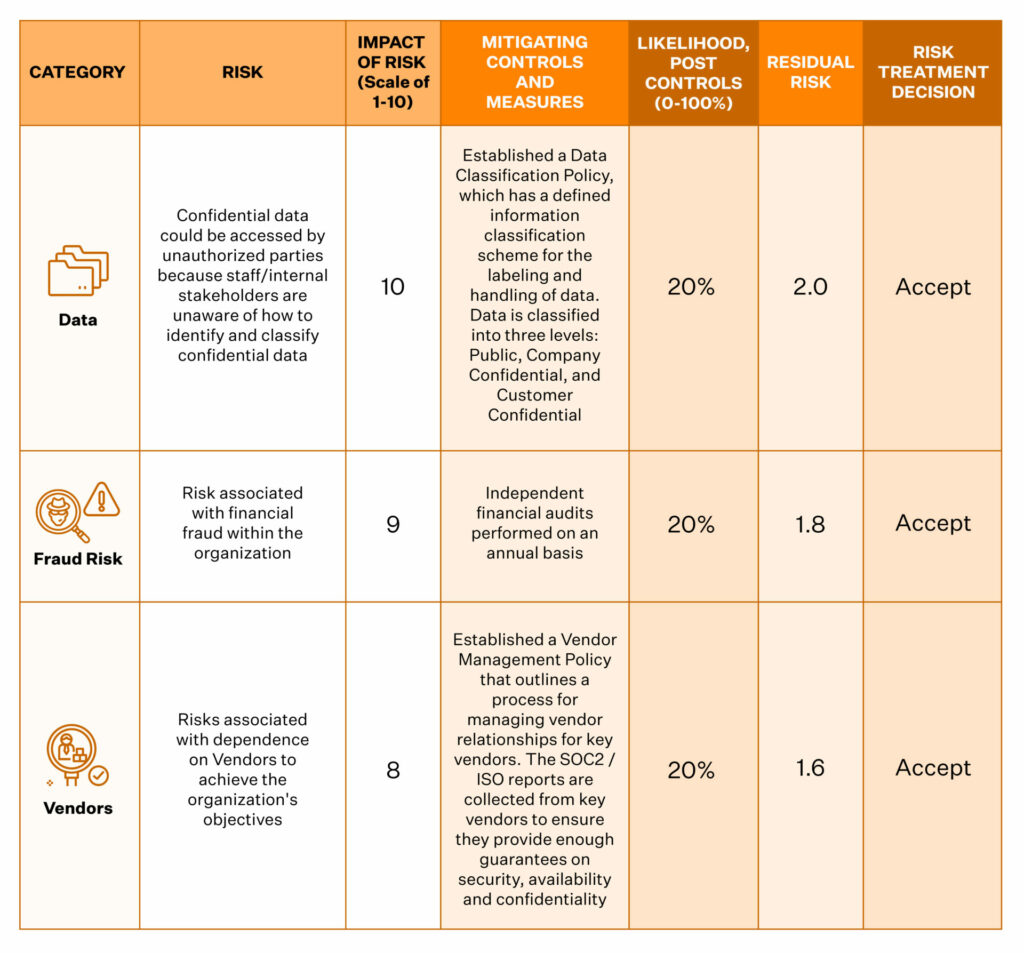
Sprinto’s integrated heat map helps you visualize the impact and likelihood of risks
5. Deploy risk mitigation and treatment plan
Risk mitigation and treatment involve prioritizing risks based on their potential impact and selecting from three response strategies: accepting the risk, rejecting the risk, or implementing controls to reduce risk likelihood or impact for residual risks.
In short, risk treatment plans document your responses to the threats, vulnerabilities, and risks you have identified in your risk assessment exercise. Know that this piece of document is critical to your ISO 27001 certification . Your external auditor will go over it in detail during your ISO 27001 certification audit and the subsequent periodical audits .
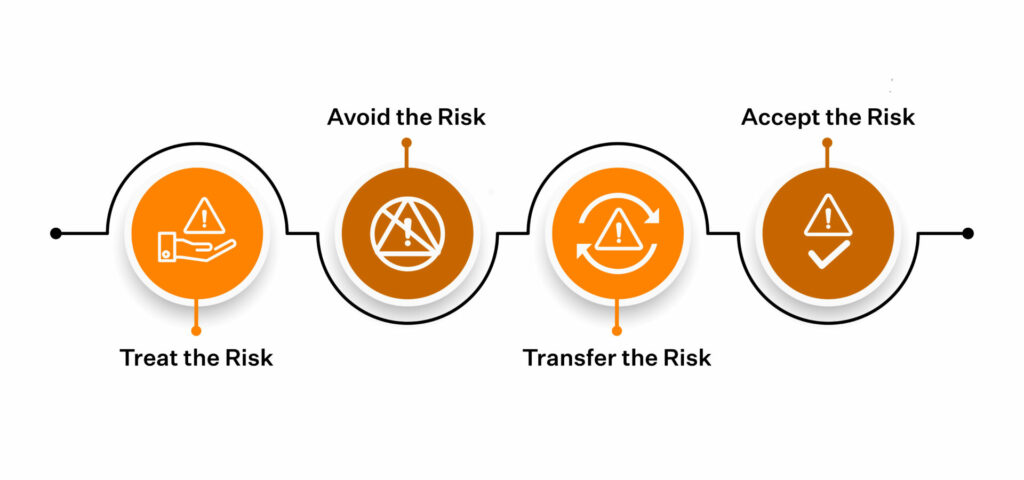
Treat the risk
If the risk score is above what’s acceptable, you can reduce its impact or likelihood by deploying the security controls as outlined in the ISO 27001 controls in Annex A. Security awareness training , access control, penetration testing , and vendor risk analysis are some of the ways you can treat risks.
Avoid the risk
Another response to the identified risk is to look for ways for avoiding the risk altogether. If the risk-return matrix is lopsided, you can choose to avoid the risk in totality. For instance , if you are a remote-only organization, you can avoid the risk of maintaining the physical security of your production infrastructure or data centers.
Transfer the risk
Where feasible, you could modify the risk by transferring it to a third party. You could do this by contracting vendors, outsourcing a particular job function, or buying insurance, for instance .
Accept the risk
The objective of your risk treatment plan is to bring the risk levels of your information assets, wherever possible, to an acceptable level. Remember, you can’t eliminate all your risks. You can devise a detailed plan on what should be done in the event of a ‘risky eventuality’. These include data breaches, cybersecurity attacks and other such incidents that risk the security of your data. Your risk treatment plan should include well-thought incident response and incident management.
Sprinto suggests you the right risk response strategy and you can accept, transfer or reject risk as per preferences.
Risk treatment plan and Statement of Applicability
Your Risk Treatment Plan and Statement of Applicability are two crucial documents in your ISO 27001 assessment journey.
Clause 6.1.3 of the ISO 27001 Standard states that an SOA must contain the following:
- List of controls identified as a response to the identified risks
- An explanation for the choice of controls, how they have been implemented, and reasons for the omission of controls, where applicable)
A Statement of Applicability outlines whether each of the controls defined within Annex A of the ISO 27001 standard will be applied or not based on your Risk Treatment Plan. For each risk, you must evaluate the options for treatment.
For instance , applying controls, accepting, avoiding or transferring risks. The SOA must comprise the actions performed based on the selected option. Again, management approval with documentation is needed for each situation where risks are accepted.
If you are finding it difficult to implement ISO risk assessment then talk to experts about how you can simplify this process.
How can we help?
If you are finding it difficult to implement ISO risk assessment, consider talking to our experts about simplifying the process. ( Click here to schedule the meeting )
ISO 27001 Risk Assessment Examples
The risks vary depending on the industry and other factors. However, here is what a risk assessment table looks like in general. Let us see some examples of ISO 27001 risk assessment.
| 1 | Malware, ransomware, and viruses | Lack of antivirus program and weak firewall defense | 7-8 | Install and regularly update the antivirus program. Have a secure firewall in place. |
| 2 | Unauthorized access to sensitive data | Weak and common system/server passwords and unorganized access controls | 8-10 | Have strong password policies in place with two-factor authentication and implement access controls |
| 3 | Social Engineering (Phishing Attacks) | Lack of security awareness training among the company’s staff | 8-10 | Conduct security awareness training sessions with employees to identify and prevent social engineering attacks |
| 4 | Physical theft or unauthorized access to server rooms | Lack of physical security measures | 5-7 | Install surveillance cameras, access control systems, and alarm systems to improve your physical security |
Also check out: Requirements of iso 27001
Check out our customer’s case study on ISO 27001 audit
ISO 27001 risk assessment template
The overall objective of the risk assessment exercise is to implement a risk treatment plan using ISO 27001 controls list such that your organization’s residual risk is acceptable. The primary objective is business continuity.
You will do well to keep this in mind while selecting a risk assessment and treatment template. While there are many free ISO 27001 risk assessment tools and templates, choose one that fits your organization’s risk universe. A simple spreadsheet with a logical approach to asset-based risk management can also help here.
Download your ISO 27001 Risk Assessment Template
ISO 27001 risk assessment r eport
The ISO 27001 risk assessment report will provide an overview of what you find. It would be reviewed meticulously during your ISO 27001 internal audits as well as certification audits. It should include the following:
- List of information assets and asset owners, risk assessment framework (includes the criteria for accepting risk), and management approval for acceptance of residual risks, to name a few.
- The risk treatment applied and the impact of the risk affecting the availability, integrity and confidentiality of each your assets after and before treatment.
- Order of priority for treating the risks, the controls applied, and target timeline for applying the treatment.
- A comprehensive risk management framework that describes all steps and relevant methods required to be carried out in terms of the risk assessment process. These include asset identification, threat & vulnerability identification, control analysis, business impact analysis, risk determination, control recommendations as well as results documentation.
These apart, your documentation should also include the evaluation periodicity of the controls. An internal audit of your controls will help find glaring gaps, if any, in the process. A gap analysis will help you ensure you are on the right track.
Sprinto simplifies ISO 27001 risk assessment
Sprinto’s newly-introduced Integrated Risk Assessment feature has been designed to ensure your approach to risk assessment is as holistic as it is sure-footed. From identifying risks to assessing their impacts to mitigating them, the entire risk management process has now been broken down into easy-to-understand, scalable and framework-agnostic steps in the app.
What’s more, you needn’t worry about having missed any pertinent risk(s), thanks to Sprinto’s expertly-organized risk library.
Here’s a look at why Sprinto’s Integrated Risk-Assessment feature can help you:
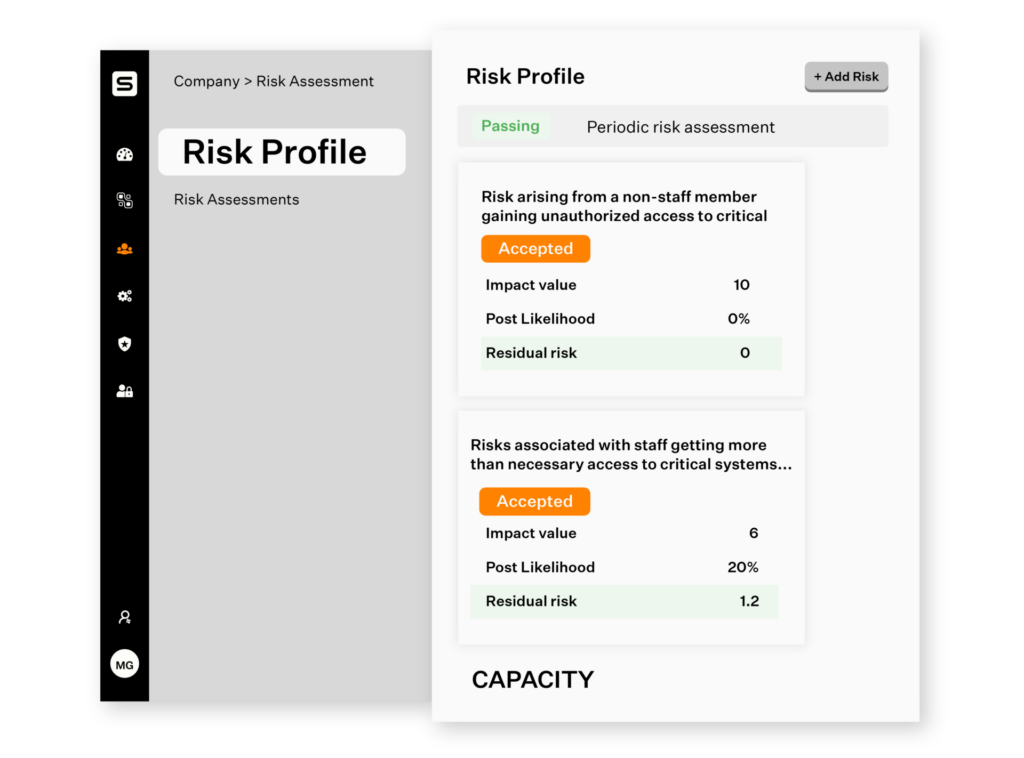
Curated risk profile
With Sprinto’s curated risk register, your risk assessment will be more exhaustive but without the exhaustion of it! With a comprehensive risk library, Sprinto will now give you a 360-degree view of org-wide, entity-down risks. As a result, you will only work with the risks relevant to your business instead of wasting time chasing tangential ones.
Continuously monitor risks
Sprinto automatically maps risks to controls and relevant compliance criteria. Compliance checks are run throughout the day and you can check the live status on the health dashboard. In case of any deviation automated alerts are sent to the risk owners to initiate proactive response.
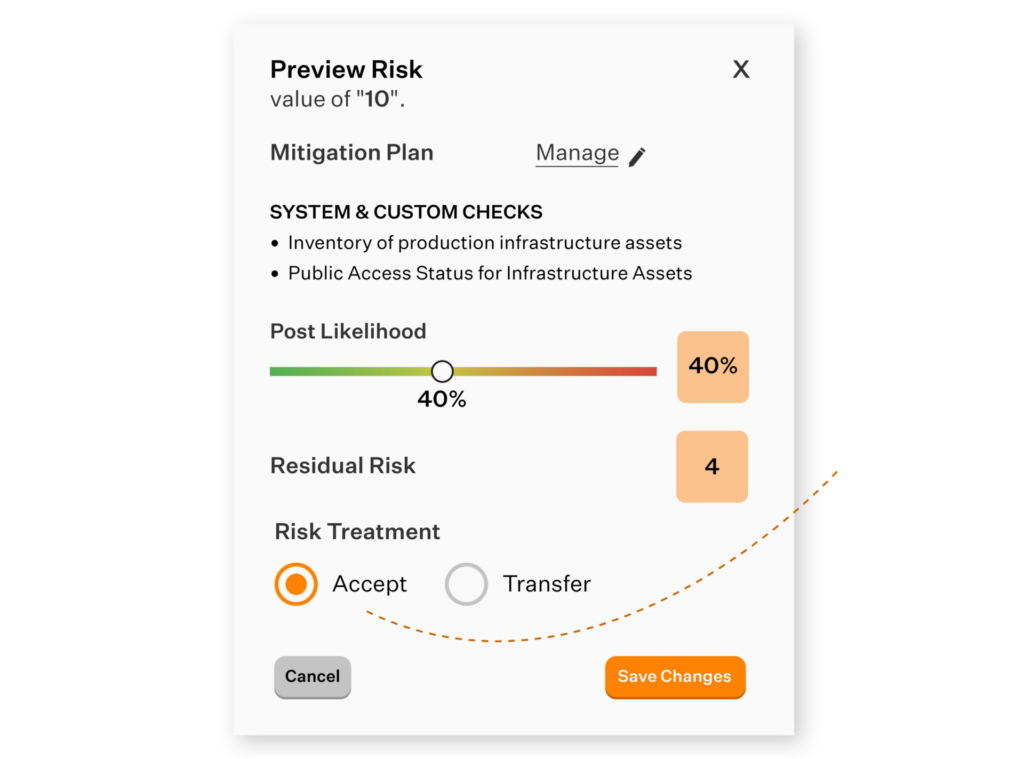
Rate your impact with insight
Rating the impact of the identified risks needn’t be just a game of intuition. You can use Sprinto’s baked-in industry benchmarks as a sounding board to ensure you are on the right track. You can then dig into Sprinto’s pre-mapped controls list to decide your risk treatment and mitigation plan. You can assign risk owners and the remediation workflows to the right individuals.
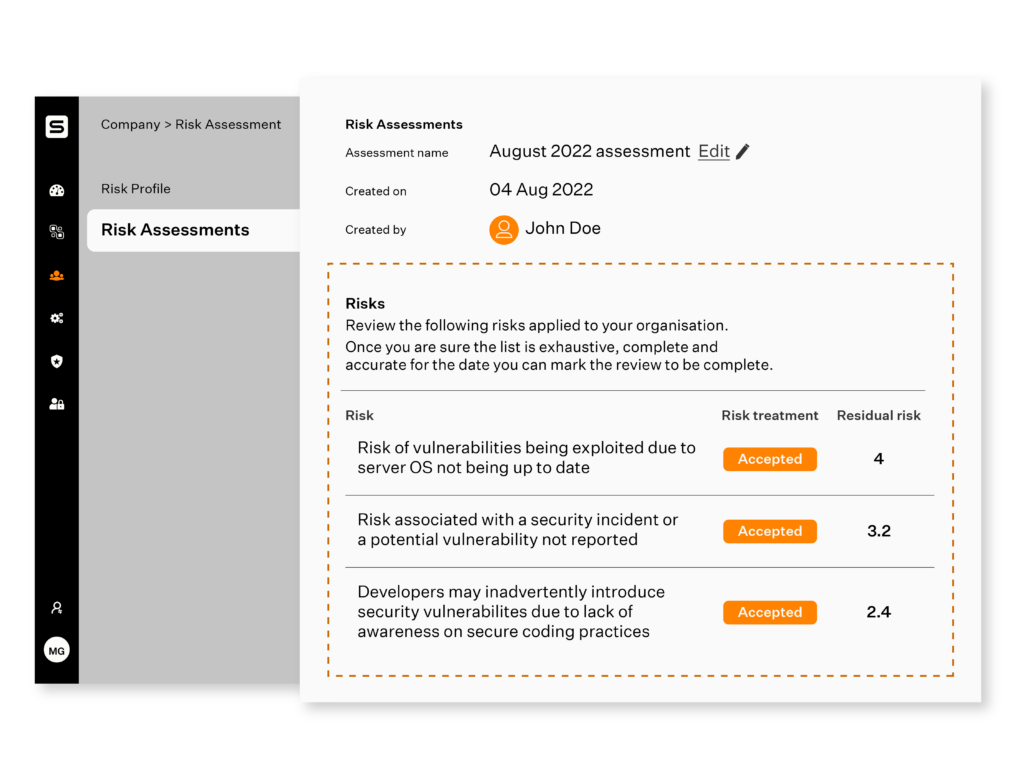
Single-screen management
You needn’t meticulously maintain versioning of spreadsheets and to and fro mailers to get management approval anymore. You can now assess, review, edit, and ready your organization’s risk profile from a centralized screen.
You can also get your management to review the risk register simply by adding them to the platform. And once you have the management buy-in, your onboarded auditors can review and audit your risk profile on their dashboard. It is that simple.
Also read how Giift completed ISO 27001 implementation in 8 weeks
Wrapping Up
So, that’s all about ISO 27001 risk assessment. The importance of risk assessment is quite evident, and you should be following the risk assessment practices not just from a compliance point of view but from an overall security aspect as well.
However, you can skip the lengthy spreadsheets and can automate most of the risk assessment processes to generate compliance-ready reports and more. Sprinto is a great risk assessment and compliance automation solution and can be a good fit for your organization. You can request a demo to see for yourself. Make risk assessment a strength. Talk to us today!
What is an ISO 27001 risk treatment plan?
A risk treatment plan documents the type of risk, their intensity, and the organization’s responses while assigning accountability for identified risks. It is typically the next step after risk assessment, detailing all action items, risk owners, mitigation activities, and timelines.
As per ISO 27001 guidelines, the company will then need to implement controls to ensure that the risk treatment plan can effectively address risks. Particularly, Annex A of ISO 27001 is a great starting point, featuring 114 controls divided into 14 sections, each targeting and detailing the activities to mitigate identified risks.
What is iso 27001 risk management framework?
ISO 27001 risk management framework is a structured approach to identifying and mitigating information security risks. It includes components such as risk assessment, analysis, risk treatment and continuous risk monitoring.
What documentation is required for ISO 27001 risk assessment?
ISO 27001 requires mandatory documentation on risk assessment and risk treatment processes. The organization must attach proofs for risk identification, analysis and initiation of risk response actions.
What is the difference between asset owner and risk owner in ISO 27001?
An asset owner is responsible for overall management and protection of information assets. A risk owner is only accountable for specific risks related to assets. Both the roles are crucial for maintaining an effective ISMS.
What is the ISO 27001 risk treatment plan?
The ISO 27001 risk treatment plan is a tactical guide to address the identified risks during risk assessment. It outlines the details of the assessed risks along with the corrective actions to be taken, the responsible stakeholders, budget and resources required and the timeline for remediation.
Is ISO 27001 risk assessment mandatory?
Yes, risk assessment is a requirement for the ISO 27001 standard. To get certified, you need to identify the risks associated with confidentiality, integrity, and availability of the assets defined in the ISMS.
Why is risk assessment important in ISO 27001?
The ISO 27001 risk assessment is important because it helps organizations identify the potential risks and vulnerabilities in the current IT security setup. By doing so, organizations can work on risk mitigation approaches to eliminate potential security threats.
Srividhya Karthik, is a Content Lead at Sprinto, she artfully transforms the complex world of compliance into accessible and intriguing reads. Srividhya has half a decade of experience under her belt in the compliance world across frameworks such as SOC 2, ISO 27001, GDPR and more. She is a formidable authority in the domain and guides readers with expertise and clarity.
How useful was this post?
5 /5 - ( 1 votes)
Grow fearless, evolve into a top 1% CISO
Strategy, tools, and tactics to help you become a better security leader.
Evolve into a top 1% cyber security leader
You may also like, soc 2 compliance checklist: a detailed guide for 2024, iso 27001 requirements – a comprehensive list [+free template], gdpr certification: the ultimate guide, a comprehensive hipaa compliance checklist (most recommended), iso 27001 mandatory documents [free template], iso 27001 certification cost: plan your compliance budget better, iso 27001 audit checklist (5 easy steps), the ultimate beginner’s guide to iso 27001 policies, how to perform compliance gap analysis, 9 best compliance automation tools in 2024, what is compliance automation: get started with a quick guide , 15 best cybersecurity tools in 2024, compliance risk assessment: what is it and how to conduct, top 6 drata alternatives & competitors in 2024, drata vs vanta: compare all differences , top 6 vanta competitors: detailed feature analysis, secureframe alternatives: compare top competitor pricing, pros, cons, & rating, drata vs secureframe: compare all differences , found this interesting share it with your friends, get a wingman for your next audit., schedule a personalized demo and scale business, here’s what to read next…..

5 Best CCPA Compliance Tools

How to get CCPA certification: All you need to know about this landmark privacy law

CCPA Compliance Checklist (This is All You Need)

A Comprehensive Guide to CCPA Compliance

The CCPA Requirements Handbook for 2024

PCI DSS Certification: Learn PCI DSS Steps, Implementation costs and more

Social Engineering Statistics: How Can Your Business Avoid Being One?

Cyber Risk Quantification: Understanding Models & How to Address Key Challenges

10 Best Compliance Management Software in 2024

10 Best Compliance Software: Feature, Pro, and Con Comparison

10 Best Risk Register Software [2024] With Reviews, Pros & Cons

Sprinto: Your growth superpower
Use Sprinto to centralize security compliance management – so nothing gets in the way of your moving up and winning big.

Automate your ISO 27001 Compliance journey end to end. Book a demo today!

The complete guide to ISO 27001 risk assessment

Table of contents
Iso 27001 risk assessment, downloadable iso 27001 risk assessment templates, what is the difference between a risk-based system and a rule-based system, when do you conduct an iso 27001 risk assessment, how do you conduct an iso 27001 risk assessment, iso 27001 risk assessment methodology, who performs the iso 27001 risk assessment, who is the risk assessment reported to, how is an iso 27001 risk assessment recorded, iso 27001 risk assessment faq.
ISO 27001 is a risk-based information security management system . In simple terms this means that the controls that you implement and the level that you implement them to, is based on the risk to your organisation. I like ISO 27001 for this reason. It is a very practical standard to implement.
Let us take a look at the risk assessment methodology as well as some practical templates you can download and start using straight away.
Before we look at the risk assessment step by step guide lets consider some helpful templates. ISO 27001 risk assessment templates can fast track your ISO 27001 risk assessments as well as guide you on what needs to be done.

DO IT YOURSELF ISO 27001
All the templates, tools, support and knowledge you need to do it yourself.

ISO 27001 is a risk based management system. This is one of the main reasons that I like it. It wants you to consider the controls you have and the level of those controls based on the risk to your business. It is not a prescriptive list or set level that you must meet. So what is the difference between a risk based system and rule based system? Let’s take a look.
Organisation implements the controls it needs based on risk
Organisation may or may not implement controls based on risk
Organisation determines the level of control required based on risk
Organisation can choose not to implement controls based on risk
You can still pass if you do not have a control as long as you are managing the risk
Organisation is given a list of controls it must implement
Organisation must implement controls provided
Organisation is told the level of required control
Organisation has no choice other than to implement controls
If you do not have the control to the required level, you fail
Unlike that other standards that require you to have controls in place to a level that the standard dictates, a risk based system is a lot more forgiving and practical. Getting the risk assessment right therefore is critical from both an implementation perspective and an audit and certification perspective.
1. When you start you ISO 27001 implementation
There are a few occasions on which an ISO 27001 risk assessment is going to need to be conducted. The first, clearly, is at the start of your ISO 27001 implementation. To start your journey you are going to want to know what risks you are trying to address and then implement the controls and rigour that addresses those risks. Why would you start and implementation of getting security guards if you don’t have any premises? An extreme example to be sure, but if we have no risk then we do not need the controls.
2. When things change
Change is a constant in any business. Risk assessment forms part of change management but is also just good practice. When things change you will asses the risk of the change itself but also whether the change effects any existing risks. Maybe it reduces existing risk, completely eliminates existing risk or just makes things a whole lot riskier.
3. At least annually
An ISO 27001 risk assessment really should be completed at least annually and recorded. It is a formal step but allows you to assess what, if anything has changed as well as what, if anything needs addressing. Budgets and resources may be required and it allows the effective planning and control.
ISO 27001 Risk Assessment in 5 Simple Steps
Risk assessments can be daunting if you haven’t done them before. They are actually very straightforward. Lets take a look at the 5 steps to ISO 27001 risk assessment.
Time needed: 4 hours
How to conduct an ISO 27001 risk assessment
Implement a risk management framework for your organisation. A good risk management framework is ISO 31000. You will want a risk management policy , a risk management process and a risk register.
Risks to information security can be identified by identifying the physical and information assets then running workshops with subject matter experts. Those experts can bring their knowledge and experience to bare to identify what could go wrong. Using the Annex A control list as a prompt you can do an assessment of where you are right now. Having a pre populated risk register can be a great kick start. The ongoing identification of risk will come via internal audits, external audits, incidents and corrective actions, dedicated risk assessments and the process of continual improvement.
Analyse risks based on the impact and likelihood of occurring. Give the risk a risk score. The risk score will be used as a guide to your risk treatment and risk treatment prioritisation.
Using the risk score as a guide evaluate the risk as it applies to your organisation.
Each risk will have a risk treatment. Decide if you are going to accept the risk, reduce the risk, avoid the risk, transfer the risk. Risks are assigned a risk owner. Risk treatments are assigned a risk treatment owner and risk treatment date. Risks are reviewed regularly. Risks are discussed with management in a structured meeting that is minuted to record the risk treatment decision.
A risk management framework, or ISO 27001 risk assessment methodology, is a requirement and the aspects of it are laid out in the ISO 27001 standard. To meet the requirements you could look to implement ISO 3001 Risk Management . We built our ISO 27001 Risk Templates to meet the requirements of this risk standard.
Ideally someone experienced and knowledgable in information security should lead the risk assessment with representation from all aspects of the business involved. Senior management need to be involved in the process of the assessment as well as ultimately they will own the risks that are identified. The more representation you can have from across the business, the better.
The output of the ISO 27001 risk assessment goes first to the Management Review Team. The Management Review Team is the formal construct that has defined roles and responsibilities in the information security management system and is set up at the beginning of an ISO 27001 implementation. Part of the role is oversight and risk management and as a decision making and reporting body it is here that the risk assessments are first presented, actions agreed and outputs formally recorded.
The risk assessment will lead to risk treatment and the management review team will continue to oversee the risk treatment on an on going basis.
A report of the risk assessment is then shared with key stakeholders and senior managers and owners.
The record of the risk assessment meeting should be recoded in the minutes of the meeting. Then risks themselves are entered into and recorded in the risk register . The risk register is the main tool for recording and managing risk. It is possible to share just the risk register as long has it has a management dashboard as is included in our risk register template but if not then you should consider creating a summary management report. The summary management report with the risk register as an appendix is a great record of the assessment and a great way to communicate to all levels of the business as required.
An ISO 27001 risk assessment helps organisations identify, analyse, and evaluate weaknesses in their information security processes . It allows them to implement effective plans to manage the risk. It allows them to prioritise the allocation of limited resources such as time and money.
Yes, you need to do a risk assessment for ISO 27001. ISO 27001 is a risk-based management system and it is an essential component of the standard.
1. Define your risk management framework. 2. Write your risk management policy. 3. Write your risk management process. 4. Create your risk register. 5. Identify your risks. 6. Analyse your risks. 7. Evaluate your risks. 8. Treat your risks. 9. Report and record your risk decisions.
A risk assessment template is available at High Table.
We value your privacy
Privacy overview.
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-advertisement | 1 year | Set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin, this cookie records the user consent for the cookies in the "Advertisement" category. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
| wp_woocommerce_session_* | 2 days | WooCommerce sets this cookie to make a unique code for each customer so that it knows where to find the cart data in the database for each one. |
| yith_wcmcs_currency | 7 days | Required for currency conversion. |
| __stripe_mid | 1 year | Stripe sets this cookie to process payments. |
| __stripe_sid | 1 hour | Stripe sets this cookie to process payments. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| yt-player-headers-readable | never | The yt-player-headers-readable cookie is used by YouTube to store user preferences related to video playback and interface, enhancing the user's viewing experience. |
| yt-remote-cast-available | session | The yt-remote-cast-available cookie is used to store the user's preferences regarding whether casting is available on their YouTube video player. |
| yt-remote-cast-installed | session | The yt-remote-cast-installed cookie is used to store the user's video player preferences using embedded YouTube video. |
| yt-remote-connected-devices | never | YouTube sets this cookie to store the user's video preferences using embedded YouTube videos. |
| yt-remote-device-id | never | YouTube sets this cookie to store the user's video preferences using embedded YouTube videos. |
| yt-remote-fast-check-period | session | The yt-remote-fast-check-period cookie is used by YouTube to store the user's video player preferences for embedded YouTube videos. |
| yt-remote-session-app | session | The yt-remote-session-app cookie is used by YouTube to store user preferences and information about the interface of the embedded YouTube video player. |
| yt-remote-session-name | session | The yt-remote-session-name cookie is used by YouTube to store the user's video player preferences using embedded YouTube video. |
| ytidb::LAST_RESULT_ENTRY_KEY | never | The cookie ytidb::LAST_RESULT_ENTRY_KEY is used by YouTube to store the last search result entry that was clicked by the user. This information is used to improve the user experience by providing more relevant search results in the future. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| sbjs_current | session | Sourcebuster sets this cookie to identify the source of a visit and stores user action information in cookies. This analytical and behavioural cookie is used to enhance the visitor experience on the website. |
| sbjs_current_add | session | Sourcebuster sets this cookie to identify the source of a visit and stores user action information in cookies. This analytical and behavioural cookie is used to enhance the visitor experience on the website. |
| sbjs_first | session | Sourcebuster sets this cookie to identify the source of a visit and stores user action information in cookies. This analytical and behavioural cookie is used to enhance the visitor experience on the website. |
| sbjs_first_add | session | Sourcebuster sets this cookie to identify the source of a visit and stores user action information in cookies. This analytical and behavioural cookie is used to enhance the visitor experience on the website. |
| sbjs_migrations | session | Sourcebuster sets this cookie to identify the source of a visit and stores user action information in cookies. This analytical and behavioural cookie is used to enhance the visitor experience on the website. |
| sbjs_session | 1 hour | Sourcebuster sets this cookie to identify the source of a visit and stores user action information in cookies. This analytical and behavioural cookie is used to enhance the visitor experience on the website. |
| sbjs_udata | session | Sourcebuster sets this cookie to identify the source of a visit and stores user action information in cookies. This analytical and behavioural cookie is used to enhance the visitor experience on the website. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| PREF | 8 months | PREF cookie is set by Youtube to store user preferences like language, format of search results and other customizations for YouTube Videos embedded in different sites. |
| VISITOR_INFO1_LIVE | 6 months | YouTube sets this cookie to measure bandwidth, determining whether the user gets the new or old player interface. |
| VISITOR_PRIVACY_METADATA | 6 months | YouTube sets this cookie to store the user's cookie consent state for the current domain. |
| YSC | session | Youtube sets this cookie to track the views of embedded videos on Youtube pages. |
| yt.innertube::nextId | never | YouTube sets this cookie to register a unique ID to store data on what videos from YouTube the user has seen. |
| yt.innertube::requests | never | YouTube sets this cookie to register a unique ID to store data on what videos from YouTube the user has seen. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| m | 1 year 1 month 4 days | No description available. |
| _monsterinsights_uj | 1 year | Description is currently not available. |

- Onsite training
3,000,000+ delegates
15,000+ clients
1,000+ locations
- KnowledgePass
- Log a ticket
01344203999 Available 24/7

ISO 27001 Risk Assessment: A Complete Guide
In this blog we have covered the methodologies, management, treatment plan and process of ISO 27001 Risk Assessment. You will also learn how to assess risks and remain compliant with ISO 27001. This assessment priorities risks which are based on the impact of the risks on organisational assets. Read this blog further to learn more!

Exclusive 40% OFF
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Share this Resource
- ISO 27001 Lead Auditor
- ISO 27001 Lead Implementer
- ISO 27001 Internal Auditor
- ISO 27002 Foundation Training
- ISO 27002 Lead Auditor Training

To gain compliance with ISO 27001, an organisation must fulfil a set of requirements as per the ISO 27001 Compliance Framework – one of which is filing in anISO 27001 Risk Assessment. However, not many organisations are aware of this standard. As per Statista , 21 per cent of all businesses and 57% of large businesses in the United Kingdom are aware of ISO 27001.If your organisation too wants to secure your user data but are unaware how, then this blog is for you. Read this blog to learn everything about an ISO 27001 Risk Assessment, including a step-by-step guide to the Risk Assessment procedure.
Table of Contents
1) What is ISO 27001 Risk Assessment?
2) Measures to take after ISO 27001 Risk Assessment
3) A step-by-step guide to the Risk Assessment procedure
4) Examples of Risk Treatment
5) Risk Management procedure for small or medium sized organisations
6) Conclusion
What is ISO 27001 Risk Assessment?
An ISO 27001 Risk Assessment helps organisations to assess and manage incidents that have the potential to harm their sensitive data. The process involves the identification of vulnerabilities that a cyber-criminal may exploit to their advantage or mistakes that employees could make. One then determines the level of risk and decides the best course of action to help prevent them from reoccurring and causing any further damage.
An ISO 27001 Risk Assessment finds, evaluates, and applies important application security measures. The assessment also focuses on preventing security flaws and vulnerabilities in applications. Risk Assessments are usually conducted across the whole organisation. Once the assessment has been conducted, compliance ISO 27001 Requirements helps an organisation to determine how to manage the risks based on its allocated resources and budget. These cover all the possible risks to which the information could be exposed, balanced against the likelihood of materialising risks and their potential impact on the organisation.
Risk Assessments are necessary for validating that your Information Security Management System (ISMS) can handle the potential risks adequately.

Measures to take after ISO 27001 Risk Assessment
Under ISO 27001, businesses must establish a series of measures to reduce recognised risks. ISO 27001 suggested measures comprising not just technological remedies but also human elements and organisational procedures. The Annex A of 27001 comprises 114 measures that span the spectrum of Information Security Management, consisting of areas such as regulating physical access, defining firewall policies, implementing security awareness initiatives for staff, establishing protocols for threat surveillance, managing incidents, and employing encryption. These measure listed in Annex A are categorised into 14 groups that are as follows:
a) Information security policies (A.5)
b) Organisation of information security (A.6)
c) Human resources security (A.7)
d) Asset management (A.8)
e) Access control (A.9)
f) Cryptography (A.10)
g) Physical and environmental security (A.11)
h) Operational security (A.12)
i) Communications security (A.13)
j) System acquisition, development, and maintenance (A.14)
k) Supplier relationships (A.15)
l) Information security incident management (A.16)
m) Information security aspects of business continuity management (A.17)
n) Compliance (A.18)
Risk Assessments are conducted comprehensively throughout the organisation, comprising all potential risks that could jeopardise information security. These assessments consider the likelihood of these risks manifesting and their potential impact. Subsequently, the organisation must determine how to manage and mitigate these risks, considering the available resources and budget allocation.
Take the first step towards securing your organisation's information with our comprehensive ISO 27001 Foundation course – Register now!
A step-by-step guide to the Risk Assessment procedure
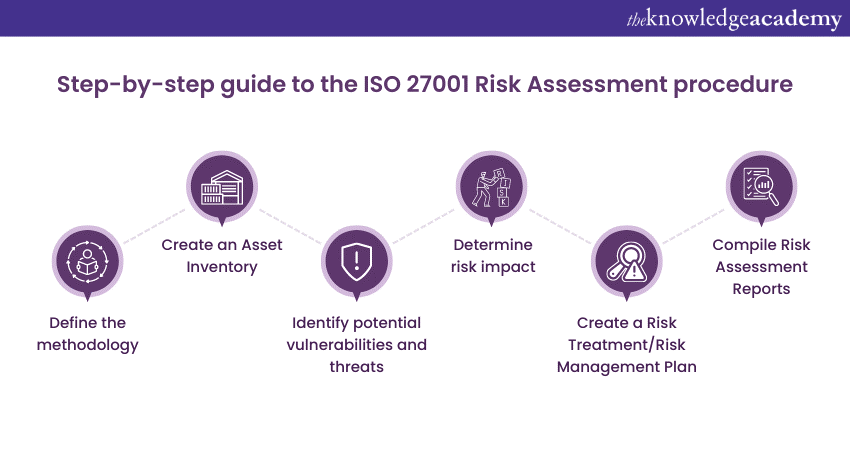
Define the methodology
As there is no standardised Risk Assessment methodology for ISO 27001, an organisation must define their methods clearly. To start, an organisation can review its unique profile by understanding the following:
1) The primary information security objectives that you aim to achieve with ISO 27001 Framework
2) Your organisation’s business, legal, and compliance obligations
3) The overall organisational goals and objectives
4) The stakeholders’ expectations and needs
One must determine whether to use a qualitative or a quantitative approach to assess risk. A qualitative approach to the assessment is subjective; it focuses on the identification of risks followed by the estimation of the risks’ likelihood of occurrence and potential impact.
On the other hand, a quantitative approach uses verifiable data to help analyse identified threats and assign a numerical value to them. One must use the method most relevant to their organisation’s unique information security goals.
Create an asset inventory
One can perform an ISO 27001 in one of two ways: one, focusing on assets (that is, the risk to information); and two, focusing on scenarios that may result in a data breach.
In a scenario-based Risk Assessment, users are more likely to identify risk situations, which often speeds up the risk identification process. However, the drawback is that users often need to catch up on some elements that might create risks. As a direct result, the risk identification process is incomplete and often results in a false (and often dangerous) sense of safety.
With the asset-based approach, the process of identification of relevant risks becomes more time-consuming. It also yields a complete review of risk posture – so this method should be considered. You should start by compiling their asset inventory, which should include their hardware, software, devices, information databases, removable devices, mobile devices and intellectual property. To compile the list, one must check with all the asset owners – the individuals responsible for controlling asset use, maintenance and security.
Identify potential vulnerabilities and threats
Next in the Risk Assessment procedure, you must identify and analyse the potential vulnerabilities and threats that might rise. Once you have the asset register, you must analyse the risk to each asset. Here's how you can assess vulnerabilities:
Firstly, any potential vulnerabilities – such as a weakness that a potential threat may exploit – must be identified. Then, you must make a list of the information assets across your organisation. These would include your software, hardware, databases, and intellectual property, only to name a few. Now you must identify the risks to every asset – risks that could impact on the confidentiality, integrity and availability of each listed asset.
Your threats and vulnerabilities for each asset could vary from unauthorised access to your database, stealing to inadequate data backup, and password management. It must be noted that the risks are subjective and dependent on the organisation’s scope of ISMS, its business type and operating environment. Any potential vulnerabilities must be identified – for example, a glitch or security vulnerability in a software or operating system can make your organisation vulnerable to any cyber criminals who could infiltrate your system and compromise your valuable information and data.
Determine risk impact
After you are done with identifying potential vulnerabilities and threats, it is time to analyse the risks that are associated with them. ISO 27001 Checklist does not define any specific way to analyse and score the risks, and hence it is essential to determine an organisation-wide standardised approach for the same. It must be noted that the risk analysis must be based on this pre-defined approach.
It must be noted that not all risks are equally severe – organisations may not want to implement extensive measures or controls to mitigate or eliminate risks that would cause little damage. This is why it is crucial to score risks based on the likelihood or probability of occurrence as well as the damage that they can cause.
You must create a Risk Assessment matrix based on different factors to compare risks, such as, risk against their risk appetite, and then identifyi and prioritisethe risks that require action.
Organisations can either analyse the identified risks by assigning a likelihood of occurrence and ranking its potential impact on a scale of 1 to 10, or from Low to Medium to High. You must also examine how the Confidentiality, Integrity and Availability of data (the “CIA” triad) could potentially be affected by every risk.
One must also consider different implications of every threat, including the legal, organisational, contractual and regulatory implications. To get going with the determination of risk impact, youcan ask questions like:
1) What may be the cost of replacing a compromised asset?
2) What is the potential for financial loss from a particular risk (such as lost income, fines and so forth)?
3) Could a security incident damage or hinder our reputation?
Create a Risk Treatment/Risk Management plan
Now that you have analysed the risks and assigned a potential impact to each of them, the next step of the process requires you to determine the way to treat every risk that has been identified. The risk treatment plan, in short, documents your responses to all the threats, vulnerabilities and risks that you have identified in your Risk Assessment.
A Risk Treatment Plan typically includes the following elements:
a) Risk identification: You need to include the identified vulnerabilities.
b) Risk analysis: Add information related to the risk's prevalence and severity. This is often expressed as a statement number or range.
c) Risk treatment options: You need to provide a strategy for every risk (dodge, reduce, shift or bear).
d) Selected controls: You must explain who will be responsible for controlling which risk.
e) Responsibilities: You must assign individuals who will work on design, and who will take the lead in each control.
f) Timeline: You need to set deadlines to implement these controls.
g) Budget/Resources: Establish adequate protection, considering funding, employees, and technology resources.
h) Monitoring and review plan: Establish a time when the plan is to be reviewed and its effectiveness will be evaluated.
Compile Risk Assessment reports
As the next step in the procedure, you must prepare reports about your findings and implement an appropriate action plan for ISO 27001 Audit and certification. You must prepare the following reports:
1) A Statement of Applicability: A Statement of Applicability must be prepared. This statement must document the various ISO 27001 controls that you will be implementing in order to tackle the identified risks. Every single control must have its own entry, and you should also explain why any controls were omitted.
2) A Risk Treatment Plan: A Risk Treatment Plan must also be prepared, which provides a comprehensive summary of each identified risk, the proposed actions to deal with each risk as well as all the parties responsible.
The certification auditor who oversees your ISO 27001 effort will use these reports as guidelines.
Want to gain the expertise to lead and conduct successful ISO 27001 audit? Sign up for our ISO 27001 Lead Auditor Course today!
Examples of Risk Treatment
The following are some examples of to treat a risk properly:
1) Example 1 - Treating unauthorised access to customer data
a) Risk: Unauthorised entry to customer data.
b) Threat: Malicious hackers.
c) Vulnerability: Inadequate password policy.
d) Impact: Financial ramifications and harm to reputation.
e) Treatment: Implement a robust password policy, mandating that users create passwords with a minimum length of 12 characters. The password should, comprise a blend of uppercase and lowercase letters, digits, and special symbols.
This risk mitigation strategy proves effective by addressing the fundamental issue, which is the weak password policy. By adopting a strong password policy, the organisation can heighten the challenge for malevolent hackers attempting to gain unauthorised access to customer data.
2) Example 2 - Treating data loss due to fire
a) Risk: Potential data loss caused by a fire.
b) Threat: Fire incidents.
c) Vulnerability: Absence of a fire suppression system.
d) Impact: Financial losses, harm to reputation, and disruption of business operations.
e) Treatment: Installation of a fire suppression system within the server room.
In this case, the Risk Treatment focuses on mitigating the risk of data loss in the event of a fire by proactively addressing the vulnerability.
Risk Management procedure for small or medium sized organisations
Smaller organisations undertaking ISO 27001 implementation projects often face challenges when adapting Risk Management procedures, which may be primarily designed for larger enterprises. To simplify Risk Management for small organisations, consider the following recommendations:
a) Choose the right framework: It is essential that you include all the five essential components that are required by ISO 27001.
b) Select the appropriate tool: Seek software or tools that align with your simplified approach. In some cases, a well-designed Excel template can be more effective than complex software solutions.
c) Involve relevant stakeholders: Avoid tackling Risk Management in isolation. Engage departmental leaders from all areas of your organisation since they possess valuable insights into their processes and potential challenges.
d) Embrace imperfection: Instead of striving for absolute perfection in identifying all risks initially, focus on completing your initial Risk Assessment and treatment. Later, revisit the process to incorporate any overlooked hazards.
Conclusion
We hope that from this blog you understood the importance of ISO 27001 Risk Assessment and how it can help an organisation identify any risk that may cause any major fatality in the future. This blog also discussed how by creating the Risk Treatment plan you can not only avoid major casualties, but also improve your organisation’s information security.
Want to elevate your organisation's cybersecurity practices? Make sure to register for our industry-leading ISO 27001 Certification Course !
Frequently Asked Questions
ISO 27001's risk assessment is specific to information security within an Information Security Management System, focusing on confidentiality, integrity, and availability, requiring periodic ISMS reviews, distinguishing it from broader risk management frameworks.
Under ISO 27001, Risk Assessments should be conducted at regular intervals or when significant changes occur that could affect information security. This ensures the ISMS remains effective and responsive to new threats, aligning with the organization's evolving security posture and compliance requirements.
The Knowledge Academy takes global learning to new heights, offering over 30,000 online courses across 490+ locations in 220 countries. This expansive reach ensures accessibility and convenience for learners worldwide.
Alongside our diverse Online Course Catalogue, encompassing 17 major categories, we go the extra mile by providing a plethora of free educational Online Resources like News updates, Blogs , videos, webinars, and interview questions. Tailoring learning experiences further, professionals can maximise value with customisable Course Bundles of TKA .
The Knowledge Academy’s Knowledge Pass , a prepaid voucher, adds another layer of flexibility, allowing course bookings over a 12-month period. Join us on a journey where education knows no bounds.
The Knowledge Academy offers various ISO 27001 Training , including ISO 27001 Foundation Course, ISO 27001 Lead Auditor Course and ISO 27001 Internal Auditor Training. These courses cater to different skill levels, providing comprehensive insights into ISO 27001 .
Our ISO & Compliance Blogs cover a range of topics related to ISO 27001 offering valuable resources, best practices, and industry insights. Whether you are a beginner or looking to advance your knowledge on Information Security, The Knowledge Academy's diverse courses and informative blogs have you covered.
Upcoming IT Security & Data Protection Resources Batches & Dates
Mon 9th Sep 2024
Mon 14th Oct 2024
Mon 11th Nov 2024
Mon 9th Dec 2024
Mon 27th Jan 2025
Mon 24th Feb 2025
Mon 24th Mar 2025
Tue 22nd Apr 2025
Tue 27th May 2025
Mon 23rd Jun 2025
Mon 28th Jul 2025
Mon 25th Aug 2025
Mon 22nd Sep 2025
Mon 27th Oct 2025
Mon 24th Nov 2025
Mon 15th Dec 2025
Get A Quote
WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
My employer
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry
- Business Analysis
- Lean Six Sigma Certification
Share this course
Our biggest summer sale.

We cannot process your enquiry without contacting you, please tick to confirm your consent to us for contacting you about your enquiry.
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry.
We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Or select from our popular topics
- ITIL® Certification
- Scrum Certification
- ISO 9001 Certification
- Change Management Certification
- Microsoft Azure Certification
- Microsoft Excel Courses
- Explore more courses
Press esc to close
Fill out your contact details below and our training experts will be in touch.
Fill out your contact details below
Thank you for your enquiry!
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go over your training requirements.
Back to Course Information
Fill out your contact details below so we can get in touch with you regarding your training requirements.
* WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
Preferred Contact Method
No preference
Back to course information
Fill out your training details below
Fill out your training details below so we have a better idea of what your training requirements are.
HOW MANY DELEGATES NEED TRAINING?
HOW DO YOU WANT THE COURSE DELIVERED?
Online Instructor-led
Online Self-paced
WHEN WOULD YOU LIKE TO TAKE THIS COURSE?
Next 2 - 4 months
WHAT IS YOUR REASON FOR ENQUIRING?
Looking for some information
Looking for a discount
I want to book but have questions
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go overy your training requirements.
Your privacy & cookies!
Like many websites we use cookies. We care about your data and experience, so to give you the best possible experience using our site, we store a very limited amount of your data. Continuing to use this site or clicking “Accept & close” means that you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about our privacy policy and cookie policy cookie policy .
We use cookies that are essential for our site to work. Please visit our cookie policy for more information. To accept all cookies click 'Accept & close'.

Conducting a risk assessment is a critical step in getting ISO 27001 certified. Your risk assessment guides your implementation and helps you identify the controls your organization needs to reduce its risk. In this article, we’ll explain what an ISO 27001 risk assessment is, how to perform a risk assessment, and how to use your findings to get ISO 27001 compliant.
What is ISO 27001 risk management?
For ISO 27001, risk management is a combination of two components: risk assessment and risk treatment. Risk assessment is the process of identifying potential risks your organization faces and risk treatment is the actions taken to minimize those risks — both are required elements of ISO 27001 compliance.
What is an ISO 27001 risk assessment?
Early in your ISO 27001 compliance project, you’ll need to conduct a risk assessment where you identify and analyze potential risks to your information security management system (ISMS). As part of your preparation process, you’ll need to determine the likelihood of each identified risk and the impact it would have on your data security if the risk were to occur.
Conducting a risk assessment is required to be ISO 27001 compliant and guides the rest of your ISO 27001 implementation. Based on what risks arise, you’ll use that information to determine which ISO 27001 controls to implement to mitigate those risks.
{{cta_withimage2="/cta-modules"}}
How to conduct an ISO 27001 risk assessment
Your ISO 27001 risk assessment is one of the earlier steps in your compliance project. In the next section, we’ve broken down the steps of a risk assessment.

Develop your risk assessment methodology
The first step in creating a comprehensive risk assessment plan is to define your methodology. This includes determining how you will identify and address security vulnerabilities, how you plan to assign an owner to each risk, and how you’ve prioritized them.
Include the following components in your methodology:
- A plan for identifying and documenting vulnerabilities that could compromise your data.
- A strategy for determining who in your organization should own each risk. This typically involves designating a staff member with knowledge of the organization to assign owners.
- A methodology for determining the likelihood that a risk will happen and the extent of the consequences if the risk does occur. It’s also important to rank the priority of each risk (such as using a numbered scale).
- Criteria for determining which risks you will address and when, based on priority rankings.
Identify risks and vulnerabilities
Next, you’ll need to determine the risks that could compromise your security. Start by taking inventory of your information assets — consider your data storage locations, any devices or hardware that can reach your data, your network, software, and so on. Then create an extensive list of potential threats; some examples could be an employee’s laptop being stolen or an office visitor accessing an employee’s password.
Analyze and prioritize risks
Now that you have a list of potential risks, determine how critical each one is to solve for and prioritize your risk treatment accordingly. This should be determined by how likely it is for this risk to occur and how severe the impact would be if it did. Go through your list of risks and determine if the likelihood is low, medium, or high for each one and do the same for each risk’s impact level.
After you’ve set the likelihood and impact levels for each risk, use that information to prioritize the risks you need to address first. The risks that have both a high likelihood and a high impact ranking should be considered high-priority.
Mitigate identified risks
Next, you’ll need to use that list to take action on those risks. Look at each risk and determine ways to make it less likely to occur and reduce its impact. Identify which of the ISO 27001 Annex A controls to use to mitigate each one. Be sure to keep records of the Annex A controls you used for each risk so you can include this in your Statement of Applicability for your auditor to review.
Complete risk reports
You’ll need evidence to prove that you’ve performed your risk assessment as well since your auditor will need to verify that you’ve done this step during your audit.
To ensure you have sufficient evidence, create the following reports for your auditor:
- Risk assessment report: A report of your risk assessment process and the steps you followed, what information assets you reviewed to identify those risks, which risks you found, and the likelihood and impact ratings you gave each risk.
- Risk summary: A shorter report explaining which risks you’ve chosen to address.
- Risk treatment plan: A plan that includes all the risks you plan to address through your ISO 27001 compliance along with your plan for mitigating each one.
You may also want to consider starting your Statement of Applicability (SoA) at this stage as well as this document details how you’ve treated the risks you’ve identified. The SoA is a detailed report of the ISO 27001 controls you’ve implemented as a result of your assessment.
Continually monitor and review your ISMS
Proper risk assessment is an ongoing process, not a one-time task. Whenever there are changes to your data storage, your network, or other aspects of your operations, new risks can arise. As part of your ISO 27001 risk assessment process, create a plan to continuously monitor for new risks or any changes that could alter the likelihood or impact of known risks. ISO 27001 certification requires you to conduct a full risk assessment at least once per year, but additional routine risk assessments will help you stay secure year-round.
Tips for successful ISO 27001 risk management
Your risk management process has a downstream impact on the reliability of your results, the likelihood that you’ll pass your audit, how secure your data is, and how efficient the process is. As you follow the above steps, keep these tips in mind to execute your risk management strategy as effectively as possible.
Align your risk methodology with your organization
There is no universal risk assessment methodology that works for every organization. Your methodology should align with the format of your organization. For instance, one organization might assign its CTO to determine risk ownership, while another organization might assign their head of security with risk ownership.
Create a plan that works for your organization and team. If your organization is restructured or significantly changes at any point, review your risk assessment methodology to determine if it needs to change as well.
Make your risk management process reasonable
Your risk management process needs to be thorough yet sustainable. If your methodology is overly ambitious and your team can’t keep up, it will be less effective. Cover as much of your risk as you can, but understand where your resources may be capped when it comes to remediating and mitigating risk.
Keep your documentation organized
As you develop your risk assessment methodology, keep your documentation in an accessible place. This will make your audit go smoother since your auditor will be able to quickly find the documentation they need. This also makes it easier for your team to access these documents when conducting internal audits or routine risk assessments.
Streamline risk assessments with Vanta
If you’re overwhelmed with ISO 27001 risk assessments, don’t worry — Vanta can help!
Vanta’s trust management platform provides guidance with step-by-step instructions for identifying gaps, assessing your risks, and implementing the applicable ISO 27001 controls. We provide a centralized repository for you to keep all your documentation and automate up to 80% of the work required to obtain ISO 27001.
{{cta_simple2="/cta-modules"}}
How much does ISO 27001 certification cost?
Your guide to the iso 27001 certification process, how long does it take to get iso certified, guide to iso 27001 risk assessment, iso 27001 statement of applicability (soa), your guide to internal iso 27001 audits, preparing for an iso 27001 audit, download the checklist.
Your checklist to ISO 27001 certification
Need to get ISO certified but not sure where to start? This guide walks you through the steps to get ISO 27001 compliant.
See how our ISO 27001 automation works
Request a demo to learn how Vanta can automate up to 80% of the work it takes to get ISO 27001 certified


Explore more ISO 27001 articles
Introduction to iso 27001, iso 27001 requirements, streamlining iso 27001 compliance, understanding iso differences, get started with iso 27001.
Start your ISO 27001 journey with these related resources.

The ISO 27001 Compliance Checklist
ISO 27001 is the global gold standard for ensuring the security of information and its supporting assets. Obtaining ISO 27001 certification can help an organization prove its security practices to potential customers anywhere in the world.

ISO 27001 Compliance for SaaS
On 10 October at 2 PM BST, join the Ask Me (Almost) Anything with Herman Errico and Kim Elias, compliance experts at Vanta. They’ll answer (almost) all your questions about ISO 27001 compliance.

ISO 27001 vs. SOC 2: Which standard is right for my business?
Complying with security standards such as ISO 27001 or SOC 2 can help boost your business, but for technology startups, security compliance is often lower on the list of company priorities.
Get compliant and build trust—fast

- Visit our Webshop
5 Steps to an Effective ISO 27001 Risk Assessment
ISO 27001 risk assessments help organisations identify, analyse and evaluate weaknesses in their information security processes.
Want to know how to get your ISO 27001 risk assessment process right?
Here are five steps to help you on your way:
- Establish a risk management framework
- Identify risks
- Analyse risks
- Evaluate risks
- Select risk responses
We’ll also go over key ISO 27001 documentation : the SoA (Statement of Applicability) and the RTP (risk treatment plan).
1. Establish a risk management framework
Your risk management framework establishes the basis of your risk assessments.
So, it must take into account:
Your organisation’s context
Naturally, your risk management framework must reflect the scope of your information security project – the context of your ISMS.
This blog explains in more detail how to determine your context.
Risk criteria
- How do you intend to measure risks?
- How will you determine their impact?
- How will you determine their likelihood?
Clearly define your answers so your risk assessments will produce “consistent, valid and comparable results”, as per the ISO 27001 requirements (Clause 6.1.2.b).
Risk acceptance criteria
What is your risk appetite (risk tolerance)?
Use that to define your risk acceptance criteria: the level at which you can simply accept a risk as-is.
2. Identify risks
Risk identification is one of the most important steps in the process. After all, you can’t address your risks if you don’t know what they are.
The Standard requires you to identify risks that can affect the confidentiality, integrity and/or availability of information. Broadly speaking, you can take one of two approaches:
- Asset-based risk assessment
- Scenario-based (event-based) risk assessment
Asset-based assessments
We favour an asset-based approach, which requires:
- An asset register;
- A list of business processes; and
- A database or list of threats and vulnerabilities to consider.
The goal is to establish the vulnerabilities of each asset, and consider what threats might exploit those vulnerabilities. Dedicated software can significantly speed up the process, particularly if it includes built-in libraries of threats and vulnerabilities.
As our head of GRC consultancy, Andrew Pattison, pointed out:
For a risk to materialise, you need all three – it’s not just having a vulnerability, but also about whether a threat could and would exploit it.
Andrew provided further expert insight into pragmatic ISO 27001 risk assessments in this interview .
Free PDF download: Risk Assessment and ISO 27001
You can learn more about information security risk assessments by downloading our free green paper: Risk Assessment and ISO 27001 .

This guide explains:
- How to produce reliable and robust results in five simple steps;
- Common challenges and their solutions; and
- The link between the risk assessment and SoA (Statement of Applicability).
3. Analyse risks
After you’ve identified your risks, you must analyse them.
For each risk, you must assess the likelihood of the threat exploiting the vulnerability. You must also assess impact: what’s the maximum possible harm?
Assign both likelihood and impact a ‘score’, as defined by your risk criteria (see step 1 ). This might look something like this:

Example likelihood criteria

Example impact criteria
4. Evaluate risks
Now that you’ve established impact and likelihood for each risk, you need to measure the overall risk level.
Most methodologies calculate the ‘risk score’ as some product of impact and likelihood. You can visualise this in a risk matrix like this:

The matrix should clearly separate different areas, usually through colour-coding. This indicates, in line with your risk appetite, which risks:
- Are unacceptable;
- Require careful monitoring and more regular reviews; and
- Are tolerable as they are.
This will also inform how to prioritise your risks.
5. Select risk responses
Where a risk is unacceptable, you must take action.
Here are four broad ways you can respond to a risk:
- Modify : Implementing a security measure to bring the risk down to an acceptable level. Annex A of ISO 27001 can offer ideas for possible controls to implement.
- Share : Sharing at least part of the risk with another party. This might be through insurance or by outsourcing . Keep in mind, however, that the risk is still yours – you’re changing it, not getting rid of it.
- Avoid : Avoiding the threat altogether – by stopping the processing activity, for example.
- Retain : Actively choosing to tolerate the risk – for example, because you can’t treat the risk. Make sure you document your reasoning for this decision.
Whatever response you choose, make sure you document it, along with your justifications. You should also review risks at least annually and after significant changes.
Risk assessment reports
Though risk management is fundamental to ISO 27001, implementing an ISMS doesn’t stop at the risk assessment.
Documentation is a vital part of any ISO 27001 ISMS. The SoA and risk treatment plan are the most important:
SoA (Statement of Applicability)
The SoA isn’t just one of the most important documents in your ISMS – it’s one of the most comprehensive.
It lists all 93 Annex A controls, their implementation status, and justifications for including or excluding them.
ISO 27001 allows you to use controls from other frameworks, or even design your own, but these must be mapped against those in Annex A to give auditors a clear point of reference. Your SoA will also be a key focus during audits.
RTP (risk treatment plan)
- Provides a summary of each identified risk;
- Identifies the parties responsible for those risks;
- Outlines your risk responses/treatments; and
- Sets out deadlines for implementing them.
Remember that both the SoA and RTP are documented information. So, use version control and review them when you review your risk assessments.
Want to speed up your ISO 27001 risk assessments? Or need help generating your ISO 27001 documentation?
CyberComply makes ISO 27001:2022 compliance simple and affordable:

- Automate, review and repeat ISO 27001 risk assessments, reducing the time spent on them by up to 80%.
- Take advantage of CyberComply’s built-in library of threats, vulnerabilities and controls to treat risks.
- Automate the creation of key documents for an ISO 27001 ISMS, including the SoA.
- Includes full access to our ISO 27001 Toolkit , containing more than 80 template documents created by ISO 27001 experts.
Don’t take our word for it
Here’s what our customers say about CyberComply:
Josh Pribanic:
We needed a way to expedite and simplify our risk assessment process and CyberComply became a clear choice after testing other solutions in the market. Customer support for the product is fantastic.
Using this for our ISO 27001 system, very easy to use and new features being added all the time. Support though is where this product excels!
We first published a version of this blog in February 2020.
Related Posts

IT Governance Europe
One response.
Hi to every one, the contents present at this web site are in fact awesome for people experience, well, keep up the nice work fellows.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
How to Conduct an ISO 27001 Risk Assessment
Published on : 25 Oct 2023

Welcome to our comprehensive guide on ‘Conducting an ISO 27001 Risk Assessment’. This blog is designed to equip you with effective strategies for a successful risk assessment, incorporating the principles of ISO 31000 risk management.
Risk assessment is a vital component of a robust information security framework and is in alignment with ISO 31000. It’s a systematic, iterative, and collaborative process that leverages insights from stakeholders and reliable information, supplemented as necessary.
This guide will detail the process to align your organization’s information security with ISO 27001 and ISO 31000 standards. Let’s enhance your risk assessment!
Before we proceed, let’s familiarize ourselves with some technical terms that will be used throughout this blog:
- Vulnerability : A system weakness that can be exploited, like outdated software.
- Threat : Anything that can potentially harm your system, such as a hacker.
- Likelihood : The probability of a threat exploiting a vulnerability.
- Impact : The potential damage resulting from a threat exploiting a vulnerability, like data loss.
- Risk : The potential loss or damage, calculated as the product of likelihood and impact. For instance, a high risk could imply a high probability of significant data loss due to a hacker exploiting a software vulnerability.
With these definitions in mind, let’s embark on our journey to conduct an effective ISO 27001 Risk Assessment!
5 Crucial Steps to Conduct an Effective ISO 27001 Risk Assessment
1.establish an iso 27001 risk assessment methodology:.
Start your effective ISO 27001 risk assessment by defining a methodology that aligns with your organization’s needs. Choose between a qualitative or quantitative approach:
- Qualitative Method : Dive into diverse scenarios and address hypothetical inquiries to identify risks.
- Quantitative Method : Use data and figures to establish risk levels.
Customize an ISO 27001 risk assessment to your organization, aligning with security goals and stakeholder expectations. Engage management in defining criteria and risk levels, ensuring method adherence.
When you manage risks, consider popular frameworks like ISO 27005:2018, OCTAVE, NIST SP 800-30, RISK IT, Value-at-Risk (VaR), and Earnings-at-Risk (EaR). Choose the one that best aligns with your organization’s needs.
2.Develop a Comprehensive Asset Inventory and Criticality-Based Categorization:
After establishing your risk assessment methodology, develop a comprehensive asset inventory. You can’t safeguard what you’re unaware of, so protection begins with awareness. Your inventory should include:
- Devices (including IoT devices, network devices, and mobile devices)
- Storage Locations
- Applications/Software
- Information databases
- Removable devices
- Intellectual property
For an ISO 27001 risk assessment, it’s key to consult all asset owners and compile a full asset inventory, including new ones in cloud environments.
Categorizing assets by their criticality is crucial, as it directs resources towards protection, recovery, and risk management. Here are some examples based on their criticality:
- High criticality assets , such as primary data centers, key network infrastructure (including routers, switches, and firewalls), and critical applications, could cause significant harm to an organization’s operations or reputation if they’re compromised.
- Medium criticality assets , such as secondary data centers (used for backing up primary data centers) and non-critical applications (supporting day-to-day operations), are important to an organization’s operations, but their compromise would not be as devastating.
- Low criticality assets , such as peripheral devices (printers, scanners, etc.) and test environments (used for testing updates or new applications), would cause minimal disruption to an organization’s operations if compromised.
A thorough risk assessment is vital to determine each asset’s criticality, as these classifications can vary based on the organization and its operations.
3.Risk Identification and Vulnerability Assessment:
To meet our goals, we need to stay alert in identifying risks, whether they advance us or hinder us. This requires using up-to-date information and various methods to detect uncertainties affecting our objectives.
Consider these factors:
- Think about both tangible and intangible risks.
- Recognize their causes and triggering events.
- Be alert to threats and opportunities.
- Understand vulnerabilities and capabilities.
- Monitor changes in your external and internal environment.
- Keep an eye out for emerging risks.
- Assess the value of your assets and resources.
- Consider potential consequences on your objectives.
- Acknowledge the limitations of your knowledge and data reliability.
- Factor in the element of time.
- Be mindful of any biases or assumptions.
Don’t miss technical issues like software glitches, tech vulnerabilities, and downtime when identifying risks.
On the admin side, consider risks related to employee turnover, documentation gaps, and security awareness. Understand that risks can come from various sources with tangible or intangible outcomes.
4.Analyze Risk:
Risk analysis is a thorough process designed to understand the characteristics of risk. It delves into uncertainties, sources of risk, outcomes, probabilities, scenarios, controls, and their effectiveness.
The approach can be qualitative, quantitative, or a combination of both, depending on the purpose, reliability and availability of information, and resources.
Key factors include:
- Event likelihood and outcomes
- Outcome type and scale
- Connectivity
- Time factors
- Control effectiveness
- Sensitivity levels
- Confidence levels
Analysis can be swayed by biases and perceptions, which should be identified and shared with decision-makers. Quantifying uncertain events is tough, but various techniques can help.
5.Risk Evaluation and Impact Assessment:
Take a comprehensive approach to risk assessment by assessing financial and customer relationship impacts of risks and prioritizing them using a risk matrix.
Keep in mind the CIA Triad’s influence on data security and assess potential costs like financial losses and reputation damage.
Assign likelihood and impact scores to each risk for efficient management and compare results with established criteria to identify areas requiring action, such as:
- Taking No Further Action: If the risk is manageable or has minimal impact, no additional steps are needed.
- Exploring Risk Treatment Options: When risks surpass acceptable levels, explore various mitigation strategies.
- In-Depth Analysis: For complex risks or uncertain analysis results, consider a deeper examination.
- Continuing Current Controls: If existing controls effectively reduce risk, maintain them.
- Reassessing Objectives: If the risk seriously endangers organizational objectives, contemplate redefining them.
This approach ensures a thorough risk evaluation and management. It aligns with ISO 31000:2018’s emphasis on transparency, shared responsibility, and continuous improvement through documentation and sharing of risk evaluation outcomes.
Download our “ ISO 27001 Checklist “
Risk Treatment:
Risk treatment involves a systematic process to address risks. It starts with understanding the risk, its potential impact, and the effectiveness of current controls.
A. Implement Risk Treatment Plan and Statement of Applicability:
The Risk Treatment Plan (RTP) in ISO 27001 certifies threat responses and is subject to audit. Each risk necessitates an owner’s approval for the plan and acceptance of residual risk. ISO 27001 offers various risk management options.
- Risk Avoidance: This involves taking preventive actions such as ending high-risk vendor partnerships to avoid the risk.
- Risk Treatment: Apply security measures like firewalls or endpoint detection solutions to reduce the likelihood of the risk.
- Risk Transfer: Share the risk with a third party through methods like outsourcing or cybersecurity insurance.
- Risk Acceptance: If meeting established criteria or reducing costs is too challenging, the risk may be accepted.
Alongside the RTP, a Statement of Applicability (SoA) is crucial. The SoA outlines your organization’s security profile, controls, and their deployment based on the ISO 27001 risk assessment. It guides your risk management approach and should align with your risk strategy.
B. Compile Risk Assessment Reports
For audit and certification, you need to prepare two crucial documents: The RTP and SoA.
The RTP should detail each identified risk, propose actions to mitigate them, and assign responsible parties.
The SoA, per ISO 27001 Standard Clause 6.1.3,
- It should list your organization’s chosen controls.
- It should justify the selection of these controls.
- It should confirm these controls’ implementation.
- It should explain any omitted controls.
In the SoA, detail each control’s selection, status, and exclusion reasons. These guide the auditor’s ISO 27001 compliance review.
C. Review, Monitor, and Audit Risks for ISMS Improvement
Monitoring and reviewing the risk management process across all stages enhances its effectiveness and integrates results into the organization’s performance management. Document handling prioritizes use, information sensitivity, and context. Reporting supports management and stakeholders, considering cost, frequency, timeliness, and relevance.
Regular risk assessments under ISO 27001 lead to an annual audit considering organizational changes and threats, including mitigation strategies and scheduling for new risk treatments or controls.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the importance of conducting a robust ISO 27001 risk assessment for your organization’s information security cannot be overstated. It is our hope that this guide has equipped you with not only valuable insights but also actionable strategies. Keep in mind, a successful risk assessment does more than just protect your information – it fortifies your brand’s reputation and nurtures customer relationships. So, here’s to leveraging risk assessment as a strategic tool for your organization’s success!

Narendra Sahoo (PCI QPA, PCI QSA, PCI SSF ASSESSOR, CISSP, CISA, CRISC, 27001 LA) is the Founder and Director of VISTA InfoSec, a global Information Security Consulting firm, based in the US, Singapore & India. Mr. Sahoo holds more than 25 years of experience in the IT Industry, with expertise in Information Risk Consulting, Assessment, & Compliance services. VISTA InfoSec specializes in Information Security audit, consulting and certification services which include GDPR, HIPAA, CCPA, NESA, MAS-TRM, PCI DSS Compliance & Audit, PCI PIN, SOC2 Compliance & Audit, PDPA, PDPB to name a few. The company has for years (since 2004) worked with organizations across the globe to address the Regulatory and Information Security challenges in their industry. VISTA InfoSec has been instrumental in helping top multinational companies achieve compliance and secure their IT infrastructure.
Recent Post
- USA: +1-415-513-5261
- Singapore: +65-3129-0397
- Mumbai: +91 99872 44769 / +91 73045 57744
- UK: +442081333131
Enquiry Form
- [email protected]
Enquire Now
Free One Session of Consultation
Essential cookies
Necessary cookies are absolutely essential for the website to function properly. This category only includes cookies that ensure basic functionalities and security features of the website. These cookies do not store any personal information.
All Cookies
Non-essential cookies.
Any cookies that may not be particularly necessary for the website to function and is used specifically to collect user personal data via analytics, ads, and other embedded contents are termed as non-necessary cookies. It is mandatory to procure user consent prior to running these cookies on your website.
Message Sent!
Thank you for sharing your contact details. our team will get back to you shortly.
- Who Are We?
- Partnership Program
- Our Clients
- Client Testimonials
- Gallery & Events
- SOC1 Advisory and Attestation
- SOC2 Audit and Attestation
- PCI DSS 4.0 Audit & Compliance
- PCI PIN Security and Certification
- PCI SSF Advisory & Certification
- ISO27001 Advisory and Certification
- ISO 20000 Advisory and Certification
- Business Continuity (ISO 22301)
- Cloud Risk – CCM / CStar / ISO27017
- Vendor Third-Party Risk Management
- Vulnerability Assessment
- Penetration Testing
- Red Team Assessment Services
- Web App Security Assessment
- Mobile Security Risk Assessment
- Thick Client Security Assessment
- Virtualization Risk Assessment
- Secure Configuration Assessment
- Source Code Review
- ATM Security Assessment
- GDPR Compliance Consulting and Audit
- HIPAA Compliance Consulting and Audit
- CCPA Consulting and Audit
- NESA Consulting and Audit
- MAS-TRM Consulting and Audit
- NCA ECC Compliance
- SAMA Compliance
- SOX Compliance & Audit
- FDA CFR Part11
- CMMC Compliance
- Adaptive Security Management
- DPO Consulting Services
- PCI SAQ Services
- CISO Advisory Services
- Managed Compliance Services
- Managed Security Services
- Infrastructure Audit
- Infrastructure Design & Advisory
- Datacenter Design & Consulting
- Training & Skill Development
- Data Privacy Laws & Standard
- Banking, Financial Service & Insurance
- Cloud-based Service Providers
- Data Analytics
- Payment Card and Processing
- Pharmaceutical
- Retail & Manufacturing
- Expert Videos
- Externally Published Articles
- Write For VISTA InfoSec
- Book A Call (Free Consultation)
- Struggling to Achieve Cyber Security & Compliance Goals? Get Expert Guidance Free Consultation ×
- Get a Quote
- Talk to an Expert

ISO 27001 Risk Assessment Methodology
| Blog , Compliance , ISO 27001

Conducting an internal ISO 27001 audit enables you to assess your company’s security equipment, systems, protocols and procedures to ensure that they are in compliance with industry standards. One of the most important aspects of this process involves determining where the vulnerabilities lie in order to see how these weaknesses may open your organization’s networks and systems to the jeopardy of data breach. By properly implementing a risk assessment, you can review, assess and correct your entire security mechanism, thus creating a more stable and safe infrastructure.
The Components of the ISO 27001 Risk Assessment Methodology
Clause 6.1.2 of the ISO 27001 standard lays out a rather minimal list of requirements that you must adhere to as you seek to determine the security of your information systems and controls. They include the following:
• Specify how you will go about identifying risks and vulnerabilities that could compromise the confidentiality, availability and/or integrity of the information you store, manage or transmit. One of the best ways is to list all threats and vulnerabilities that you detect; • Discuss how you will identify the risk owners. Find a person or team who has the training, knowledge and ability to deal with the risk and the power or position in your company to accomplish the task. • Identify what criteria you will use to gauge the likelihood that the risk might occur as well as potential consequences. Many teams rate risks as low, medium or high priority or use a numerical scale; • Recount how you will calculate the risk; • Describe the criteria you will use to accept risks. You might, for example, choose to address all risks that you have rated as “high” before any others.
In short, a strong ISO risk assessment methodology is the first step of an entire risk management structure. It provides your organisation with a qualitative or quantitative framework that you and your management team can use to assess your company’s success in the implementation of this important standard. Once you have put it in place, you can move on to the other elements of your effective risk management steps.
Talk to our experts today!
Implement Your Risk Treatment Plan
Once you have identified risks and prioritized them according to threat level via the risk assessment methodology, you are ready to move on to a treatment plan. This, of course, involves dealing with your highest-priority or unacceptable risks first. To that end, you have four possible options: • Implement security controls to minimize the risk; • Change ownership of the risk by transferring it. For instance, by insurance, thereby making the risk the problem of the insurance provider; • Avoid the risk by ceasing the risky behavior or by finding another way to achieve your goal; • Accept the risk as long as you know the potential consequences.
Now that you have applied this protocol to your highest risks, you can proceed to mid- and low-level concerns until you have a thorough picture of the known challenges facing your organisation.
Write A Risk Assessment Report
After all of your hard work of identifying, ranking and treating your risks, the time has come to chronicle your activities in an isms risk assessment report. This document is designed to create a tangible statement that you and your team can show to stakeholders or use later during a compliance audit from an internal or third-party expert.
Statement of Applicability
Another important piece in your cyber compliance process is the Statement of Applicability, a document that details all of the security processes that you have implemented as a result of your risk assessments, your reasons for putting them in place and exactly how they work. This is a vitally important component of any third-party certification audit. Keep in mind that it is your team’s job to show that your data and systems are secure and that you comply with the ISO 27001 standard.
Move Forward With Your Risk Treatment Plan
With all of the preliminaries in place, you can now implement your practical strategy to assess and address risks in order to protect your hardware, network, software and even human assets. To that end, you need to establish a plan for each goal: Who is going to achieve it? What is the target date? How much will it cost, and from what budget will the funds come? With this framework as your guide, your path is clear and your results become verifiable.
The Elements of a Successful ISO Risk Assessment
Above all else, your team must produce a robust, consistent, verifiable risk assessment document that is designed to reflect your organisation’s view toward the various risks it faces as well as how to address them. Required documentation reports should be very specific in regards to all tasks to be completed, who will be given the job and the deadline for each.
An iso 27001 risk assessment template provides companies with an easy-to-use way to organize all aspects of the project that range from inception to completion. Whether your company is a global player or a smaller actor on the commercial stage, this template should be an indispensable part of your basic reports toolkit as you set about documenting your compliance with ISO standards.
Whether you are preparing to consult with a third-party compliance auditor or you simply are conducting some preemptive self-examinations, an ISO 27001 risk assessment report can provide your organisation with invaluable information. When your IT risk assessment methodology is well-conceived, this documentation truly can provide a framework that will ultimately lead to greater security and accountability with fewer compliance errors.

Related Posts

Mastering Compliance Risk: A Comprehensive Guide

Continuous Compliance: Your Key to Regulatory Success

Conquer Compliance Chaos: Your Guide to Compliance Management Software
Secure your business with TrustNet’s top-tier compliance services. Talk to an expert today.
7 steps to run ISO 27001 risk assessment

Risk assessment is at the heart of the ISO 27001 compliance process for any organisation. ISO 27001 risk assessment is necessary to verify whether your Information Security Management System (ISMS), which is the outcome of applying the standard, can adequately handle risks.
All to make sure your information security setup is on point, and you are ready to brace for whatever cyber threat may come your way.
Dive into the essentials of risk assessment and management, uncover the effectiveness of ISO 27001, and follow a straightforward 7-step plan to streamline risk analysis within your organization.
In this blog post, we'll cover:
What is information security risk management, what is information security risk assessment, and why is it important, how does an iso 27001 risk assessment work, how does reviewing and monitoring isms continuously help you prepare for a risk assessment, how does iso 27001 define and treat risks, what does iso 27001 require when conducting a risk assessment, what are the seven simple steps to an effective iso 27001 risk assessment, how can small or medium organisations conduct risk management, should you conduct an iso 27001 risk assessment.
- How does ISO 27001 help with risk management?
Risk management is likely the most difficult aspect of ISO 27001 implementation. Still, it's also the most important phase at the start of any information security project, as it lays the groundwork for information security in your organisation.
It entails recognising, analysing, and responding to threats to your organisation's asset confidentiality, integrity, and availability. The end objective of this approach is to address risks in accordance with the overall risk tolerance of an organisation.
The aim is to determine and attain an acceptable risk threshold for your organisation rather than expecting to remove all hazards.
On the other hand, risk assessment (also known as risk analysis) and risk treatment are the two fundamental components of risk management. Let's take an in-depth look below.
A security risk assessment finds, evaluates, and applies application security measures. It also focuses on preventing security flaws and vulnerabilities in applications.
An enterprise may see its application portfolio holistically from the standpoint of an attacker by conducting a risk assessment. It assists you in making well-informed decisions about resource allocation, tools, and security control implementation. As a result, completing an evaluation is an important aspect of an organisation's risk management strategy .
In general, risk assessments are conducted across the whole organisation. Once the risk assessment has been conducted, your organisation needs to decide how to manage the risks based on allocated resources and budget.
They cover all the possible risks to which information could be exposed, balanced against the likelihood of materialising risks and their potential impact. Now that we've covered the description of risk assessment let's take a look at how a risk assessment works.
The complexity of risk assessment is affected by factors like size, growth rate, resources, and asset portfolio. When faced with money or time restrictions, organisations might conduct generic evaluations. However, generalised evaluations may not always include precise mappings of assets, related threats, recognised risks, effects, and mitigation mechanisms.
If the findings of the generalised assessment do not offer enough of a link between these areas, an in-depth evaluation is required. The results of a risk assessment form the basis of an ISMS. To reduce recognised risks, organisations must develop a set of controls.
Information security risk assessments must be performed at regular intervals, and if adjustments are required – both must be fully recorded.
ISO 27001 mandates that the information security management system (ISMS) be reviewed, updated and improved on a regular basis to ensure that it is working properly and adapting to the environment.
An internal audit is one component of evaluating and testing. This necessitates the ISMS manager generating a set of reports demonstrating that risks are being effectively addressed.
While an information security risk assessment may be conducted in a spreadsheet on a basic level, it is significantly better to have a tool that simplifies the documentation side of the risk assessment .
Risk is defined as the "impact of uncertainty on objectives" by ISO 27001, and "uncertainty" is the reason we can't entirely control all risks (after all, you can't defend against what you don't know or understand). However, you can plan for this.
An RTP (risk treatment plan) is an important aspect of the ISO 27001 implementation process that outlines how your organisation will respond to recognised threats. Organisations should modify the risk by:
- Implementing a control to reduce the likelihood of it occurring
- Avoiding the risk by ceasing any activity that causes it
- Sharing the risk with a third party by outsourcing security efforts to another organisation and purchasing cyber insurance to ensure you have the funds to respond appropriately in the event of a disaster
- Retaining the risk by accepting it and believing that the cost of treating it will be less than the cost of preventing it
ISO 27001 mandates you to record the whole risk assessment process (Clause 6.1.2), which is completed in the Risk Assessment Methodology document.
Typically, most organisations find this challenging as they begin risk assessment without a methodology. You need a clear plan and instructions to set up your organisation for success.
As a starting point, here is what Clause 6.1.2 requires:
- Define how to spot the threats that might compromise your data's confidentiality, integrity, and/or availability
- Establish a method for identifying the risk owners
- Define the criteria for evaluating repercussions and determining the risk's likelihood
- Define the method for calculating risk
- Define the risk-acceptance criteria
In short, you need to identify these five aspects, and anything less will not be sufficient. Use this as a foundation for your plan.
A risk assessment process that meets the requirements of ISO 27001 should have seven steps:
1. Establish an ISO 27001 risk assessment framework
This is the first stage in your ISO 27001 risk assessment journey. It’s important for your organisation to handle risk assessment consistently. As a result, you need to develop guidelines that explain how the process is undertaken.
The largest difficulty with risk assessment is when various portions of your organisation do it differently. As a result, you must decide if you want a qualitative or quantitative risk assessment, which scales to use for qualitative evaluation, and what amount of risk is acceptable, among other things.
Several concerns must be addressed in a formal risk assessment methodology:
- The most important security criteria for your organisation
- The scale of risk
- Appetite for risk
- Methodology: Risk assessment based on scenarios or assets
2. Create a list of your organisation's information assets
Making a list of your information assets is one method to undertake a risk assessment for your company.
The first method is asset-based, which implies that your company must concentrate on the risk to its information assets. This method takes longer to detect concerns, but it provides a more comprehensive picture of risk.
The second method is scenario-based, which means your company must concentrate on scenarios that might lead to a data breach. Users are more likely to recognise risk circumstances in this report, which frequently speeds up the risk identification process. However, one downside of this strategy is that users frequently overlook some factors that may pose a risk. As a result, the risk assessment is lacking.
3. Identify risks
Once you understand the rules, you can determine which potential problems may affect you. First, list all of your assets, then threats and vulnerabilities related to those assets, assess the impact and likelihood of each combination of assets/threats/vulnerabilities, and finally calculate your risk level.
4. Evaluate risk impact
Some risks are more serious than others, so you will need to figure out which ones are the most pressing at this point. That is why it is critical to rank risks according to their chance of occurrence and the potential damage they can inflict.
Create a checklist based on these characteristics to evaluate risks to your risk appetite, as well as identify and prioritise hazards that need to be addressed. You will benefit from a consistent and comparative evaluation of the hazards your organisations face by analysing the risks in this manner.
5. Create a Statement of Applicability
The Statement of Applicability (SoA) depicts your organisation’s security profile; you must identify all the controls you have installed, why you have implemented them, and how you have implemented them, based on the results of the risk assessment in ISO 27001.
This document is crucial since it will be used as the audit's major guideline by the certification auditor.
6. Create a risk treatment plan
You must identify risk owners for all risks, according to ISO 27001. This body is in charge of approving any risk mitigation strategies as well as accepting the residual risk level.
Human error introduces numerous risks to an organisation, and it's rare that you will be able to eliminate them entirely. As a result, most risks will have to be modified. This entails implementing controls as described in ISO 27001 Annex A as part of the mitigation strategy.
7. Review, monitor and audit internally
To guarantee that you have accounted for changes in how your organisation functions as well as the evolving threat environment, you will need to repeat the assessment process every year.
Mitigation techniques, responsibilities, budget, and timeline should all be included in the risk assessment strategy.
You should also take advantage of this chance to seek methods to improve your ISMS. This might include moving to a new risk treatment option or adopting a different control to handle risks.
Many smaller organisations are attempting to adopt risk management software as part of their ISO 27001 implementation project. However, some of these are designed keeping large organisations in mind.
Here are some suggestions for making risk management easier for small organisations:
Select the appropriate framework
The framework should be streamlined to include the ISO 27001-required parts. If you end up employing a framework that you replicated from a major organisation, risk assessment and treatment will take months instead of days.
Select the appropriate instrument
Look for software that follows your (simplified) technique. In certain circumstances, a well-designed Excel template will outperform more complex software.
Include the relevant individuals
You should not try to accomplish this on your own; you should enlist the help of the leaders of all of your departments since they are the most knowledgeable about their processes, which means they are the most aware of possible difficulties.
Make no attempt to be faultless
Instead of attempting to uncover all of the risks the first time around, you should complete your risk assessment and treatment first, then return later to include any hazards that were missed.
To summarise, risk assessment and treatment are the pillars of ISO 27001, but they do not have to be difficult. Always remember to adapt the process to fit your organisational needs.
The ISO 27001 risk assessment is a method for systematically evaluating your organisation's risks, understanding how they could affect your information security, and implementing a strategy to reduce those risks.
ISO 27001 focuses on risk assessment and treatment, allowing you to not only identify which incidents may compromise your information security but also establish the best strategies to prevent or mitigate them.
You may also prioritise each risk so that instead of wasting time, effort, or money treating all risks, you can concentrate your efforts on the most important ones. An ISO 27001 risk assessment might be advantageous for your organisation for all of these reasons.
The risk assessment framework is outlined clearly in ISO 27001 and elaborated in ISO 27005 ; information security risk assessment focuses on maintaining confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
How does ISO 27005 help with risk management?
ISO 27005 is a standard dedicated completely to the management of information security risks. It is extremely beneficial if you want to better understand information security risk assessment and treatment.
Start risk assessment to protect your organisation
Risk assessments are not only an audit exercise, regardless of whether your organisation adopts ISO 27001. A dynamic risk assessment is a real-time procedure that addresses issues as they arise. On a daily level, everyone is responsible for risk management.
Need some guidance on your ISO 27001 risk assessment? DataGuard's information security experts are there for you. We can help manage your information security, conduct risk analysis and get you ISO 27001 certified.
Check out our ISO 27001 solution or book a free consultation with us.

Essential steps for ISO 27001 risk assessment
Dive into our exclusive 8-step guide to a thorough and streamlined ISO 27a001 risk assessment. This essential guide provides clarity and practical steps for your organisation to effectively manage risk and comply with ISMS standards. Secure your path to compliance and optimal risk management with our expert insights.
Don't forget to share this post!
About the author.

Tips and best practices on successfully getting certifications like ISO 27001 or TISAX®, the importance of robust security programmes, efficient risk mitigation... you name it! Our certified (Chief) Information Security Officers and InfoSec Consultants from Germany, the UK, and Austria use their year-long experience to set you up for long-term success. How? By giving you the tools and knowledge to protect your company, its information assets and people from common risks such as cyber-attacks. What makes our specialists qualified? These are some of the certifications of our privacy experts: Certified Information Privacy Professional Europe (IAPP), ITIL® 4 Foundation Certificate for IT Service Management, ISO 27001 Lead Implementer/Lead Auditor/Master, Certificate in Information Security Management Principles (CISMP), Certified TickIT+ Lead Auditor, Certified ISO 9001 Lead Auditor, Cyber Essentials
Don’t miss these topics:
Related articles.

The EU AI Act: What are the obligations for deployers?
Learn how deployers are defined under the EU AI Act. Understand your obligations as a deployer and prepare for upcoming regulatory changes.

How a risk assessment consultant can help your business ?
A risk assessment consultant helps businesses identify and manage risks, fostering a proactive culture and ensuring compliance for long-term success.

Risk management tool: the key to effective risk management
Discover the essentials of data collection in business—learn how gathering, organizing, and analyzing data drives informed decisions and strategic growth.

Mastering the data collection process: essential steps, tools, and software

How to build a culture of compliance (and why you should)
Ready to boost your business with a strong compliance culture? Discover practical steps and real-world examples to get started today.

Streamlining compliance with advanced policy management software solutions
Streamline compliance with policy management software. Ensure easy access to up-to-date policies, reduce challenges, and boost operational efficiency.
Contact Sales
See what dataguard can do for you..
Find out how our Privacy, InfoSec and Compliance solutions can help you boost trust, reduce risks and drive revenue.
- 100% success in ISO 27001 audits to date
- 40% total cost of ownership (TCO) reduction
- A scalable easy-to-use web-based platform
- Actionable business advice from in-house experts
Trusted by customers
Get to know DataGuard
Simplify compliance.
- External data protection officer
- Audit of your privacy status-quo
- Ongoing GDPR support from a industry experts
- Automate repetitive privacy tasks
- Priority suppor t during breaches and emergencies
- Get a defensible GDPR position - fast!
- Continuous support on your journey towards the certifications on ISO 27001 and TISAX ®️ , as well as NIS2 Compliance .
- Benefit from 1:1 consulting
- Set up an easy-to-use ISMS with our Info-Sec platform
- Automatically generate mandatory policies
100% success in ISO 27001 audits to date
TISAX ® is a registered trademark of the ENX Association. DataGuard is not affiliated with the ENX Association. We provide consultation and support for the assessment on TISAX ® only. The ENX Association does not take any responsibility for any content shown on DataGuard's website.
- Transparent consent collection
- Comply with GDPR, CCPA, LGPD, ePrivacy , and more
- Consolidate consents across multiple touchpoints
- Support from privacy experts
- Integrates with your marketing tools and CRM
- Proactive support
- Create essential documents and policies
- Staff compliance training
- Advice from industry experts
- Comply with the EU Whistleblowing Directive
- Centralised digital whistleblowing system
- Fast implementation
- Guidance from compliance experts
- Transparent reporting
- Create account
- Your account
- Your subscriptions
- Your downloads
- Your orders
- Training course bookings
- Self-paced training bookings
- E-learning course bookings
- CyberComply portal
- GRC e-learning platform
- DocumentKits platform
- Asia Pacific

ISO 27001 Risk Assessments
- ISO 27001 benefits
- ISO 27001 implementation
- ISO 27001 certification
- ISO 27001 certification costs
- The benefits of implementing an ISMS
- ISO 27001 and the GDPR
- ISO 27001 and ISO 27002: 2022 updates
- ISO 27001 compliance software
- ISO 27001 consultancy
- ISO 27001 Implementation and Certification
- ISO 27001 documentation toolkit
- ISO 27001 gap analysis
- ISO 27001 penetration testing
- ISO 27001 risk assessments
- ISO 27001 risk assessment tool
- ISO 27000 series of standards
- ISO 27005 information security risk assessment standard
- ISO 27017 and ISO 27018 Cloud security standards
- ISO 27701 privacy information management standard
- ISO 27001 training and qualifications
- ISO 27001 information classification
Speak to an ISO 27001 expert
Speak to an expert.
One of our qualified ISO 27001 lead implementers are ready to offer you practical advice about the best approach to take for implementing an ISO 27001 project and discuss different options to suit your budget and business needs.
ISO 27001 and ISO 27002 2022 updates
ISO/IEC 27001:2022 – the newest version of ISO 27001 – was published in October 2022.
Organisations that are certified to ISO/IEC 27001:2013 have a three-year transition period to make the necessary changes to their ISMS (information security management system).
For more information about ISO 27001:2022 and its companion standard, ISO 27002:2022, and what they mean for your organisation, please visit ISO 27001 and ISO 27002: 2022 updates
Download your copy of ISO 27001:2022 here
Download your copy of ISO 27002:2022 here
The assessment and management of information security risks is at the core of ISO 27001
Section 6.1.2 of the ISO/IEC 27001 standard states the ISO 27001 risk assessment procedure must:
- Establish and maintain specific information security risk criteria.
- Ensure that repeated risk assessments “produce consistent, valid and comparable results”.
- Identify risks associated with the loss of confidentiality, integrity and availability of information within the information security management system’s scope.
- Identify the owners of those risks.
- Analyse and evaluate information security risks according to specific criteria.
Conduct error-free and compliant risk assessments with vsRisk
vsRisk is the leading ISO 27001 risk assessment software from Vigilant Software. Vigilant Software is a sister company of IT Governance.
Find out more
Speak to one of our experts for more information on implementing an ISO 27001 risk assessment. Our team of experts are on hand to offer specialist advice and can help you find the best solution for your requirements. Call 01474556685 or request a call back using the form below.
Five simple steps to an effective ISO 27001 risk assessment
A risk assessment process that meets the requirements of ISO 27001:2013 should have five steps:
Establish a risk management framework
These are the rules governing how you intend to identify risks, to whom you will assign risk ownership, how the risks impact the confidentiality, integrity and availability of the information and the method of calculating the estimated impact and likelihood of the risk occurring. A formal risk assessment methodology needs to address four issues and should be approved by top management:
- Baseline security criteria
- Risk appetite
- Scenario- or asset-based risk assessment
Identify risks
Identifying the risks that can affect the confidentiality, integrity and availability of information is the most time-consuming part of the risk assessment process. IT Governance recommends following an asset-based risk assessment process. Developing a list of information assets is a good place to start. It will be easiest to work from an existing list of information assets that includes hard copies of information, electronic files, removable media, mobile devices and intangibles, such as intellectual property.
Analyse risks
Identify the threats and vulnerabilities that apply to each asset. For instance, the threat could be ‘theft of mobile device’, and the vulnerability could be ‘lack of formal policy for mobile devices’. Assign impact and likelihood values based on your risk criteria.
Evaluate risks
You need to weigh each risk against your predetermined levels of acceptable risk and prioritise which risks need to be addressed in which order.
Select risk treatment options
There are four suggested ways to treat risks:
- ‘Avoid’ the risk by eliminating it.
- ‘Modify’ the risk by applying security controls.
- ‘Share’ the risk to a third party (through insurance or outsourced).
- ‘Retain’ the risk (if the risk falls within established risk acceptance criteria).
Download our free guide to risk assessments and ISO 27001
Discover the challenges you may face in the risk assessment process and learn how to produce robust and reliable results.
Download now
Applying information security controls in the risk assessment
Compiling risk reports based on the risk assessment.
ISO 27001 requires the organisation to produce reports based on the risk assessment for audit and certification purposes. The following two reports are the most important:
Statement of Applicability (SoA)
The SoA should create a list of all controls as recommended by Annex A of ISO/IEC 27001:2013, together with a statement of whether or not the control has been applied and a justification for its inclusion or exclusion.
Risk treatment plan (RTP)
The RTP describes how the organisation plans to deal with the risks identified in the risk assessment.
Review, monitor and audit to continually improve the ISMS
ISO 27001 requires the organisation to continually review, update and improve the information security management system (ISMS) to ensure it is functioning optimally and adjusting to the constantly changing threat environment.
One aspect of reviewing and testing is an internal audit . This requires the ISMS manager to produce a set of reports that provide evidence that risks are being adequately treated.
An even more effective way for the organisation to obtain the assurance that its ISMS is working as intended is by obtaining accredited certification.
Find out more about our internal audit service
How an ISO 27001 risk assessment works
An ISMS is based on the outcomes of a risk assessment. Businesses need to produce a set of controls to minimise identified risks.
Controls recommended by ISO 27001 are not only technological solutions but also cover people and organisational processes. There are 114 controls in Annex A covering the breadth of information security management, including physical access control, firewall policies, security staff awareness programmes, procedures for monitoring threats, incident management processes and encryption.
Controls from Annex A fall into 14 categories:
- A.5 Information security policies.
- A.6 Organisation of information security.
- A.7 Human resources security.
- A.8 Asset management.
- A.9 Access control.
- A.10 Cryptography.
- A.11 Physical and environmental security.
- A.12 Operational security.
- A.13 Communications security.
- A.14 System acquisition, development and maintenance.
- A.15 Supplier relationships.
- A.16 Information security incident management.
- A.17 Information security aspects of business continuity management.
- A.18 Compliance.
Risk assessments are conducted across the whole organisation. They cover all the possible risks to which information could be exposed, balanced against the likelihood of those risks materialising and their potential impact. Once the risk assessment has been conducted, the organisation needs to decide how to manage and mitigate those risks, based on allocated resources and budget.
Risk assessment standards
Several other information security and risk assessment standards support ISO 27001:
- ISO/IEC 27005:2011 – Guidance for information security risk management.
- ISO/IEC 31010:2009 – International standard for risk assessment techniques.
Let’s get started on your ISO 27001 risk assessment project
IT Governance has the widest range of affordable risk assessment solutions that are easy to use and ready to deploy.
Certified ISO 27005 ISMS Risk Management
ISO 27001 Toolkit
Nine Steps to Success – An ISO 27001 Implementation Overview
Fundamentals of Information Risk Management Auditing
Data Protection and the Cloud – Are you really managing the risks?
Get a 50% discount on ISO 22301 when you buy ISO 27001 ! Click here to download
- Project Management
- ITSM Templates
- Compliance Automation
- ISO 27001 Automation
- NIST Automation
- SOC 2 Automation
- GDPR Automation
- HIPAA Automation
- Book A Demo

Sign up today and we'll send you a 10% discount code towards your first purchase.
How to Conduct an ISO 27001 Risk Assessment?
Conducting an ISO 27001 risk assessment is a critical step in establishing and maintaining an effective Information Security Management System (ISMS). Here are the key steps to conduct an ISO 27001 risk assessment:

- Establish the Context : Begin by defining the scope of your risk assessment. Identify the assets to be protected, the boundaries of your ISMS, and the objectives you want to achieve. Understanding the context is essential for a focused assessment.
- Identify Information Assets : Create an inventory of all information assets within the scope of your ISMS. This includes data, hardware, software, facilities, personnel, and external resources that are critical to your organization's operations.
- Identify Threats and Vulnerabilities : Identify potential threats that could exploit vulnerabilities in your information assets. Threats can include natural disasters, human errors, malicious insiders, cyberattacks, and more. Vulnerabilities are weaknesses in your security controls that could be exploited by these threats.
- Assess Risks : Evaluate the likelihood and potential impact of each threat exploiting a vulnerability. You can use qualitative or quantitative methods to assess risks, but ensure consistency and accuracy in your assessments.
- Determine Risk Levels : Once you've assessed the risks, determine their levels based on a predefined risk matrix. Typically, risks are categorized as low, medium, or high based on their likelihood and impact.
- Identify Risk Owners : Assign responsibility for each identified risk to specific individuals or teams within the organization. These individuals are responsible for risk mitigation and management.
- Select and Implement Controls : Based on the risk assessment, identify and prioritize security controls from the ISO 27001 Annex A controls or other sources that are appropriate for mitigating the identified risks. These controls should address the specific threats and vulnerabilities in your context.
- Document the Risk Assessment : Ensure that all your risk assessment activities, findings, and decisions are thoroughly documented. This documentation will be essential for future audits and reviews.
- Monitor and Review : Regularly review and update your risk assessment. As your organization evolves and new threats emerge, your risk landscape may change. Ensure that your ISMS remains effective by monitoring and revising risk assessments as needed.
- Integration with ISMS : Integrate the risk assessment process into your broader ISMS framework. Ensure that risk management becomes an integral part of your organization's culture and operations.
- Communication and Training : Share the results of your risk assessment with relevant stakeholders, including employees, management, and external parties. Provide training on risk management and security controls to ensure everyone understands their roles and responsibilities.
- Continuous Improvement : Use the results of your risk assessment to drive continuous improvement of your ISMS. Regularly review and refine your security controls and risk management processes to adapt to changing threats and business needs.
Conducting an ISO 27001 risk assessment is not a one-time activity; it's an ongoing process that is essential for maintaining the security of your organization's information assets. By following these steps, you can systematically identify, assess, and mitigate risks to protect your sensitive information and achieve ISO 27001 compliance.

- Advisera Home
- ISO in General
Partner Panel
Company Training Account
Products by framework:
Implementation, maintenance, training, and knowledge products for Information Security Management Systems (ISMS) according to the ISO 27001 standard.
Automate your ISMS implementation and maintenance with the Risk Register, Statement of Applicability, and wizards for all required documents.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement an ISMS according to ISO 27001.
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful ISMS.
Accredited courses for individuals and security professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 27001 and the ISMS using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Compliance and training products for critical infrastructure organizations for the European Union’s Network and Information Systems cybersecurity directive.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to comply with the NIS 2 cybersecurity directive.
Company-wide training program for employees and senior management to comply with Article 20 of the NIS 2 cybersecurity directive.
Compliance and training products for personal data protection according to the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to comply with the EU GDPR privacy regulation.
Accredited courses for individuals and privacy professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for Quality Management Systems (QMS) according to the ISO 9001 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement a QMS according to ISO 9001.
Accredited courses for individuals and quality professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 9001 and the QMS using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for Environmental Management Systems (EMS) according to the ISO 14001 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement an EMS according to ISO 14001.
Accredited courses for individuals and environmental professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 14001 and the EMS using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation and training products for Occupational Health & Safety Management Systems (OHSMS) according to the ISO 45001 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement an OHSMS according to ISO 45001.
Accredited courses for individuals and health & safety professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Implementation and training products for medical device Quality Management Systems (QMS) according to the ISO 13485 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement a medical device QMS according to ISO 13485.
Accredited courses for individuals and medical device professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Compliance products for the European Union’s Medical Device Regulation.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to comply with the EU MDR.
Implementation products for Information Technology Service Management Systems (ITSMS) according to the ISO 20000 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement an ITSMS according to ISO 20000.
Implementation products for Business Continuity Management Systems (BCMS) according to the ISO 22301 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement a BCMS according to ISO 22301.
Implementation products for testing and calibration laboratories according to the ISO 17025 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement ISO 17025 in a laboratory.
Implementation products for automotive Quality Management Systems (QMS) according to the IATF 16949 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement an automotive QMS according to IATF 16949.
Implementation products for aerospace Quality Management Systems (QMS) according to the AS9100 standard.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement an aerospace QMS according to AS9100.
Solutions for industries:
- Consultants
- IT & SaaS companies
- Critical infrastructure
- Manufacturing
- Transportation & distribution
- Telecommunications
- Banking & finance
- Health organizations
- Medical device
- Laboratories
Implementation, maintenance, training, and knowledge products for consultancies.
Handle multiple ISO 27001 projects by automating repetitive tasks during ISMS implementation.
All required policies, procedures, and forms to implement various standards and regulations for your clients.
Organize company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for your client’s employees and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Accredited ISO 27001, 9001, 14001, 45001, and 13485 courses for professionals who want the highest-quality training and recognized certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 27001 (ISMS), ISO 9001 (QMS), and ISO 14001 (EMS) using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Find new clients, potential partners, and collaborators and meet a community of like-minded professionals locally and globally.
Implementation, maintenance, training, and knowledge products for the IT industry.
Documentation to comply with ISO 27001 (cybersecurity), ISO 22301 (business continuity), ISO 20000 (IT service management), GDPR (privacy), and NIS 2 (cybersecurity).
Company-wide cybersecurity awareness program for all employees, to decrease incidents and support a successful cybersecurity program.
Compliance, training, and knowledge products for essential and important organizations.
Documentation to comply with NIS 2 (cybersecurity), GDPR (privacy), ISO 27001 (cybersecurity), and ISO 22301 (business continuity).
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for manufacturing companies.
Documentation to comply with ISO 9001 (quality), ISO 14001 (environmental), and ISO 45001 (health & safety).
Accredited courses for individuals and professionals who want the highest-quality training and certification.
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 9001 (QMS) and ISO 14001 (EMS) using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for transportation & distribution companies.
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for schools, universities, and other educational organizations.
Documentation to comply with ISO 27001 (cybersecurity), ISO 9001 (quality), and GDPR (privacy).
Get instant answers to any questions related to ISO 27001 (ISMS) and ISO 9001 (QMS) using Advisera’s proprietary AI-powered knowledge base.
Implementation, maintenance, training, and knowledge products for telecoms.
Implementation, maintenance, training, and knowledge products for banks, insurance companies, and other financial organizations.
Documentation to comply with ISO 27001 (cybersecurity), ISO 22301 (business continuity), GDPR (privacy), and NIS 2 (cybersecurity).
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for local, regional, and national government entities.
Documentation to comply with ISO 27001 (cybersecurity), ISO 9001 (quality), GDPR (privacy), and NIS 2 (cybersecurity).
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for hospitals and other health organizations.
Documentation to comply with ISO 27001 (cybersecurity), ISO 9001 (quality), ISO 14001 (environmental), ISO 45001 (health & safety), and GDPR (privacy).
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for the medical device industry.
Documentation to comply with MDR and ISO 13485 (medical device), ISO 27001 (cybersecurity), ISO 9001 (quality), ISO 14001 (environmental), ISO 45001 (health & safety), and GDPR (privacy).
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for the aerospace industry.
Documentation to comply with AS9100 (aerospace), ISO 9001 (quality), ISO 14001 (environmental), and ISO 45001 (health & safety).
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for the automotive industry.
Documentation to comply with IATF 16949 (automotive), ISO 9001 (quality), ISO 14001 (environmental), and ISO 45001 (health & safety).
Implementation, training, and knowledge products for laboratories.
Documentation to comply with ISO 17025 (testing and calibration laboratories) and ISO 9001 (quality).
- White Papers
- Templates & Tools
By Standard
- Live Consultations
- Consultant Directory

Dejan Kosutic
- Talk to Sales
ISO 27001 / ISO 22301 document template:
Risk assessment and risk treatment methodology.
The purpose of this document is to define the methodology for assessment and treatment of information risks, and to define the acceptable level of risk.
The document is optimized for small and medium-sized organizations – we believe that overly complex and lengthy documents are just overkill for you.
There are 3 appendices related to this document. The appendices are not included in the price of this document and can be purchased separately: Risk Assessment Table , Risk Treatment Table , Risk Assessment and Treatment Report .
TEMPLATE LANGUAGE
CUSTOMERS FROM 107 COUNTRIES
THIS TEMPLATE IS ALSO AVAILABLE AS PART OF THESE DOCUMENTATION TOOLKITS

DOCUMENT FEATURES
- Price US$ 79.90
- Compliant with ISO/IEC 27001 6.1.2, 6.1.3, 8.2, and 8.3; ISO 22301 8.2.1, 8.2.3
- Format MS Word 2013, MS Word 2016, MS Word 2019
- Number of pages 7
- Document language English. For other languages click here: Deutsch , Español , Nederlands , Français , Português
- Can I edit the document? Yes. The document is fully editable – just enter information specific to your company.
- Can I use this to become certified? Yes. The documentation template may be used for ISO 27001 and ISO 22301 certification audit purposes.
- Well-defined instructions Document templates contain an average of twenty comments each, and offer clear guidance for filling them out.
- Designed with your company in mind The template was created for small and medium-sized businesses.
VIDEO TUTORIAL INCLUDED
- The tutorial How to Write the ISO 27001 Risk Assessment Methodology will show you how to insert your real data into the document. The tutorial is included in the price of the template.
Schedule a free presentation, and our representative will show you any document you're interested in.
WHAT OUR CUSTOMERS SAY ABOUT US
The documentation is brilliant. I worked through the BS 25999 package last year, combined with a bit of reading around the subject (mainly from Dejan's blog!) and we've got ourselves a business continuity plan. I'm just starting to do the same now with ISO 27001, and then we're going to work towards getting both of them certified.
Managing Director Click Travel Ltd
I am new to ISO 27001 and did not know where to start. The documentation templates helped me get started and have provided a good road map for where I need to go from here.
Compliance Manager
I used the template to aid me in preparing a third party management policy for my company. I did change a lot of the language but it was helpful to be sure of what sections needed to be included. Helped me work smarter, not harder.
It saved me hours of work, I really appreciated the template.
Sinometis International Pty Ltd
Well designed, well documented, a lot of time saved. Best ISO templates Business, no doubt.
RTI Surgical, Inc.
The document helped me to put in order the topics that needed to be covered.
Senior Partner Evolutionary Methodologies Consulting
The ISO 22301 documentation helped me reach a level of granularity which is appropriate and yet not so detailed as to bog down the implementation.
ONVENTIS GmbH
OUR CLIENTS

Preview Risk Assessment and Risk Treatment Methodology template
- The document is fully editable so that you can adapt it to your company design.
- Documents include placeholder marks for all information you need to complete.
- Each document includes comments and information , which guides you through completion.
- Comments with video tutorials support you with practical instructions.
Buy Risk Assessment and Risk Treatment Methodology
Sold in 107 countries
FAQS: PURCHASING INDIVIDUAL ISO 27001 / ISO 22301 DOCUMENT TEMPLATES
How will l receive the template.
After payment confirmation, we'll send you an email that contains a link to download the document. It's super easy.
What payments do you accept?
You may pay with major credit card, or via wire transfer from your bank account.
How do you protect my payment details?
We use Secure Socket Layer (SSL) technology, which is the industry standard and considered one of the safest systems for online payment. Your account details and credit card information are encrypted and go straight to the payment processor. We won’t have access to your payment information, and we won’t store it in any form.
Which currencies are accepted?
We can accept 50-plus common currencies for payment, including Swiss Francs, US Dollars, British Pounds and Euros.
Information
- Author Services
Initiatives
You are accessing a machine-readable page. In order to be human-readable, please install an RSS reader.
All articles published by MDPI are made immediately available worldwide under an open access license. No special permission is required to reuse all or part of the article published by MDPI, including figures and tables. For articles published under an open access Creative Common CC BY license, any part of the article may be reused without permission provided that the original article is clearly cited. For more information, please refer to https://www.mdpi.com/openaccess .
Feature papers represent the most advanced research with significant potential for high impact in the field. A Feature Paper should be a substantial original Article that involves several techniques or approaches, provides an outlook for future research directions and describes possible research applications.
Feature papers are submitted upon individual invitation or recommendation by the scientific editors and must receive positive feedback from the reviewers.
Editor’s Choice articles are based on recommendations by the scientific editors of MDPI journals from around the world. Editors select a small number of articles recently published in the journal that they believe will be particularly interesting to readers, or important in the respective research area. The aim is to provide a snapshot of some of the most exciting work published in the various research areas of the journal.
Original Submission Date Received: .
- Active Journals
- Find a Journal
- Proceedings Series
- For Authors
- For Reviewers
- For Editors
- For Librarians
- For Publishers
- For Societies
- For Conference Organizers
- Open Access Policy
- Institutional Open Access Program
- Special Issues Guidelines
- Editorial Process
- Research and Publication Ethics
- Article Processing Charges
- Testimonials
- Preprints.org
- SciProfiles
- Encyclopedia

Article Menu
- Subscribe SciFeed
- Recommended Articles
- Author Biographies
- Google Scholar
- on Google Scholar
- Table of Contents
Find support for a specific problem in the support section of our website.
Please let us know what you think of our products and services.
Visit our dedicated information section to learn more about MDPI.
JSmol Viewer
Impact of iso certifications on corporate financial performance: evidence from istanbul stock exchange-listed manufacturing companies.

1. Introduction
- What is the effect of ISO certification on manufacturing companies’ CFP?
- Which underlying mechanism explains the ISO certification-CFP relationship at best?
- What are the impacts of different ISO certifications on manufacturing companies’ CFP?
2. Literature Review on ISO Certifications and CFP
2.1. scientometric analysis, 2.2. literature review on iso certifications and cfp, 2.3. theoretical background and hypothesis development, 3. estimation framework, 3.1. data set, 3.2. variables, 4. results and discussion, 4.1. impact of number of iso certifications on cfp, 4.2. impact of different iso certifications on cfp, 4.3. robustness, 4.4. theoretical and policy implications, 5. conclusions, institutional review board statement, informed consent statement, data availability statement, conflicts of interest, appendix a. review of studies evaluating the link between iso certification and cfp.
| Arocena, Orcos, and Zouaghi [ ] | 2021 | 2009–2018 | 583 | Multiple Sectors | Multiple Countries | Tons of CO emitted by the firm per unit of output, return on assets (ROA) | ISO 140001 Certification | Company size, environmental awareness of society | Two-step system generalized method of moments | positive significant effect |
| Aslam, Rehman, Naeem, and Taghizadeh-Hesary [ ] | 2022 | 2007–2018 | 237 | Multiple Sectors | USA and Japan | Tobin’s Q | Total carbon emissions in tons | Company size (log total assets), capital expenditure to total assets, research & development (R&D) expenditure to total sales, leverage-total debt to total assets, board size, clean technology-binary variable | Generalized Method of Moments | negative significant effect (The market penalizes companies with high carbon emissions) |
| Chakroun, Salhi, Ben Amar, and Jarboui [ ] | 2019 | 2010–2017 | 311 | Multiple | France | ROA, Return on Equity (ROE), Tobin’s Q and Marris ratio | Sum of the affirmative responses per item/number of sub-items per item regarding ISO 26000 standards | Company size, debt, and firm age | generalized least squares (FGLS) | positive significant effect |
| de Paula, Vélez, Ceballos, and Trujillo [ ] | 2020 | 2014–2016 | 5169 | Multiple Sectors | Colombia | ROA | ISO 140001 Certification | Asset ratio, industry | Random-effects panel regression | positive significant effect |
| Durak Uşar, Aylak, and Kayıkcı [ ] | 2021 | 2010–2018 | 165 | Manufacturing | Türkiye | ROA | ISO 9001 Certification | Company size, leverage, industry, market concentration, market certification concentration, industry, supply chain position | Random Effects Model | positive significant effect |
| Franceschini, Galetto, and Mastrogiacomo [ ] | 2018 | 2008–2010 | 63,400 | Manufacturing | Italy | Synthetising a set of economic/ financial indexes | ISO 9000 certification | Company size, regional development | three-factor ANOVA | negative significant effect |
| Galetto, Franceschini, and Mastrogiacomo [ ] | 2017 | 2008–2010 | 63,400 | Manufacturing | Italy | Synthetising a set of economic/ financial indexes | not certified companies, certified for less than three years, certified for more than three years | Company size, regional development and manufacturing sub-sector. | analysis of variance (ANOVA) and contingency tables | no significant effect |
| Hanjani and Kusumadewi [ ] | 2023 | 2015–2019 | 174 | Multiple Sectors | Indonesia | Environmental performance, financial performance | ISO 140001 Certification and PROPER ranking | Company size | Regression | positive significant effect |
| He, Ren, and Zeng [ ] | 2022 | 2008–2016 | 1325 | Manufacturing | China | Annual operating income (AOI), ROA, Tobin’s Q | ISO 140001 Certification | Company size, ownership, financial leverage, board independence, organizational slack, ISO 9000 certification, Emission trading system | Fixed-effects panel regression | positive significant effect on annual operating income (AOI) and Tobin’s q, but no significant effect on return on assets (ROA) |
| Hernandez-Vivanco, Domingues, Sampaio, Bernardo, and Cruz-Cázares [ ] | 2019 | 2007–2015 | 247 | Multiple Sectors | Portugal | Return on Sales (ROS), Return on Capital Employed (ROCE) and ROA | ISO 9001, ISO 14001 and OHSAS 18001 Certification | Industry dummies, company size, year | Generalized Method of Moments | positive significant effect of ISO 9001, positive significant effect of 140001 when combined with ISO 9001, no significant effect of OHSAS 18001 |
| Iyer, Saranga, and Seshadri [ ] | 2013 | 1993–2006 | 220 | Auto component industry | India | Productivity change calculated with Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA) | ISO 9001 Certification | Timig of certification, age, company size, average inventory, distribution expenses, working capital cycle, capital intensity, proportion of debt | fixed effect, Cobb–Douglas production function-based parametric estimation | positive significant effect |
| Miroshnychenko, Barontini, and Testa [ ] | 2017 | 2002–2014 | 3490 | Multiple Sectors | Multiple Countries | Tobin’s Q and ROE | Pollution Prevention, Green Supply Chain Management, Green product development and ISO 14001 Certification | leverage, sales growth, company size, country, industry and year dummies | OLS regression | negative significant effect |
| Muda and Wahyuni [ ] | 2019 | 2012–2016 | 20 | Manufacturing | Indonesia | Earning Per Share | ISO 140001 Certification and Environmental Performance (PROPER ranking) | N/A | Random-effects panel regression | no significant effect |
| Neves, Reis, Reis, and Dias [ ] | 2023 | 2015–2019 | 33 | Multiple sectors excluding financial companies and sports corporations | Portugal | ROA, ROE, Tobin’s Q, and earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization (EBITDA) Margin | ISO 9001& ISO 14000 Certification | Company size (ln total assets), leverage, Current ratio (ratio of current assets to liabilities), Sustainability report (binary variable), Tangible Fixed Assets, Personnel expenses | Generalized Method of Moments | inconclusive |
| Sampaio, Saraiva, and Rodrigues [ ] | 2011 | 2003–2005 | 207 | Multiple Sectors | Portugal | Sales growth (SG), Productivity (Prod), Operational results over Asset (OR/A), Operational results over Sales (OR/S) | ISO 9001 Certification | N/A | Wilcoxon–Mann–Whitney non-parametric test, t-test | positive significant effect |
| San, Heng, Hwa, and Bee [ ] | 2015 | N/A | 68 | Multiple Sectors | Malaysia | ROA, ROE | ISO 140001 Certification | Company size, ownership | Regression, ANOVA | positive significant effect |
| Soedjatmiko, Tjahjadi, and Soewarno [ ] | 2021 | 2012–2017 | 144 | Manufacturing | Indonesia | ROA, Tobin’s Q | ISO 140001 Certification and PROPER ranking | N/A | Multiple regression | no significant effect |
| Starke, Eunni, Fouto, and de Angelo [ ] | 2012 | 1995–2006 | 44 | Multiple sectors excluding financial companies | Brazil | Sales revenue, cost of goods sold/sales revenue, ROS | ISO 9000 certification | Company size, operating risk, profitability measured by net margin, long-term debt to equity ratio, | the pooling of cutting data with ordinary least squares, the fixed effects and the random effects | positive significant effect |
| Teng, Wu, and Chou [ ] | 2014 | 1996–2008 | 975 | Multiple Sectors | Taiwan | Market value to book value ratio, ROA and ROE | ISO 140001 certification and the duration | Company size, age and the R&D ratio, year dummies | Fixed-effects panel regression | U-shaped relationship |
| Terlaak and King [ ] | 2006 | 1988–1998 | 19713 | Manufacturing | U.S.A | Growth-changes in production volume | ISO 9000 certification, R&D intensity and advertising intensity | Operational performance, industry size, Industry Certification (percentage of certified facilities in each subindustry and year.), Company size, log of the (annual) number of employees, percentage of exports of shipments, year fixed effect | general estimation equations (GEE) model | positive significant effect |
| Wang and Mao [ ] | 2020 | 2008–2016 | 1751 | Manufacturing | China | ROE, ratio of operating cost to sales revenue, the ratio of marketing and sales expenses to sales revenue, ratio of general and administrative expenses to sales revenue | ISO 140001 Certification | Ratio of the number of ISO 14001-certified companies to the number of listed companies, registered capital, age, number of employees, liability/asset ratio, gross revenue, ownership, sub- industry | Sobel test, PROCESS procedure analysis and causal mediation analysis | no significant effect |
| Wang and Liu [ ] | 2023 | 2009–2019 | 2037 | Multiple sectors | China | ROE, ROA, earnings before interests and taxes (EBIT)/asset, sustainable growth rate (SGR), sales growth, Tobin’s Q, operating efficiency and operating cycle | ISO 9001 and ISO 14001 certification, impact of three integration strategies | 3-levels: firm characteristics (age, natural logarithm of total assets to measure firm size, strategic orientation, cost-leadership and differentiation, slack resources using the three variables of debt to equity, debt to assets and working capital to assets), industry, institutional development in various regions | Mann–Whitney non-parametric test-difference between certified and non certificed firms, cross-sectional time-series feasible generalized least squares (FGLS) regression model | significant effect: simultaneous integration strategy has a positive impact, whereas sequential integration strategy has negative impact |
| Zayas-Mateo and Martínez-Lorente [ ] | 2021 | 2004–2012 | 333 | Manufacturing and Services | Spain | Net sales and operating income | ISO 9001 Certification | N/A | Mann–Whitney non-parametric test | Positive significant effect, results more profound for manufacturing companies compared to service companies |
- Le, D.-N.; Nguyen, V.-H. Does Quality Certification or Product Diversification Improve the Performance of Small and Medium Enterprises? Sustainability 2024 , 16 , 2023. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Pacheco, L.; Lobo, C.; Maldonado, I. Do ISO Certifications Enhance Internationalization? The Case of Portuguese Industrial SMEs. Sustainability 2022 , 14 , 1335. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Zimon, D.; Madzik, P.; Sroufe, R. The Influence of ISO 9001 & ISO 14001 on Sustainable Supply Chain Management in the Textile Industry. Sustainability 2020 , 12 , 4282. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- ISO 50001:2018 ; Energy Management Systems—Requirements with Guidance for Use—Amendment 1. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018.
- Uriarte-Romero, R.; Gil-Samaniego, M.; Valenzuela-Mondaca, E.; Ceballos-Corral, J. Methodology for the Successful Integration of an Energy Management System to an Operational Environmental System. Sustainability 2017 , 9 , 1304. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Viswanathan, K.; Johnson, M.S.; Toffel, M.W. Do safety management system standards indicate safer operations? Evidence from the OHSAS 18001 occupational health and safety standard. Saf. Sci. 2024 , 171 , 106383. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Lo, C.K.Y.; Pagell, M.; Fan, D.; Wiengarten, F.; Yeung, A.C.L. OHSAS 18001 certification and operating performance: The role of complexity and coupling. J. Oper. Manag. 2014 , 32 , 268–280. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- ISO/IEC 27001:2022 ; Information Security, Cybersecurity and Privacy Protection—Information Security Management Systems —Requirements—Amendment 1. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022.
- Podrecca, M.; Culot, G.; Nassimbeni, G.; Sartor, M. Information security and value creation: The performance implications of ISO/IEC 27001. Comput. Ind. 2022 , 142 , 103744. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Wu, W. Research on the Impact of Information Security Certification and Concealment on Financial Performance: Impact of ISO 27001 and Concealment on Performance. J. Glob. Inf. Manag. 2022 , 30 , 1–16. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Preston, L.E.; O’Bannon, D.P. The Corporate Social-Financial Performance Relationship: A Typology and Analysis. Bus. Soc. 1997 , 36 , 419–429. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Mazzi, A.; Toniolo, S.; Manzardo, A.; Ren, J.; Scipioni, A. Exploring the Direction on the Environmental and Business Performance Relationship at the Firm Level. Lessons from a Literature Review. Sustainability 2016 , 8 , 1200. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Heras-Saizarbitoria, I.; Molina-Azorín, J.F.; Dick, G.P.M. ISO 14001 certification and financial performance: Selection-effect versus treatment-effect. J. Clean. Prod. 2011 , 19 , 1–12. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- ISO 9001:2015 ; Quality Management Systems—Requirements—Amendment 1. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015.
- ISO 14001:2015 ; Environmental Management Systems—Requirements with Guidance for Use—Amendment 1. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2015.
- ISO 45001:2018 ; Occupational Health and Safety Management Systems—Requirements with Guidance for Use—Amendment 1. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2018.
- ISO 26000:2010 ; Guidance on Social Responsibility. International Organization for Standardization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2010.
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. Syst. Rev. 2021 , 10 , 89. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ] [ PubMed ]
- Sampaio, P.; Saraiva, P.; Rodrigues, A.G. The economic impact of quality management systems in Portuguese certified companies: Empirical evidence. Int. J. Qual. Reliab. Manag. 2011 , 28 , 929–950. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Iyer, A.; Saranga, H.; Seshadri, S. Effect of Quality Management Systems and Total Quality Management on Productivity Before and After: Empirical Evidence from the Indian Auto Component Industry. Prod. Oper. Manag. 2013 , 22 , 283–301. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Durak Uşar, D.; Aylak, B.L.; Kayıkcı, Y. The Effect of Supply Chain Tier on the ISO 9001 Quality Management Certification and Financial Performance Relationship: The Case of Turkey. J. Yaşar Univ. 2021 , 16 , 1454–1479. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Zayas-Mateo, R.A.; Martínez-Lorente, A.R. ISO 9001: A vaccine for time of crisis. Meas. Bus. Excell. 2021 , 25 , 287–299. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- San, O.T.; Heng, T.B.; Hwa, G.H.; Bee, T.S. ISO14001 Certification and Financial Performance of Companies. Asia-Pac. Manag. Account. J. 2015 , 10 , 58–77. [ Google Scholar ]
- de Paula, L.B.; Vélez, S.L.P.; Ceballos, H.V.; Trujillo, V.M.O. Exploring the Link between Environmental Practices and Financial Performance: An Empirical Study. J. Environ. Sci. Manag. 2020 , 23 , 29–39. [ Google Scholar ]
- Wang, J.; Mao, Y.S. Pains and gains of environmental management system certification for the sustainable development of manufacturing companies: Heterogeneous effects of industry peer learning. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2020 , 29 , 2092–2109. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Hanjani, A.; Kusumadewi, R.K. Environmental performance and financial performance: Empirical evidence from Indonesian companies. Corp. Soc. Responsib. Environ. Manag. 2023 , 30 , 1508–1513. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Chakroun, S.; Salhi, B.; Ben Amar, A.; Jarboui, A. The impact of ISO 26000 social responsibility standard adoption on firm financial performance Evidence from France. Manag. Res. Rev. 2019 , 43 , 545–571. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Neves, M.E.D.; Reis, S.; Reis, P.; Dias, A.G. Impact of ISO 14001 and ISO 9001 adoption on corporate performance: Evidence on a bank-based system. Int. J. Product. Perform. Manag. 2023 , 73 , 1641–1667. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Miroshnychenko, I.; Barontini, R.; Testa, F. Green practices and financial performance: A global outlook. J. Clean. Prod. 2017 , 147 , 340–351. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Teng, M.J.; Wu, S.Y.; Chou, S.J. Environmental Commitment and Economic Performance—Short-Term Pain for Long-Term Gain. Environ. Policy Gov. 2014 , 24 , 16–27. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Galetto, M.; Franceschini, F.; Mastrogiacomo, L. ISO 9001 certification and corporate performance of Italian companies. Int. J. Qual. Reliab. Manag. 2017 , 34 , 231–250. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Wang, J.G.; Liu, F.H. Examining the link between integrated management systems and firm performance: Do the integration strategies matter? Int. J. Oper. Prod. Manag. 2023 , 43 , 332–372. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Hernandez-Vivanco, A.; Domingues, P.; Sampaio, P.; Bernardo, M.; Cruz-Cázares, C. Do multiple certifications leverage firm performance? A dynamic approach. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2019 , 218 , 386–399. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Arocena, P.; Orcos, R.; Zouaghi, F. The impact of ISO 14001 on firm environmental and economic performance: The moderating role of size and environmental awareness. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2021 , 30 , 955–967. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Starke, F.; Eunni, R.V.; Fouto, N.M.M.D.; de Angelo, C.F. Impact of ISO 9000 certification on firm performance: Evidence from Brazil. Manag. Res. Rev. 2012 , 35 , 974–997. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Muda, I.; Wahyuni, E. An Analysis on the Effect of Environmental Performance and the Implementation of Environmental Management System (ISO 14001) on the Issuer Financial Performance. Qual.-Access Success 2019 , 20 , 113–117. [ Google Scholar ]
- Soedjatmiko, S.; Tjahjadi, B.; Soewarno, N. Do Environmental Performance and Environmental Management Have a Direct Effect on Firm Value? J. Asian Financ. Econ. Bus. 2021 , 8 , 687–696. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Aslam, S.; Rehman, R.U.; Naeem, M.A.; Taghizadeh-Hesary, F. Nexus of Corporate Environmental Strategy, Environmental Performance, and Financial Performance. Singap. Econ. Rev. 2022 , 1–21. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Franceschini, F.; Galetto, M.; Mastrogiacomo, L. ISO 9001 certification and failure risk: Any relationship? Total Qual. Manag. Bus. Excell. 2018 , 29 , 1279–1293. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- He, W.; Shen, R. ISO 14001 Certification and Corporate Technological Innovation: Evidence from Chinese Firms. J. Bus. Ethics 2019 , 158 , 97–117. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Baltagi, B.H. Econometric Analysis of Panel Data: Third Edition ; Wiley Publisher: Chichester, West Sussex, UK, 2005; pp. 135–168. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bansal, P.; Hunter, T. Strategic explanations for the early adoption of ISO 14001. J. Bus. Ethics 2003 , 46 , 289–299. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Terlaak, A.; King, A.A. The effect of certification with the ISO 9000 Quality Management Standard: A signaling approach. J. Econ. Behav. Organ. 2006 , 60 , 579–602. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Zhang, Y.; Ruan, H.; Tang, G.; Tong, L. Power of sustainable development: Does environmental management system certification affect a firm’s access to finance? Bus. Strategy Environ. 2021 , 30 , 3772–3788. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Russo MVFout, P.A. A resource-based perspective on corporate environmental performance and profitability. Acad. Manag. J. 1997 , 40 , 534–559. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- He, D.; Ren, S.; Zeng, H. Environmental labeling certification and firm environmental and financial performance: A resource management perspective. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2022 , 31 , 751–767. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Russo, M.V. Explaining the impact of ISO 14001 on emission performance: A dynamic. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2009 , 18 , 307–319. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Nishitani, K. An empirical study of the initial adoption of ISO 14001 in Japanese manufacturing firms. Ecol. Econ. 2009 , 68 , 669–679. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Hernandez-Vivanco, A.; Bernardo, M. Are certified firms more prone to eco-product innovation? The moderating role of slack resources. J. Clean. Prod. 2022 , 377 , 134364. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Lafuente, E.; Bayo-Moriones, A.; Garcia-Cestona, M. ISO-9000 Certification and Ownership Structure: Effects upon Firm Performance. Br. J. Manag. 2009 , 21 , 649–665. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Donaldson, L. The Contingency Theory of Organizational Design: Challenges and Opportunities. In Organization Design. Information and Organization Design Series ; Burton, R.M., Håkonsson, D.D., Eriksen, B., Snow, C.C., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2006; pp. 19–40. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Sea-Jin, C.; van Witteloostuijn, A.; Eden, L. From the Editors: Common method variance in international business research. J. Int. Bus. Stud. 2010 , 41 , 178–184. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Corbett, C.J.; Montes-Sancho, M.J.; Kirsch, D.A. The financial impact of ISO 9000 certification: An empirical analysis. Manag. Sci. 2005 , 51 , 1046–1059. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Naveh, E.; Marcus, A. Achieving competitive advantage through implementing a replicable management standard: Installing and using ISO 9000. J. Oper. Manag. 2005 , 24 , 1–26. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Lo, C.K.Y.; Yeung, A.C.L.; Cheng, T.C.E. The impact of environmental management systems on financial performance in fashion and textiles industries. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2012 , 135 , 561–567. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Hansen, L.P. Large sample properties of generalized method of moment estimators. Econometrica 1982 , 50 , 1029–1054. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Arellano, M.; Bond, S. Some Tests of Specification for Panel Data: Monte Carlo Evidence and an Application to Employment Equations. Rev. Econ. Stud. 1991 , 58 , 277–297. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Driscoll, J.C.; Kraay, A.C. Consistent covariance matrix estimation with spatially dependent panel data. Rev. Econ. Stat. 1998 , 80 , 549–560. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Hoechle, D. Robust standard errors for panel regressions with cross-sectional dependence. Stata J. 2007 , 7 , 281–312. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Chen, Y.-Y.; Wu, L.; Zhai, Q.-G. Does ISO 9000 Certification Benefit Service Firms? Sustainability 2019 , 11 , 5886. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Goedhuys, M.; Sleuwaegen, L. The Impact of International Standards Certification on the Performance of Firms in Less Developed Countries. World Dev. 2013 , 47 , 87–101. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
- Terziovski, M.; Guerrero, J. ISO 9000 quality system certification and its impact on product and process innovation performance. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2014 , 158 , 197–207. [ Google Scholar ] [ CrossRef ]
Click here to enlarge figure
| Data Base: ISI Web of Science (WoS) | Reports Assessed for Eligibility | Reports Excluded for | Studies Included in Review | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Literature Review | Qualitative Studies & Small Sample Size | Survey & Cross Sectional Data | Event Study | Statistical Matching & Difference-In Difference Model | |||
| ISO 9001 | 82 | 4 | 9 | 41 | 6 | 11 | 11 |
| ISO 14000 | 60 | 3 | 10 | 14 | 9 | 6 | 18 |
| ISO 50001 | 6 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| ISO 45001/OHSAS 18001 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| ISO 26000 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| ISO 27001 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 |
| Multiple Certification | 17 | 4 | 2 | 6 | 0 | 2 | 3 |
| Total | 173 | 11 | 25 | 62 | 19 | 21 | 35 |
| | |||||||
| | |||||||
| ISO 9001 | 4 | 2 | 1 | 1 | |||
| ISO 14000 | 2 | 1 | 1 | ||||
| ISO 50001 | 0 | ||||||
| ISO 45001/OHSAS 18001 | 0 | ||||||
| ISO 26000 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| ISO 27001 | 1 | 1 | |||||
| Multiple Certification | 2 | 2 | |||||
| Total | 10 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 2 | ||
| Sectors | SIC Codes | Supply Chain Position | n = 146 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OEM | Tier 1 | Tier 2 | Total | % | ||
| Food and Kindred Products | 20, 21 | 21 | 1 | 4 | 26 | 17.81% |
| Textile Mill Products, Apparel and other Finished Products, Leather and Leather Products | 22, 23, 31 | 9 | 4 | 8 | 21 | 14.38% |
| Lumber and Wood Products, Furniture and Fixtures | 24, 25 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 2.05% |
| Paper Allied Products, Printing, Publishing, and Allied Industries | 26, 27 | 4 | 4 | 3 | 11 | 7.53% |
| Chemicals and Allied Products, Petroleum Refining and Related Industries, Rubber and Miscellaneous Plastic Products | 28, 29, 30 | 14 | 2 | 8 | 24 | 16.44% |
| Stone, Slay, Glass and Concrete Products | 32 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 13 | 8.90% |
| Primary Metal Industries | 33 | 0 | 3 | 7 | 10 | 6.85% |
| Fabricated Metal Products, Industrial and Commercial Machinery, Electronic and other Electrical Equipment, Transportation Equipment | 34, 35, 36, 37, 38 | 17 | 12 | 6 | 35 | 23.97% |
| Miscellaneous Manufacturing Industries | 39 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 2.05% |
| Total | 74 | 31 | 41 | 146 | 100% | |
| Observations | Mean | Std. Dev. | Min | Max | Skewness | Kurtosis | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total Assets (Million TL) | 1897 | 3079.635 | 11,608.39 | 1.134 | 174,893.6 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| Stakeholder Equity (Million TL) | 1898 | 1344.398 | 5595.906 | −390.7246 | 118,662.2 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| Revenue (Million TL) | 1894 | 2837.542 | 14,836.77 | 0 | 481,764.7 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| Net Income (Million TL) | 1894 | 256.8924 | 1478.861 | −2422.925 | 41,260.57 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| Cost of Goods Sold (GOGS) (Million TL) | 1872 | 2239.435 | 12,530.75 | 0 | 418,987.7 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| Marketvalue (Million TL) | 1809 | 2799.828 | 11,507.43 | 2.368651 | 248,999.6 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| Number of Employees (Thousand) | 1882 | 2.463083 | 30.86817 | 0.001 | 1330 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| Long Term Debt (Million TL) | 1898 | 439.3414 | 1900.053 | 0 | 28,324.38 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| R&D Expenditure (Million TL) | 1888 | 14.93951 | 81.91762 | 0 | 1532.88 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| Age by 2022 | 146 | 50.26 | 15.23 | 12 | 95 | 0.7945 | 0.2510 |
| R&D Expenditure/revenue | 1873 | 0.004794 | 0.018231 | 0 | 0.303121 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| GOGS/Revenue | 1855 | 0.7782437 | 0.2473318 | 0 | 4.509441 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| ROA | 1893 | 0.04684 | 0.120191 | −2.05094 | 1.57487 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| ROE | 1894 | 0.045196 | 1.4451 | −48.9169 | 24.1917 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| Tobin’s Q | 1782 | 1.293835 | 2.710669 | 0.0574678 | 61.20941 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| Leverage (Long Term Dept/Total Asset) | 1897 | 0.098771 | 0.140826 | 0 | 3.103579 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| Age (ln age) | 1898 | 3.731494 | 0.4536431 | 0 | 4.564348 | 0.0000 | 0.0000 |
| Model 1.1 (R&D Intensity) | Model 1.2 (GOGS/Revenue) | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coefficient | Robust Std. Err. | Z | p > |z| | Coefficient | Robust Std. Err. | z | p >|z| | |
| dependent variable.lag | 0.9164655 | 0.0913792 | 10.03 | 0.000 | −1.013724 | 3.224766 | −0.31 | 0.753 |
| Number of certificates | −0.0000871 | 0.0001377 | −0.63 | 0.527 | −0.0712818 | 0.1621543 | −0.44 | 0.660 |
| Leverage | 0.0004668 | 0.0006543 | 0.71 | 0.476 | −0.3885818 | 1.118042 | −0.35 | 0.728 |
| Number of employees | 6.27 × 10 | 0.0000247 | 0.25 | 0.799 | −0.0090246 | 0.0228205 | −0.40 | 0.693 |
| Lnage | 0.0000766 | 0.0002531 | 0.30 | 0.762 | 0.0361254 | 0.2793436 | 0.13 | 0.897 |
| tier_1 | −0.0000915 | 0.000503 | −0.18 | 0.856 | −0.3283477 | 0.6719115 | −0.49 | 0.625 |
| tier_2 | −0.0001806 | 0.0004711 | −0.38 | 0.701 | −0.2583642 | 0.6512045 | −0.40 | 0.692 |
| _cons | 0.000084 | 0.0010413 | 0.08 | 0.936 | 1.523519 | 2.694314 | 0.57 | 0.572 |
| Number of Observations | 1554 | 1556 | ||||||
| Hansen J statistic | 0.886, Chi-sq(1) p-val = 0.6421 | 0.793, Chi-sq(1) p-val = 0.6728 | ||||||
| AR (1) p value | z = −1.09 Pr > z = 0.2752 | z = −0.91 Pr > z = 0.3611 | ||||||
| AR (2) p value | z = −1.43 Pr > z = 0.1516 | z = −0.91 Pr > z = 0.3611 | ||||||
| > |z| | >|z| | |||||||
| dependent variable.lag | 0.5520088 | 0.0817362 | 6.75 | 0.000 | 0.6076748 | 0.0922316 | 6.59 | 0.000 |
| Number of certificates | 0.0115833 | 0.0023409 | 4.95 | 0.000 | 0.1086216 | 0.0401953 | 2.70 | 0.007 |
| Leverage | −0.1118339 | 0.0317571 | −3.52 | 0.000 | −1.316951 | 0.6421696 | −2.05 | 0.040 |
| Number of employees | −0.0012794 | 0.0003529 | −3.63 | 0.000 | −0.0426905 | 0.0096442 | −4.43 | 0.000 |
| Lnage | 0.0144103 | 0.0065979 | 2.18 | 0.029 | 0.4155525 | 0.1869997 | 2.22 | 0.026 |
| tier_1 | 0.0181414 | 0.0072843 | 2.49 | 0.013 | 0.2380513 | 0.1456362 | 1.63 | 0.102 |
| tier_2 | 0.0074475 | 0.0065956 | 1.13 | 0.259 | 0.1885341 | 0.111777 | 1.69 | 0.092 |
| _cons | −0.0411942 | 0.0292477 | −1.41 | 0.159 | −0.9932993 | 0.6480631 | −1.53 | 0.125 |
| Number of Observations | 1578 | 1504 | ||||||
| Hansen J statistic | 4.681, Chi-sq(1) p-val = 0.0963 | 2.083, Chi-sq(1) p-val = 0.3530 | ||||||
| AR (1) p value | z = −1.40 Pr > z = 0.1629 | z = −2.29 Pr > z = 0.0221 | ||||||
| AR (2) p value | z = 1.81 Pr > z = 0.0706 | z = 1.77 Pr > z = 0.0766 | ||||||
| Model 2.1 | Model 2.2 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coefficient | Robust Std. Err. | Z | p > |z| | Coefficient | Robust Std. Err. | Z | p > |z| | |
| roa.lag | 0.5607376 | 0.0809877 | 6.92 | 0.000 | 0.5614217 | 0.0815476 | 6.88 | 0.000 |
| ISO 9001 | 0.0154015 | 0.0062461 | 2.47 | 0.014 | 0.0153144 | 0.006311 | 2.43 | 0.015 |
| ISO 14001 | 0.0133234 | 0.0082635 | 1.61 | 0.107 | 0.0161586 | 0.0083233 | 1.94 | 0.052 |
| ISO 45001 | 0.0076847 | 0.007421 | 1.04 | 0.300 | ||||
| ISO 50001 | 0.0100436 | 0.0070965 | 1.42 | 0.157 | 0.0118694 | 0.0067144 | 1.77 | 0.077 |
| ISO 27001 | 0.0113846 | 0.0074897 | 1.52 | 0.129 | −0.1099235 | 0.0313568 | −3.51 | 0.000 |
| Leverage | −0.111983 | 0.0308079 | −3.63 | 0.000 | −0.0012523 | 0.000356 | −3.52 | 0.000 |
| Number of employees | −0.0012635 | 0.0003541 | −3.57 | 0.000 | −0.0012523 | 0.0003561 | −3.52 | 0.000 |
| lnage | 0.0144944 | 0.00645 | 2.25 | 0.025 | 0.0147369 | 0.006543 | 2.25 | 0.024 |
| tier_1 | 0.0170392 | 0.0071405 | 2.39 | 0.017 | 0.0165838 | 0.0073803 | 2.25 | 0.025 |
| tier_2 | 0.0062727 | 0.0068192 | 0.92 | 0.358 | 0.0067138 | 0.0068101 | 0.99 | 0.324 |
| Constant | −0.0395708 | 0.0287254 | −1.38 | 0.168 | −0.0386828 | 0.0290922 | −1.33 | 0.184 |
| industry | industry effects are included in the estimations | industry effects are included in the estimations | ||||||
| Number of Observations | 1437 | 1437 | ||||||
| Hansen J statistic | 9.796, Chi-sq(10) p-val = 0.4585 | 9.652, Chi-sq(8) p-val = 0.2903 | ||||||
| AR (1) p value | z = −1.59 Pr > z = 0.1123 | z = −1.65 Pr > z = 0.0983 | ||||||
| AR (2) p value | z = 1.74 Pr > z = 0.0815 | z = 1.74 Pr > z = 0.0824 | ||||||
| Model 2.3 | Model 2.4 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coefficient | Robust Std. Err. | Z | p > |z| | Coefficient | Robust Std. Err. | z | p > |z| | |
| TobinsQ.lag | 0.5652461 | 0.0853422 | 6.62 | 0.000 | 0.536038 | 0.0888145 | 6.04 | 0.000 |
| ISO 9001 | 0.1822074 | 0.0891764 | 2.04 | 0.041 | 0.1877296 | 0.0888575 | 2.11 | 0.035 |
| ISO 14001 | −0.0800243 | 0.1412061 | −0.57 | 0.571 | −0.1542967 | 0.144231 | −1.07 | 0.285 |
| ISO 45001 | 0.0856484 | 0.1369664 | 0.63 | 0.532 | ||||
| ISO 50001 | −0.1126909 | 0.0987593 | −1.14 | 0.254 | −0.1234731 | 0.1009166 | −1.22 | 0.221 |
| ISO 27001 | 0.1606696 | 0.1117754 | 1.44 | 0.151 | 0.198241 | 0.1080534 | 1.83 | 0.067 |
| Leverage | −1.222295 | 0.5838707 | −2.09 | 0.036 | −1.32432 | 0.5872056 | −2.26 | 0.024 |
| Number of employees | −0.0260502 | 0.0059737 | −4.36 | 0.000 | −0.0305983 | 0.0068743 | −4.45 | 0.000 |
| lnage | 0.34378 | 0.1348504 | 2.55 | 0.011 | 0.6563635 | 0.2835178 | 2.32 | 0.021 |
| tier_1 | 0.2223122 | 0.1370581 | 1.62 | 0.105 | 0.2295241 | 0.1379038 | 1.66 | 0.096 |
| tier_2 | 0.2463476 | 0.1146058 | 2.15 | 0.032 | 0.282484 | 0.115056 | 2.46 | 0.014 |
| Constant | −0.6307342 | 0.4730502 | −1.33 | 0.182 | −1.624504 | 0.942284 | −1.72 | 0.085 |
| Industry | industry effects are included in the estimations | industry effects are included in the estimations | ||||||
| Number of Observations | 1378 | 1378 | ||||||
| Hansen J statistic | 14.958, Chi-sq(10) p-val = 0.1336 | 13.484, Chi-sq(8) p-val =0.0963 | ||||||
| AR (1) p value | z = −1.06 Pr > z = 0.2898 | z = −0.70 Pr > z = 0.4833 | ||||||
| AR (2) p value | z = 1.79 Pr > z = 0.0733 | z = 1.85 Pr > z = 0.0646 | ||||||
| Model 1.1 (R&D Intensity) | Model 1.2 (GOGS/Revenue) | Model 1.3 (ROA) | Model 1.4 (Tobins’ Q) | Model 2.1 (ROA) | Model 2.3 (Tobins’ Q) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of certificates | −0.0000673 | −0.3389804 | 0.0099449 *** | 0.0634517 | ||
| ISO 9001 | 0.0090738 * | 0.226618 ** | ||||
| ISO 14001 | 0.0150345 *** | −0.1237565 | ||||
| ISO 45001 | 0.0048694 | 0.3384095 | ||||
| ISO 50001 | 0.0061371 * | −0.2619176 | ||||
| ISO 27001 | 0.0166118 *** | 0.1724123 | ||||
| dependent variable.lag | 0.8505042 *** | −6.408547 | 0.5695793 *** | 0.5929838 *** | 0.569488 *** | 0.5865831 *** |
| Leverage | 0.0001237 | −1.703022 | −0.105576 *** | −1.405957 *** | −0.1099927 *** | −1.352853 *** |
| Number of employees | 0.0000388 | −0.0434484 | −0.001071 | −0.0405156 *** | −0.0009245 | −0.0339429 *** |
| lnage | −0.0000135 | 0.2097061 | 0.0143774 ** | 0.690438 * | 0.0144684 ** | 0.6287225 * |
| tier_1 | 0.0003776 | −1.491006 | 0.0119395 * | 0.297591 ** | 0.0131486 ** | 0.2892051 ** |
| tier_2 | −0.0001857 | −1.334499 | 0.0037172 | 0.2427555 ** | 0.0052754 ** | 0.2744535 *** |
| Constant | 0.0004785 | 5.536562 | −0.0348519 | −1.846177 | −0.032749 | −1.70171 |
| industry | industry effects are included in all estimations | |||||
| Number of Observations | 1559 | 1561 | 1583 | 1509 | 1583 | 1509 |
| Hypotheses | Findings |
|---|---|
| H1: According to signaling theory, ISO certification leads to improved accounting-based financial performance. | Supported |
| H2: Based on the organizational legitimacy perspective, ISO certification leads to improved market-based financial performance. | partially supported |
| H3: According to resource-based view, ISO certification leads to improved operational performance. | not supported |
| H4: According to dynamic capabilities theory, ISO certification leads to improved R&D performance. | not supported |
| H5: According to slack resources theory, companies with slack resources are more likely to adopt ISO certification. | Supported |
| H6: Companies with certain characteristics such as size and age are more likely to acquire ISO certification. | Supported |
| H7: According to the contingency theory, subsectors influence the ISO certification-CFP relationship. | not supported |
| H8: Different ISO certifications have unique impacts on CFP | Supported |
| The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
Share and Cite
Durak Uşar, D. Impact of ISO Certifications on Corporate Financial Performance: Evidence from Istanbul Stock Exchange-Listed Manufacturing Companies. Sustainability 2024 , 16 , 7021. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16167021
Durak Uşar D. Impact of ISO Certifications on Corporate Financial Performance: Evidence from Istanbul Stock Exchange-Listed Manufacturing Companies. Sustainability . 2024; 16(16):7021. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16167021
Durak Uşar, Damla. 2024. "Impact of ISO Certifications on Corporate Financial Performance: Evidence from Istanbul Stock Exchange-Listed Manufacturing Companies" Sustainability 16, no. 16: 7021. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16167021
Article Metrics
Article access statistics, further information, mdpi initiatives, follow mdpi.

Subscribe to receive issue release notifications and newsletters from MDPI journals

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Many companies make risk assessment and treatment too difficult by defining the wrong ISO 27001 risk assessment methodology and process (or by not defining the methodology at all). ... Example of risk assessment In the table below, you'll see an example of a simple risk assessment using an asset-based approach. Asset: Threat: Vulnerability:
A risk assessment is a requirement for the ISO 27001 standard. If you want to be ISO 27001 certified, you'll need to: Identify the risks your organization faces. Determine the probability of each risk actually occurring. Estimate the potential impact on your business. A risk treatment plan involves deciding how you will respond to each risk ...
The ISO 27001 risk assessment process usually involves the following steps: 1. Identify the information assets to be assessed. 2. Identify potential threats and vulnerabilities. 3. Determine the likelihood and impact of each risk. 4. Evaluate the risks and prioritise them based on their likelihood and impact.
Explore ISO 27001 Hub. Drata is a security and compliance automation platform that continuously monitors and collects evidence of a company's security controls, while streamlining workflows to ensure audit-readiness. Conducting an effective ISO 27001 risk assessment is fundamental to achieving compliance.
ISO 27001 Risk Assessment Examples. The risks vary depending on the industry and other factors. However, here is what a risk assessment table looks like in general. ... A comprehensive risk management framework that describes all steps and relevant methods required to be carried out in terms of the risk assessment process. These include asset ...
3. At least annually. An ISO 27001 risk assessment really should be completed at least annually and recorded. It is a formal step but allows you to assess what, if anything has changed as well as what, if anything needs addressing. Budgets and resources may be required and it allows the effective planning and control.
To simplify Risk Management for small organisations, consider the following recommendations: a) Choose the right framework: It is essential that you include all the five essential components that are required by ISO 27001. b) Select the appropriate tool: Seek software or tools that align with your simplified approach.
Risk assessments can be daunting, but we've simplified the ISO 27001 risk assessment process into seven steps: 1. Define your risk assessment methodology. There is no set ISO 27001 risk assessment procedure. Instead, you should tailor your approach to the needs of your organisation. To do this, you need to review certain things.
ISO 27001 employs a top-down, technology-agnostic, risk-based approach. The standard specifies six planning procedures: Defining a security policy. Defining the scope of ISMS. Conducting risk assessments. Managing evaluated risks. Selecting control goals for implementation. Preparing the statement of applicability.
As you develop your risk assessment methodology, keep your documentation in an accessible place. ... Six steps to conducting an ISO 27001 risk assessment. ... Then create an extensive list of potential threats; some examples could be an employee's laptop being stolen or an office visitor accessing an employee's password. ...
Here are five steps to help you on your way: Establish a risk management framework. Identify risks. Analyse risks. Evaluate risks. Select risk responses. We'll also go over key ISO 27001 documentation: the SoA (Statement of Applicability) and the RTP (risk treatment plan). 1. Establish a risk management framework.
Start your effective ISO 27001 risk assessment by defining a methodology that aligns with your organization's needs. Choose between a qualitative or quantitative approach: Qualitative Method: Dive into diverse scenarios and address hypothetical inquiries to identify risks. Quantitative Method: Use data and figures to establish risk levels ...
ISO 27001 does not prescribe a specific risk assessment methodology. Choosing the correct methodology for your organisation is essential in order to define the rules by which you will perform the risk assessment. The methodology needs to address four issues: baseline security criteria, risk scale, risk appetite, and a scenario-based or asset ...
ISO 27001 Risk assessment and treatment. V2.0 May 2022. O 27001 risk assessment and treatment This document is intended to provide a high level overview of the concept of risk assessmen. and treatment in an ISO 27001 context. As ISO 27001 is being used globally, there are significant preparatory resources which are easily acces.
Key Steps in Conducting a Risk Assessment. Establish the Context: Begin by defining the scope of your risk assessment. Identify the assets, systems, processes, and stakeholders relevant to your ISMS. This provides the foundation for a targeted and effective assessment. Identify Assets:Catalogue all the assets within your scope, tangible ...
The ISO 27001 risk assessment methodology is crucial for organizations to identify, analyze, and mitigate potential risks. By following a systematic approach, risks can be effectively managed to ensure the security of information assets. This methodology includes risk identification, analysis, and the creation of a risk treatment plan.
Step 3 - Risk assessment. Ranking risks based on their consequences and likelihood would help your organisation deploy its resources effectively and reduce redundancy. Through this, you can determine which hazards need to be prioritised and controlled immediately to prevent a possible security breach. Overall Risk = Likelihood x Consequences.
The Components of the ISO 27001 Risk Assessment Methodology. ... You might, for example, choose to address all risks that you have rated as "high" before any others. In short, a strong ISO risk assessment methodology is the first step of an entire risk management structure. It provides your organisation with a qualitative or quantitative ...
A risk assessment process that meets the requirements of ISO 27001 should have seven steps: 1. Establish an ISO 27001 risk assessment framework. This is the first stage in your ISO 27001 risk assessment journey. It's important for your organisation to handle risk assessment consistently.
The assessment and management of information security risks is at the core of ISO 27001. Section 6.1.2 of the ISO/IEC 27001 standard states the ISO 27001 risk assessment procedure must: Establish and maintain specific information security risk criteria. Ensure that repeated risk assessments "produce consistent, valid and comparable results".
Here are the key steps to conduct an ISO 27001 risk assessment: Establish the Context: Begin by defining the scope of your risk assessment. Identify the assets to be protected, the boundaries of your ISMS, and the objectives you want to achieve. Understanding the context is essential for a focused assessment. Identify Information Assets: Create ...
The ISO 27001 implementation and review processes revolve around risk assessments. This is where organisations identify the threats to their information security and outline which of the Standard's controls they must implement.. The process begins by defining a methodology, i.e. a set of rules defining how to calculate risks. Some organisations ignore this step, going straight into the ...
Yes. The documentation template may be used for ISO 27001 and ISO 22301 certification audit purposes. Well-defined instructions Document templates contain an average of twenty comments each, and offer clear guidance for filling them out. Designed with your company in mind The template was created for small and medium-sized businesses.
The literature has reached a consensus that ISO standardization enhances the Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) performance of companies, which in turn has a positive effect on corporate financial performance (CFP). There is less understanding in terms of the effect of different certifications and underlying mechanisms between the effect of the ISO certification on the CFP. The ...