- The 25 Most Influential Psychological Experiments in History

While each year thousands and thousands of studies are completed in the many specialty areas of psychology, there are a handful that, over the years, have had a lasting impact in the psychological community as a whole. Some of these were dutifully conducted, keeping within the confines of ethical and practical guidelines. Others pushed the boundaries of human behavior during their psychological experiments and created controversies that still linger to this day. And still others were not designed to be true psychological experiments, but ended up as beacons to the psychological community in proving or disproving theories.
This is a list of the 25 most influential psychological experiments still being taught to psychology students of today.

1. A Class Divided
Study conducted by: jane elliott.
Study Conducted in 1968 in an Iowa classroom

Experiment Details: Jane Elliott’s famous experiment was inspired by the assassination of Dr. Martin Luther King Jr. and the inspirational life that he led. The third grade teacher developed an exercise, or better yet, a psychological experiment, to help her Caucasian students understand the effects of racism and prejudice.
Elliott divided her class into two separate groups: blue-eyed students and brown-eyed students. On the first day, she labeled the blue-eyed group as the superior group and from that point forward they had extra privileges, leaving the brown-eyed children to represent the minority group. She discouraged the groups from interacting and singled out individual students to stress the negative characteristics of the children in the minority group. What this exercise showed was that the children’s behavior changed almost instantaneously. The group of blue-eyed students performed better academically and even began bullying their brown-eyed classmates. The brown-eyed group experienced lower self-confidence and worse academic performance. The next day, she reversed the roles of the two groups and the blue-eyed students became the minority group.
At the end of the experiment, the children were so relieved that they were reported to have embraced one another and agreed that people should not be judged based on outward appearances. This exercise has since been repeated many times with similar outcomes.
For more information click here
2. Asch Conformity Study
Study conducted by: dr. solomon asch.
Study Conducted in 1951 at Swarthmore College

Experiment Details: Dr. Solomon Asch conducted a groundbreaking study that was designed to evaluate a person’s likelihood to conform to a standard when there is pressure to do so.
A group of participants were shown pictures with lines of various lengths and were then asked a simple question: Which line is longest? The tricky part of this study was that in each group only one person was a true participant. The others were actors with a script. Most of the actors were instructed to give the wrong answer. Strangely, the one true participant almost always agreed with the majority, even though they knew they were giving the wrong answer.
The results of this study are important when we study social interactions among individuals in groups. This study is a famous example of the temptation many of us experience to conform to a standard during group situations and it showed that people often care more about being the same as others than they do about being right. It is still recognized as one of the most influential psychological experiments for understanding human behavior.
3. Bobo Doll Experiment
Study conducted by: dr. alburt bandura.
Study Conducted between 1961-1963 at Stanford University

In his groundbreaking study he separated participants into three groups:
- one was exposed to a video of an adult showing aggressive behavior towards a Bobo doll
- another was exposed to video of a passive adult playing with the Bobo doll
- the third formed a control group
Children watched their assigned video and then were sent to a room with the same doll they had seen in the video (with the exception of those in the control group). What the researcher found was that children exposed to the aggressive model were more likely to exhibit aggressive behavior towards the doll themselves. The other groups showed little imitative aggressive behavior. For those children exposed to the aggressive model, the number of derivative physical aggressions shown by the boys was 38.2 and 12.7 for the girls.
The study also showed that boys exhibited more aggression when exposed to aggressive male models than boys exposed to aggressive female models. When exposed to aggressive male models, the number of aggressive instances exhibited by boys averaged 104. This is compared to 48.4 aggressive instances exhibited by boys who were exposed to aggressive female models.
While the results for the girls show similar findings, the results were less drastic. When exposed to aggressive female models, the number of aggressive instances exhibited by girls averaged 57.7. This is compared to 36.3 aggressive instances exhibited by girls who were exposed to aggressive male models. The results concerning gender differences strongly supported Bandura’s secondary prediction that children will be more strongly influenced by same-sex models. The Bobo Doll Experiment showed a groundbreaking way to study human behavior and it’s influences.
4. Car Crash Experiment
Study conducted by: elizabeth loftus and john palmer.
Study Conducted in 1974 at The University of California in Irvine

The participants watched slides of a car accident and were asked to describe what had happened as if they were eyewitnesses to the scene. The participants were put into two groups and each group was questioned using different wording such as “how fast was the car driving at the time of impact?” versus “how fast was the car going when it smashed into the other car?” The experimenters found that the use of different verbs affected the participants’ memories of the accident, showing that memory can be easily distorted.
This research suggests that memory can be easily manipulated by questioning technique. This means that information gathered after the event can merge with original memory causing incorrect recall or reconstructive memory. The addition of false details to a memory of an event is now referred to as confabulation. This concept has very important implications for the questions used in police interviews of eyewitnesses.
5. Cognitive Dissonance Experiment
Study conducted by: leon festinger and james carlsmith.
Study Conducted in 1957 at Stanford University
Experiment Details: The concept of cognitive dissonance refers to a situation involving conflicting:
This conflict produces an inherent feeling of discomfort leading to a change in one of the attitudes, beliefs or behaviors to minimize or eliminate the discomfort and restore balance.
Cognitive dissonance was first investigated by Leon Festinger, after an observational study of a cult that believed that the earth was going to be destroyed by a flood. Out of this study was born an intriguing experiment conducted by Festinger and Carlsmith where participants were asked to perform a series of dull tasks (such as turning pegs in a peg board for an hour). Participant’s initial attitudes toward this task were highly negative.
They were then paid either $1 or $20 to tell a participant waiting in the lobby that the tasks were really interesting. Almost all of the participants agreed to walk into the waiting room and persuade the next participant that the boring experiment would be fun. When the participants were later asked to evaluate the experiment, the participants who were paid only $1 rated the tedious task as more fun and enjoyable than the participants who were paid $20 to lie.
Being paid only $1 is not sufficient incentive for lying and so those who were paid $1 experienced dissonance. They could only overcome that cognitive dissonance by coming to believe that the tasks really were interesting and enjoyable. Being paid $20 provides a reason for turning pegs and there is therefore no dissonance.
6. Fantz’s Looking Chamber
Study conducted by: robert l. fantz.
Study Conducted in 1961 at the University of Illinois
Experiment Details: The study conducted by Robert L. Fantz is among the simplest, yet most important in the field of infant development and vision. In 1961, when this experiment was conducted, there very few ways to study what was going on in the mind of an infant. Fantz realized that the best way was to simply watch the actions and reactions of infants. He understood the fundamental factor that if there is something of interest near humans, they generally look at it.
To test this concept, Fantz set up a display board with two pictures attached. On one was a bulls-eye. On the other was the sketch of a human face. This board was hung in a chamber where a baby could lie safely underneath and see both images. Then, from behind the board, invisible to the baby, he peeked through a hole to watch what the baby looked at. This study showed that a two-month old baby looked twice as much at the human face as it did at the bulls-eye. This suggests that human babies have some powers of pattern and form selection. Before this experiment it was thought that babies looked out onto a chaotic world of which they could make little sense.
7. Hawthorne Effect
Study conducted by: henry a. landsberger.
Study Conducted in 1955 at Hawthorne Works in Chicago, Illinois

Landsberger performed the study by analyzing data from experiments conducted between 1924 and 1932, by Elton Mayo, at the Hawthorne Works near Chicago. The company had commissioned studies to evaluate whether the level of light in a building changed the productivity of the workers. What Mayo found was that the level of light made no difference in productivity. The workers increased their output whenever the amount of light was switched from a low level to a high level, or vice versa.
The researchers noticed a tendency that the workers’ level of efficiency increased when any variable was manipulated. The study showed that the output changed simply because the workers were aware that they were under observation. The conclusion was that the workers felt important because they were pleased to be singled out. They increased productivity as a result. Being singled out was the factor dictating increased productivity, not the changing lighting levels, or any of the other factors that they experimented upon.
The Hawthorne Effect has become one of the hardest inbuilt biases to eliminate or factor into the design of any experiment in psychology and beyond.
8. Kitty Genovese Case
Study conducted by: new york police force.
Study Conducted in 1964 in New York City
Experiment Details: The murder case of Kitty Genovese was never intended to be a psychological experiment, however it ended up having serious implications for the field.
According to a New York Times article, almost 40 neighbors witnessed Kitty Genovese being savagely attacked and murdered in Queens, New York in 1964. Not one neighbor called the police for help. Some reports state that the attacker briefly left the scene and later returned to “finish off” his victim. It was later uncovered that many of these facts were exaggerated. (There were more likely only a dozen witnesses and records show that some calls to police were made).
What this case later become famous for is the “Bystander Effect,” which states that the more bystanders that are present in a social situation, the less likely it is that anyone will step in and help. This effect has led to changes in medicine, psychology and many other areas. One famous example is the way CPR is taught to new learners. All students in CPR courses learn that they must assign one bystander the job of alerting authorities which minimizes the chances of no one calling for assistance.
9. Learned Helplessness Experiment
Study conducted by: martin seligman.
Study Conducted in 1967 at the University of Pennsylvania

Seligman’s experiment involved the ringing of a bell and then the administration of a light shock to a dog. After a number of pairings, the dog reacted to the shock even before it happened. As soon as the dog heard the bell, he reacted as though he’d already been shocked.
During the course of this study something unexpected happened. Each dog was placed in a large crate that was divided down the middle with a low fence. The dog could see and jump over the fence easily. The floor on one side of the fence was electrified, but not on the other side of the fence. Seligman placed each dog on the electrified side and administered a light shock. He expected the dog to jump to the non-shocking side of the fence. In an unexpected turn, the dogs simply laid down.
The hypothesis was that as the dogs learned from the first part of the experiment that there was nothing they could do to avoid the shocks, they gave up in the second part of the experiment. To prove this hypothesis the experimenters brought in a new set of animals and found that dogs with no history in the experiment would jump over the fence.
This condition was described as learned helplessness. A human or animal does not attempt to get out of a negative situation because the past has taught them that they are helpless.
10. Little Albert Experiment
Study conducted by: john b. watson and rosalie rayner.
Study Conducted in 1920 at Johns Hopkins University

The experiment began by placing a white rat in front of the infant, who initially had no fear of the animal. Watson then produced a loud sound by striking a steel bar with a hammer every time little Albert was presented with the rat. After several pairings (the noise and the presentation of the white rat), the boy began to cry and exhibit signs of fear every time the rat appeared in the room. Watson also created similar conditioned reflexes with other common animals and objects (rabbits, Santa beard, etc.) until Albert feared them all.
This study proved that classical conditioning works on humans. One of its most important implications is that adult fears are often connected to early childhood experiences.
11. Magical Number Seven
Study conducted by: george a. miller.
Study Conducted in 1956 at Princeton University
Experiment Details: Frequently referred to as “ Miller’s Law,” the Magical Number Seven experiment purports that the number of objects an average human can hold in working memory is 7 ± 2. This means that the human memory capacity typically includes strings of words or concepts ranging from 5-9. This information on the limits to the capacity for processing information became one of the most highly cited papers in psychology.
The Magical Number Seven Experiment was published in 1956 by cognitive psychologist George A. Miller of Princeton University’s Department of Psychology in Psychological Review . In the article, Miller discussed a concurrence between the limits of one-dimensional absolute judgment and the limits of short-term memory.
In a one-dimensional absolute-judgment task, a person is presented with a number of stimuli that vary on one dimension (such as 10 different tones varying only in pitch). The person responds to each stimulus with a corresponding response (learned before).
Performance is almost perfect up to five or six different stimuli but declines as the number of different stimuli is increased. This means that a human’s maximum performance on one-dimensional absolute judgment can be described as an information store with the maximum capacity of approximately 2 to 3 bits of information There is the ability to distinguish between four and eight alternatives.
12. Pavlov’s Dog Experiment
Study conducted by: ivan pavlov.
Study Conducted in the 1890s at the Military Medical Academy in St. Petersburg, Russia

Pavlov began with the simple idea that there are some things that a dog does not need to learn. He observed that dogs do not learn to salivate when they see food. This reflex is “hard wired” into the dog. This is an unconditioned response (a stimulus-response connection that required no learning).
Pavlov outlined that there are unconditioned responses in the animal by presenting a dog with a bowl of food and then measuring its salivary secretions. In the experiment, Pavlov used a bell as his neutral stimulus. Whenever he gave food to his dogs, he also rang a bell. After a number of repeats of this procedure, he tried the bell on its own. What he found was that the bell on its own now caused an increase in salivation. The dog had learned to associate the bell and the food. This learning created a new behavior. The dog salivated when he heard the bell. Because this response was learned (or conditioned), it is called a conditioned response. The neutral stimulus has become a conditioned stimulus.
This theory came to be known as classical conditioning.
13. Robbers Cave Experiment
Study conducted by: muzafer and carolyn sherif.
Study Conducted in 1954 at the University of Oklahoma
Experiment Details: This experiment, which studied group conflict, is considered by most to be outside the lines of what is considered ethically sound.
In 1954 researchers at the University of Oklahoma assigned 22 eleven- and twelve-year-old boys from similar backgrounds into two groups. The two groups were taken to separate areas of a summer camp facility where they were able to bond as social units. The groups were housed in separate cabins and neither group knew of the other’s existence for an entire week. The boys bonded with their cabin mates during that time. Once the two groups were allowed to have contact, they showed definite signs of prejudice and hostility toward each other even though they had only been given a very short time to develop their social group. To increase the conflict between the groups, the experimenters had them compete against each other in a series of activities. This created even more hostility and eventually the groups refused to eat in the same room. The final phase of the experiment involved turning the rival groups into friends. The fun activities the experimenters had planned like shooting firecrackers and watching movies did not initially work, so they created teamwork exercises where the two groups were forced to collaborate. At the end of the experiment, the boys decided to ride the same bus home, demonstrating that conflict can be resolved and prejudice overcome through cooperation.
Many critics have compared this study to Golding’s Lord of the Flies novel as a classic example of prejudice and conflict resolution.
14. Ross’ False Consensus Effect Study
Study conducted by: lee ross.
Study Conducted in 1977 at Stanford University
Experiment Details: In 1977, a social psychology professor at Stanford University named Lee Ross conducted an experiment that, in lay terms, focuses on how people can incorrectly conclude that others think the same way they do, or form a “false consensus” about the beliefs and preferences of others. Ross conducted the study in order to outline how the “false consensus effect” functions in humans.
Featured Programs
In the first part of the study, participants were asked to read about situations in which a conflict occurred and then were told two alternative ways of responding to the situation. They were asked to do three things:
- Guess which option other people would choose
- Say which option they themselves would choose
- Describe the attributes of the person who would likely choose each of the two options
What the study showed was that most of the subjects believed that other people would do the same as them, regardless of which of the two responses they actually chose themselves. This phenomenon is referred to as the false consensus effect, where an individual thinks that other people think the same way they do when they may not. The second observation coming from this important study is that when participants were asked to describe the attributes of the people who will likely make the choice opposite of their own, they made bold and sometimes negative predictions about the personalities of those who did not share their choice.
15. The Schachter and Singer Experiment on Emotion
Study conducted by: stanley schachter and jerome e. singer.
Study Conducted in 1962 at Columbia University
Experiment Details: In 1962 Schachter and Singer conducted a ground breaking experiment to prove their theory of emotion.
In the study, a group of 184 male participants were injected with epinephrine, a hormone that induces arousal including increased heartbeat, trembling, and rapid breathing. The research participants were told that they were being injected with a new medication to test their eyesight. The first group of participants was informed the possible side effects that the injection might cause while the second group of participants were not. The participants were then placed in a room with someone they thought was another participant, but was actually a confederate in the experiment. The confederate acted in one of two ways: euphoric or angry. Participants who had not been informed about the effects of the injection were more likely to feel either happier or angrier than those who had been informed.
What Schachter and Singer were trying to understand was the ways in which cognition or thoughts influence human emotion. Their study illustrates the importance of how people interpret their physiological states, which form an important component of your emotions. Though their cognitive theory of emotional arousal dominated the field for two decades, it has been criticized for two main reasons: the size of the effect seen in the experiment was not that significant and other researchers had difficulties repeating the experiment.
16. Selective Attention / Invisible Gorilla Experiment
Study conducted by: daniel simons and christopher chabris.
Study Conducted in 1999 at Harvard University
Experiment Details: In 1999 Simons and Chabris conducted their famous awareness test at Harvard University.
Participants in the study were asked to watch a video and count how many passes occurred between basketball players on the white team. The video moves at a moderate pace and keeping track of the passes is a relatively easy task. What most people fail to notice amidst their counting is that in the middle of the test, a man in a gorilla suit walked onto the court and stood in the center before walking off-screen.
The study found that the majority of the subjects did not notice the gorilla at all, proving that humans often overestimate their ability to effectively multi-task. What the study set out to prove is that when people are asked to attend to one task, they focus so strongly on that element that they may miss other important details.
17. Stanford Prison Study
Study conducted by philip zimbardo.
Study Conducted in 1971 at Stanford University

The Stanford Prison Experiment was designed to study behavior of “normal” individuals when assigned a role of prisoner or guard. College students were recruited to participate. They were assigned roles of “guard” or “inmate.” Zimbardo played the role of the warden. The basement of the psychology building was the set of the prison. Great care was taken to make it look and feel as realistic as possible.
The prison guards were told to run a prison for two weeks. They were told not to physically harm any of the inmates during the study. After a few days, the prison guards became very abusive verbally towards the inmates. Many of the prisoners became submissive to those in authority roles. The Stanford Prison Experiment inevitably had to be cancelled because some of the participants displayed troubling signs of breaking down mentally.
Although the experiment was conducted very unethically, many psychologists believe that the findings showed how much human behavior is situational. People will conform to certain roles if the conditions are right. The Stanford Prison Experiment remains one of the most famous psychology experiments of all time.
18. Stanley Milgram Experiment
Study conducted by stanley milgram.
Study Conducted in 1961 at Stanford University
Experiment Details: This 1961 study was conducted by Yale University psychologist Stanley Milgram. It was designed to measure people’s willingness to obey authority figures when instructed to perform acts that conflicted with their morals. The study was based on the premise that humans will inherently take direction from authority figures from very early in life.
Participants were told they were participating in a study on memory. They were asked to watch another person (an actor) do a memory test. They were instructed to press a button that gave an electric shock each time the person got a wrong answer. (The actor did not actually receive the shocks, but pretended they did).
Participants were told to play the role of “teacher” and administer electric shocks to “the learner,” every time they answered a question incorrectly. The experimenters asked the participants to keep increasing the shocks. Most of them obeyed even though the individual completing the memory test appeared to be in great pain. Despite these protests, many participants continued the experiment when the authority figure urged them to. They increased the voltage after each wrong answer until some eventually administered what would be lethal electric shocks.
This experiment showed that humans are conditioned to obey authority and will usually do so even if it goes against their natural morals or common sense.
19. Surrogate Mother Experiment
Study conducted by: harry harlow.
Study Conducted from 1957-1963 at the University of Wisconsin
Experiment Details: In a series of controversial experiments during the late 1950s and early 1960s, Harry Harlow studied the importance of a mother’s love for healthy childhood development.
In order to do this he separated infant rhesus monkeys from their mothers a few hours after birth and left them to be raised by two “surrogate mothers.” One of the surrogates was made of wire with an attached bottle for food. The other was made of soft terrycloth but lacked food. The researcher found that the baby monkeys spent much more time with the cloth mother than the wire mother, thereby proving that affection plays a greater role than sustenance when it comes to childhood development. They also found that the monkeys that spent more time cuddling the soft mother grew up to healthier.
This experiment showed that love, as demonstrated by physical body contact, is a more important aspect of the parent-child bond than the provision of basic needs. These findings also had implications in the attachment between fathers and their infants when the mother is the source of nourishment.
20. The Good Samaritan Experiment
Study conducted by: john darley and daniel batson.
Study Conducted in 1973 at The Princeton Theological Seminary (Researchers were from Princeton University)
Experiment Details: In 1973, an experiment was created by John Darley and Daniel Batson, to investigate the potential causes that underlie altruistic behavior. The researchers set out three hypotheses they wanted to test:
- People thinking about religion and higher principles would be no more inclined to show helping behavior than laymen.
- People in a rush would be much less likely to show helping behavior.
- People who are religious for personal gain would be less likely to help than people who are religious because they want to gain some spiritual and personal insights into the meaning of life.
Student participants were given some religious teaching and instruction. They were then were told to travel from one building to the next. Between the two buildings was a man lying injured and appearing to be in dire need of assistance. The first variable being tested was the degree of urgency impressed upon the subjects, with some being told not to rush and others being informed that speed was of the essence.
The results of the experiment were intriguing, with the haste of the subject proving to be the overriding factor. When the subject was in no hurry, nearly two-thirds of people stopped to lend assistance. When the subject was in a rush, this dropped to one in ten.
People who were on the way to deliver a speech about helping others were nearly twice as likely to help as those delivering other sermons,. This showed that the thoughts of the individual were a factor in determining helping behavior. Religious beliefs did not appear to make much difference on the results. Being religious for personal gain, or as part of a spiritual quest, did not appear to make much of an impact on the amount of helping behavior shown.
21. The Halo Effect Experiment
Study conducted by: richard e. nisbett and timothy decamp wilson.
Study Conducted in 1977 at the University of Michigan
Experiment Details: The Halo Effect states that people generally assume that people who are physically attractive are more likely to:
- be intelligent
- be friendly
- display good judgment
To prove their theory, Nisbett and DeCamp Wilson created a study to prove that people have little awareness of the nature of the Halo Effect. They’re not aware that it influences:
- their personal judgments
- the production of a more complex social behavior
In the experiment, college students were the research participants. They were asked to evaluate a psychology instructor as they view him in a videotaped interview. The students were randomly assigned to one of two groups. Each group was shown one of two different interviews with the same instructor. The instructor is a native French-speaking Belgian who spoke English with a noticeable accent. In the first video, the instructor presented himself as someone:
- respectful of his students’ intelligence and motives
- flexible in his approach to teaching
- enthusiastic about his subject matter
In the second interview, he presented himself as much more unlikable. He was cold and distrustful toward the students and was quite rigid in his teaching style.
After watching the videos, the subjects were asked to rate the lecturer on:
- physical appearance
His mannerisms and accent were kept the same in both versions of videos. The subjects were asked to rate the professor on an 8-point scale ranging from “like extremely” to “dislike extremely.” Subjects were also told that the researchers were interested in knowing “how much their liking for the teacher influenced the ratings they just made.” Other subjects were asked to identify how much the characteristics they just rated influenced their liking of the teacher.
After responding to the questionnaire, the respondents were puzzled about their reactions to the videotapes and to the questionnaire items. The students had no idea why they gave one lecturer higher ratings. Most said that how much they liked the lecturer had not affected their evaluation of his individual characteristics at all.
The interesting thing about this study is that people can understand the phenomenon, but they are unaware when it is occurring. Without realizing it, humans make judgments. Even when it is pointed out, they may still deny that it is a product of the halo effect phenomenon.
22. The Marshmallow Test
Study conducted by: walter mischel.
Study Conducted in 1972 at Stanford University

In his 1972 Marshmallow Experiment, children ages four to six were taken into a room where a marshmallow was placed in front of them on a table. Before leaving each of the children alone in the room, the experimenter informed them that they would receive a second marshmallow if the first one was still on the table after they returned in 15 minutes. The examiner recorded how long each child resisted eating the marshmallow and noted whether it correlated with the child’s success in adulthood. A small number of the 600 children ate the marshmallow immediately and one-third delayed gratification long enough to receive the second marshmallow.
In follow-up studies, Mischel found that those who deferred gratification were significantly more competent and received higher SAT scores than their peers. This characteristic likely remains with a person for life. While this study seems simplistic, the findings outline some of the foundational differences in individual traits that can predict success.
23. The Monster Study
Study conducted by: wendell johnson.
Study Conducted in 1939 at the University of Iowa
Experiment Details: The Monster Study received this negative title due to the unethical methods that were used to determine the effects of positive and negative speech therapy on children.
Wendell Johnson of the University of Iowa selected 22 orphaned children, some with stutters and some without. The children were in two groups. The group of children with stutters was placed in positive speech therapy, where they were praised for their fluency. The non-stutterers were placed in negative speech therapy, where they were disparaged for every mistake in grammar that they made.
As a result of the experiment, some of the children who received negative speech therapy suffered psychological effects and retained speech problems for the rest of their lives. They were examples of the significance of positive reinforcement in education.
The initial goal of the study was to investigate positive and negative speech therapy. However, the implication spanned much further into methods of teaching for young children.
24. Violinist at the Metro Experiment
Study conducted by: staff at the washington post.
Study Conducted in 2007 at a Washington D.C. Metro Train Station

During the study, pedestrians rushed by without realizing that the musician playing at the entrance to the metro stop was Grammy-winning musician, Joshua Bell. Two days before playing in the subway, he sold out at a theater in Boston where the seats average $100. He played one of the most intricate pieces ever written with a violin worth 3.5 million dollars. In the 45 minutes the musician played his violin, only 6 people stopped and stayed for a while. Around 20 gave him money, but continued to walk their normal pace. He collected $32.
The study and the subsequent article organized by the Washington Post was part of a social experiment looking at:
- the priorities of people
Gene Weingarten wrote about the social experiment: “In a banal setting at an inconvenient time, would beauty transcend?” Later he won a Pulitzer Prize for his story. Some of the questions the article addresses are:
- Do we perceive beauty?
- Do we stop to appreciate it?
- Do we recognize the talent in an unexpected context?
As it turns out, many of us are not nearly as perceptive to our environment as we might like to think.
25. Visual Cliff Experiment
Study conducted by: eleanor gibson and richard walk.
Study Conducted in 1959 at Cornell University
Experiment Details: In 1959, psychologists Eleanor Gibson and Richard Walk set out to study depth perception in infants. They wanted to know if depth perception is a learned behavior or if it is something that we are born with. To study this, Gibson and Walk conducted the visual cliff experiment.
They studied 36 infants between the ages of six and 14 months, all of whom could crawl. The infants were placed one at a time on a visual cliff. A visual cliff was created using a large glass table that was raised about a foot off the floor. Half of the glass table had a checker pattern underneath in order to create the appearance of a ‘shallow side.’
In order to create a ‘deep side,’ a checker pattern was created on the floor; this side is the visual cliff. The placement of the checker pattern on the floor creates the illusion of a sudden drop-off. Researchers placed a foot-wide centerboard between the shallow side and the deep side. Gibson and Walk found the following:
- Nine of the infants did not move off the centerboard.
- All of the 27 infants who did move crossed into the shallow side when their mothers called them from the shallow side.
- Three of the infants crawled off the visual cliff toward their mother when called from the deep side.
- When called from the deep side, the remaining 24 children either crawled to the shallow side or cried because they could not cross the visual cliff and make it to their mother.
What this study helped demonstrate is that depth perception is likely an inborn train in humans.
Among these experiments and psychological tests, we see boundaries pushed and theories taking on a life of their own. It is through the endless stream of psychological experimentation that we can see simple hypotheses become guiding theories for those in this field. The greater field of psychology became a formal field of experimental study in 1879, when Wilhelm Wundt established the first laboratory dedicated solely to psychological research in Leipzig, Germany. Wundt was the first person to refer to himself as a psychologist. Since 1879, psychology has grown into a massive collection of:
- methods of practice
It’s also a specialty area in the field of healthcare. None of this would have been possible without these and many other important psychological experiments that have stood the test of time.
- 20 Most Unethical Experiments in Psychology
- What Careers are in Experimental Psychology?
- 10 Things to Know About the Psychology of Psychotherapy
About Education: Psychology
Explorable.com
Mental Floss.com
About the Author
After earning a Bachelor of Arts in Psychology from Rutgers University and then a Master of Science in Clinical and Forensic Psychology from Drexel University, Kristen began a career as a therapist at two prisons in Philadelphia. At the same time she volunteered as a rape crisis counselor, also in Philadelphia. After a few years in the field she accepted a teaching position at a local college where she currently teaches online psychology courses. Kristen began writing in college and still enjoys her work as a writer, editor, professor and mother.
- 5 Best Online Ph.D. Marriage and Family Counseling Programs
- Top 5 Online Doctorate in Educational Psychology
- 5 Best Online Ph.D. in Industrial and Organizational Psychology Programs
- Top 10 Online Master’s in Forensic Psychology
- 10 Most Affordable Counseling Psychology Online Programs
- 10 Most Affordable Online Industrial Organizational Psychology Programs
- 10 Most Affordable Online Developmental Psychology Online Programs
- 15 Most Affordable Online Sport Psychology Programs
- 10 Most Affordable School Psychology Online Degree Programs
- Top 50 Online Psychology Master’s Degree Programs
- Top 25 Online Master’s in Educational Psychology
- Top 25 Online Master’s in Industrial/Organizational Psychology
- Top 10 Most Affordable Online Master’s in Clinical Psychology Degree Programs
- Top 6 Most Affordable Online PhD/PsyD Programs in Clinical Psychology
- 50 Great Small Colleges for a Bachelor’s in Psychology
- 50 Most Innovative University Psychology Departments
- The 30 Most Influential Cognitive Psychologists Alive Today
- Top 30 Affordable Online Psychology Degree Programs
- 30 Most Influential Neuroscientists
- Top 40 Websites for Psychology Students and Professionals
- Top 30 Psychology Blogs
- 25 Celebrities With Animal Phobias
- Your Phobias Illustrated (Infographic)
- 15 Inspiring TED Talks on Overcoming Challenges
- 10 Fascinating Facts About the Psychology of Color
- 15 Scariest Mental Disorders of All Time
- 15 Things to Know About Mental Disorders in Animals
- 13 Most Deranged Serial Killers of All Time

Site Information
- About Online Psychology Degree Guide
15 Famous Experiments and Case Studies in Psychology

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process

Psychology has seen thousands upon thousands of research studies over the years. Most of these studies have helped shape our current understanding of human thoughts, behavior, and feelings.
The psychology case studies in this list are considered classic examples of psychological case studies and experiments, which are still being taught in introductory psychology courses up to this day.
Some studies, however, were downright shocking and controversial that you’d probably wonder why such studies were conducted back in the day. Imagine participating in an experiment for a small reward or extra class credit, only to be left scarred for life. These kinds of studies, however, paved the way for a more ethical approach to studying psychology and implementation of research standards such as the use of debriefing in psychology research .
Case Study vs. Experiment
Before we dive into the list of the most famous studies in psychology, let us first review the difference between case studies and experiments.
- It is an in-depth study and analysis of an individual, group, community, or phenomenon. The results of a case study cannot be applied to the whole population, but they can provide insights for further studies.
- It often uses qualitative research methods such as observations, surveys, and interviews.
- It is often conducted in real-life settings rather than in controlled environments.
- An experiment is a type of study done on a sample or group of random participants, the results of which can be generalized to the whole population.
- It often uses quantitative research methods that rely on numbers and statistics.
- It is conducted in controlled environments, wherein some things or situations are manipulated.
See Also: Experimental vs Observational Studies
Famous Experiments in Psychology
1. the marshmallow experiment.
Psychologist Walter Mischel conducted the marshmallow experiment at Stanford University in the 1960s to early 1970s. It was a simple test that aimed to define the connection between delayed gratification and success in life.
The instructions were fairly straightforward: children ages 4-6 were presented a piece of marshmallow on a table and they were told that they would receive a second piece if they could wait for 15 minutes without eating the first marshmallow.
About one-third of the 600 participants succeeded in delaying gratification to receive the second marshmallow. Mischel and his team followed up on these participants in the 1990s, learning that those who had the willpower to wait for a larger reward experienced more success in life in terms of SAT scores and other metrics.
This case study also supported self-control theory , a theory in criminology that holds that people with greater self-control are less likely to end up in trouble with the law!
The classic marshmallow experiment, however, was debunked in a 2018 replication study done by Tyler Watts and colleagues.
This more recent experiment had a larger group of participants (900) and a better representation of the general population when it comes to race and ethnicity. In this study, the researchers found out that the ability to wait for a second marshmallow does not depend on willpower alone but more so on the economic background and social status of the participants.
2. The Bystander Effect
In 1694, Kitty Genovese was murdered in the neighborhood of Kew Gardens, New York. It was told that there were up to 38 witnesses and onlookers in the vicinity of the crime scene, but nobody did anything to stop the murder or call for help.
Such tragedy was the catalyst that inspired social psychologists Bibb Latane and John Darley to formulate the phenomenon called bystander effect or bystander apathy .
Subsequent investigations showed that this story was exaggerated and inaccurate, as there were actually only about a dozen witnesses, at least two of whom called the police. But the case of Kitty Genovese led to various studies that aim to shed light on the bystander phenomenon.
Latane and Darley tested bystander intervention in an experimental study . Participants were asked to answer a questionnaire inside a room, and they would either be alone or with two other participants (who were actually actors or confederates in the study). Smoke would then come out from under the door. The reaction time of participants was tested — how long would it take them to report the smoke to the authorities or the experimenters?
The results showed that participants who were alone in the room reported the smoke faster than participants who were with two passive others. The study suggests that the more onlookers are present in an emergency situation, the less likely someone would step up to help, a social phenomenon now popularly called the bystander effect.
3. Asch Conformity Study
Have you ever made a decision against your better judgment just to fit in with your friends or family? The Asch Conformity Studies will help you understand this kind of situation better.
In this experiment, a group of participants were shown three numbered lines of different lengths and asked to identify the longest of them all. However, only one true participant was present in every group and the rest were actors, most of whom told the wrong answer.
Results showed that the participants went for the wrong answer, even though they knew which line was the longest one in the first place. When the participants were asked why they identified the wrong one, they said that they didn’t want to be branded as strange or peculiar.
This study goes to show that there are situations in life when people prefer fitting in than being right. It also tells that there is power in numbers — a group’s decision can overwhelm a person and make them doubt their judgment.
4. The Bobo Doll Experiment
The Bobo Doll Experiment was conducted by Dr. Albert Bandura, the proponent of social learning theory .
Back in the 1960s, the Nature vs. Nurture debate was a popular topic among psychologists. Bandura contributed to this discussion by proposing that human behavior is mostly influenced by environmental rather than genetic factors.
In the Bobo Doll Experiment, children were divided into three groups: one group was shown a video in which an adult acted aggressively toward the Bobo Doll, the second group was shown a video in which an adult play with the Bobo Doll, and the third group served as the control group where no video was shown.
The children were then led to a room with different kinds of toys, including the Bobo Doll they’ve seen in the video. Results showed that children tend to imitate the adults in the video. Those who were presented the aggressive model acted aggressively toward the Bobo Doll while those who were presented the passive model showed less aggression.
While the Bobo Doll Experiment can no longer be replicated because of ethical concerns, it has laid out the foundations of social learning theory and helped us understand the degree of influence adult behavior has on children.
5. Blue Eye / Brown Eye Experiment
Following the assassination of Martin Luther King Jr. in 1968, third-grade teacher Jane Elliott conducted an experiment in her class. Although not a formal experiment in controlled settings, A Class Divided is a good example of a social experiment to help children understand the concept of racism and discrimination.
The class was divided into two groups: blue-eyed children and brown-eyed children. For one day, Elliott gave preferential treatment to her blue-eyed students, giving them more attention and pampering them with rewards. The next day, it was the brown-eyed students’ turn to receive extra favors and privileges.
As a result, whichever group of students was given preferential treatment performed exceptionally well in class, had higher quiz scores, and recited more frequently; students who were discriminated against felt humiliated, answered poorly in tests, and became uncertain with their answers in class.
This study is now widely taught in sociocultural psychology classes.
6. Stanford Prison Experiment
One of the most controversial and widely-cited studies in psychology is the Stanford Prison Experiment , conducted by Philip Zimbardo at the basement of the Stanford psychology building in 1971. The hypothesis was that abusive behavior in prisons is influenced by the personality traits of the prisoners and prison guards.
The participants in the experiment were college students who were randomly assigned as either a prisoner or a prison guard. The prison guards were then told to run the simulated prison for two weeks. However, the experiment had to be stopped in just 6 days.
The prison guards abused their authority and harassed the prisoners through verbal and physical means. The prisoners, on the other hand, showed submissive behavior. Zimbardo decided to stop the experiment because the prisoners were showing signs of emotional and physical breakdown.
Although the experiment wasn’t completed, the results strongly showed that people can easily get into a social role when others expect them to, especially when it’s highly stereotyped .
7. The Halo Effect
Have you ever wondered why toothpastes and other dental products are endorsed in advertisements by celebrities more often than dentists? The Halo Effect is one of the reasons!
The Halo Effect shows how one favorable attribute of a person can gain them positive perceptions in other attributes. In the case of product advertisements, attractive celebrities are also perceived as intelligent and knowledgeable of a certain subject matter even though they’re not technically experts.
The Halo Effect originated in a classic study done by Edward Thorndike in the early 1900s. He asked military commanding officers to rate their subordinates based on different qualities, such as physical appearance, leadership, dependability, and intelligence.
The results showed that high ratings of a particular quality influences the ratings of other qualities, producing a halo effect of overall high ratings. The opposite also applied, which means that a negative rating in one quality also correlated to negative ratings in other qualities.
Experiments on the Halo Effect came in various formats as well, supporting Thorndike’s original theory. This phenomenon suggests that our perception of other people’s overall personality is hugely influenced by a quality that we focus on.
8. Cognitive Dissonance
There are experiences in our lives when our beliefs and behaviors do not align with each other and we try to justify them in our minds. This is cognitive dissonance , which was studied in an experiment by Leon Festinger and James Carlsmith back in 1959.
In this experiment, participants had to go through a series of boring and repetitive tasks, such as spending an hour turning pegs in a wooden knob. After completing the tasks, they were then paid either $1 or $20 to tell the next participants that the tasks were extremely fun and enjoyable. Afterwards, participants were asked to rate the experiment. Those who were given $1 rated the experiment as more interesting and fun than those who received $20.
The results showed that those who received a smaller incentive to lie experienced cognitive dissonance — $1 wasn’t enough incentive for that one hour of painstakingly boring activity, so the participants had to justify that they had fun anyway.
Famous Case Studies in Psychology
9. little albert.
In 1920, behaviourist theorists John Watson and Rosalie Rayner experimented on a 9-month-old baby to test the effects of classical conditioning in instilling fear in humans.
This was such a controversial study that it gained popularity in psychology textbooks and syllabi because it is a classic example of unethical research studies done in the name of science.
In one of the experiments, Little Albert was presented with a harmless stimulus or object, a white rat, which he wasn’t scared of at first. But every time Little Albert would see the white rat, the researchers would play a scary sound of hammer and steel. After about 6 pairings, Little Albert learned to fear the rat even without the scary sound.
Little Albert developed signs of fear to different objects presented to him through classical conditioning . He even generalized his fear to other stimuli not present in the course of the experiment.
10. Phineas Gage
Phineas Gage is such a celebrity in Psych 101 classes, even though the way he rose to popularity began with a tragic accident. He was a resident of Central Vermont and worked in the construction of a new railway line in the mid-1800s. One day, an explosive went off prematurely, sending a tamping iron straight into his face and through his brain.
Gage survived the accident, fortunately, something that is considered a feat even up to this day. He managed to find a job as a stagecoach after the accident. However, his family and friends reported that his personality changed so much that “he was no longer Gage” (Harlow, 1868).
New evidence on the case of Phineas Gage has since come to light, thanks to modern scientific studies and medical tests. However, there are still plenty of mysteries revolving around his brain damage and subsequent recovery.
11. Anna O.
Anna O., a social worker and feminist of German Jewish descent, was one of the first patients to receive psychoanalytic treatment.
Her real name was Bertha Pappenheim and she inspired much of Sigmund Freud’s works and books on psychoanalytic theory, although they hadn’t met in person. Their connection was through Joseph Breuer, Freud’s mentor when he was still starting his clinical practice.
Anna O. suffered from paralysis, personality changes, hallucinations, and rambling speech, but her doctors could not find the cause. Joseph Breuer was then called to her house for intervention and he performed psychoanalysis, also called the “talking cure”, on her.
Breuer would tell Anna O. to say anything that came to her mind, such as her thoughts, feelings, and childhood experiences. It was noted that her symptoms subsided by talking things out.
However, Breuer later referred Anna O. to the Bellevue Sanatorium, where she recovered and set out to be a renowned writer and advocate of women and children.
12. Patient HM
H.M., or Henry Gustav Molaison, was a severe amnesiac who had been the subject of countless psychological and neurological studies.
Henry was 27 when he underwent brain surgery to cure the epilepsy that he had been experiencing since childhood. In an unfortunate turn of events, he lost his memory because of the surgery and his brain also became unable to store long-term memories.
He was then regarded as someone living solely in the present, forgetting an experience as soon as it happened and only remembering bits and pieces of his past. Over the years, his amnesia and the structure of his brain had helped neuropsychologists learn more about cognitive functions .
Suzanne Corkin, a researcher, writer, and good friend of H.M., recently published a book about his life. Entitled Permanent Present Tense , this book is both a memoir and a case study following the struggles and joys of Henry Gustav Molaison.
13. Chris Sizemore
Chris Sizemore gained celebrity status in the psychology community when she was diagnosed with multiple personality disorder, now known as dissociative identity disorder.
Sizemore has several alter egos, which included Eve Black, Eve White, and Jane. Various papers about her stated that these alter egos were formed as a coping mechanism against the traumatic experiences she underwent in her childhood.
Sizemore said that although she has succeeded in unifying her alter egos into one dominant personality, there were periods in the past experienced by only one of her alter egos. For example, her husband married her Eve White alter ego and not her.
Her story inspired her psychiatrists to write a book about her, entitled The Three Faces of Eve , which was then turned into a 1957 movie of the same title.
14. David Reimer
When David was just 8 months old, he lost his penis because of a botched circumcision operation.
Psychologist John Money then advised Reimer’s parents to raise him as a girl instead, naming him Brenda. His gender reassignment was supported by subsequent surgery and hormonal therapy.
Money described Reimer’s gender reassignment as a success, but problems started to arise as Reimer was growing up. His boyishness was not completely subdued by the hormonal therapy. When he was 14 years old, he learned about the secrets of his past and he underwent gender reassignment to become male again.
Reimer became an advocate for children undergoing the same difficult situation he had been. His life story ended when he was 38 as he took his own life.
15. Kim Peek
Kim Peek was the inspiration behind Rain Man , an Oscar-winning movie about an autistic savant character played by Dustin Hoffman.
The movie was released in 1988, a time when autism wasn’t widely known and acknowledged yet. So it was an eye-opener for many people who watched the film.
In reality, Kim Peek was a non-autistic savant. He was exceptionally intelligent despite the brain abnormalities he was born with. He was like a walking encyclopedia, knowledgeable about travel routes, US zip codes, historical facts, and classical music. He also read and memorized approximately 12,000 books in his lifetime.
This list of experiments and case studies in psychology is just the tip of the iceberg! There are still countless interesting psychology studies that you can explore if you want to learn more about human behavior and dynamics.
You can also conduct your own mini-experiment or participate in a study conducted in your school or neighborhood. Just remember that there are ethical standards to follow so as not to repeat the lasting physical and emotional harm done to Little Albert or the Stanford Prison Experiment participants.
Asch, S. E. (1956). Studies of independence and conformity: I. A minority of one against a unanimous majority. Psychological Monographs: General and Applied, 70 (9), 1–70. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0093718
Bandura, A., Ross, D., & Ross, S. A. (1961). Transmission of aggression through imitation of aggressive models. The Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology, 63 (3), 575–582. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0045925
Elliott, J., Yale University., WGBH (Television station : Boston, Mass.), & PBS DVD (Firm). (2003). A class divided. New Haven, Conn.: Yale University Films.
Festinger, L., & Carlsmith, J. M. (1959). Cognitive consequences of forced compliance. The Journal of Abnormal and Social Psychology, 58 (2), 203–210. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0041593
Haney, C., Banks, W. C., & Zimbardo, P. G. (1973). A study of prisoners and guards in a simulated prison. Naval Research Review , 30 , 4-17.
Latane, B., & Darley, J. M. (1968). Group inhibition of bystander intervention in emergencies. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 10 (3), 215–221. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0026570
Mischel, W. (2014). The Marshmallow Test: Mastering self-control. Little, Brown and Co.
Thorndike, E. (1920) A Constant Error in Psychological Ratings. Journal of Applied Psychology , 4 , 25-29. http://dx.doi.org/10.1037/h0071663
Watson, J. B., & Rayner, R. (1920). Conditioned emotional reactions. Journal of experimental psychology , 3 (1), 1.

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ Free Social Skills Worksheets
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 10 Reasons you’re Perpetually Single
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 20 Montessori Toddler Bedrooms (Design Inspiration)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 21 Montessori Homeschool Setups
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

- Virginia Beach
- History & facts
- Famous people
- Famous landmarks
- AI interviews
- Science & Nature
- Tech & Business
Discover something new every day
- Famous places
- Food & Drinks
- Tech & Business
20 Famous Psychology Experiments That Shaped Our Understanding

Read Next →

Where to Swim in Lisbon

How to find English speaking movies in Paris

Top 15 Interesting Facts about The Renaissance
1.stanford prison experiment.

2.Milgram Experiment
3.little albert experiment.

4.Asch Conformity Experiment
5.harlow’s monkey experiment.

6.Bobo Doll Experiment
7.the marshmallow test.

8.Robbers Cave Experiment
9.the monster study.

10.The Standford Marshmallow Experiment
11.the hawthorne effect.

12.The Strange Situation
13.the still face experiment.

14.Pavlov’s Dogs
15.the milgram experiment.

16.The Robbers Cave Experiment
17.the harlow monkey experiment, 18.the bystander effect, 19.the zimbardo prison experiment.

20.The Ainsworth Strange Situation Experiment
Planning a trip to Paris ? Get ready !
These are Amazon’s best-selling travel products that you may need for coming to Paris.
- The best travel book : Rick Steves – Paris 2023 – Learn more here
- Fodor’s Paris 2024 – Learn more here
Travel Gear
- Venture Pal Lightweight Backpack – Learn more here
- Samsonite Winfield 2 28″ Luggage – Learn more here
- Swig Savvy’s Stainless Steel Insulated Water Bottle – Learn more here
Check Amazon’s best-seller list for the most popular travel accessories. We sometimes read this list just to find out what new travel products people are buying.
Beatrice is a vibrant content creator and recent law graduate residing in Nairobi, Kenya. Beyond the legal world, Beatrice has a true love for writing. Originally from the scenic county of Baringo, her journey weaves a rich tapestry of culture and experiences. Whether immersing herself in the bustling streets of Nairobi or reminiscing about her Baringo roots, her words paint vivid tales. She enjoys writing about law and literature, crafting a narrative that bridges her legal acumen, cultural heritage, and the sheer joy of putting pen to paper.
Hello & Welcome

Popular Articles

Top 20 Streets to See in Paris

Paris in two days

Top 15 Things to do Around the Eiffel Tower

The Best Way to Visit Paris Museums

Top 15 Fashion Stores in Le Marais
Visit europe with discover walks.
- Paris walking tours
- Montmartre walking tour
- Lisbon walking tours
- Prague walking tours
- Barcelona walking tours
- Private tours in Europe
- Privacy policy
© 2025 Charing Cross Corporation
We are a Parisian travel company so you will be getting tips on where to stay, what to see, restaurants and much more from local specialists!

No thanks, I’m not interested!
7 Famous Psychology Experiments

Many famous experiments studying human behavior have impacted our fundamental understanding of psychology. Though some could not be repeated today due to breaches in ethical boundaries, that does not diminish the significance of those psychological studies. Some of these important findings include a greater awareness of depression and its symptoms, how people learn behaviors through the process of association and how individuals conform to a group.
Below, we take a look at seven famous psychological experiments that greatly influenced the field of psychology and our understanding of human behavior.
The Little Albert Experiment, 1920
A John’s Hopkins University professor, Dr. John B. Watson, and a graduate student wanted to test a learning process called classical conditioning. Classical conditioning involves learning involuntary or automatic behaviors by association, and Dr. Watson thought it formed the bedrock of human psychology.
A nine-month-old toddler, dubbed “Albert B,” was volunteered for Dr. Watson and Rosalie Rayner ‘s experiment. Albert played with white furry objects, and at first, the toddler displayed joy and affection. Over time, as he played with the objects, Dr. Watson would make a loud noise behind the child’s head to frighten him. After numerous trials, Albert was conditioned to be afraid when he saw white furry objects.
The study proved that humans could be conditioned to enjoy or fear something, which many psychologists believe could explain why people have irrational fears and how they may have developed early in life. This is a great example of experimental study psychology.
Stanford Prison Experiment, 1971
Stanford professor Philip Zimbardo wanted to learn how individuals conformed to societal roles. He wondered, for example, whether the tense relationship between prison guards and inmates in jails had more to do with the personalities of each or the environment.
During Zimbardo’s experiment , 24 male college students were assigned to be either a prisoner or a guard. The prisoners were held in a makeshift prison inside the basement of Stanford’s psychology department. They went through a standard booking process designed to take away their individuality and make them feel anonymous. Guards were given eight-hour shifts and tasked to treat the prisoners just like they would in real life.
Zimbardo found rather quickly that both the guards and prisoners fully adapted to their roles; in fact, he had to shut down the experiment after six days because it became too dangerous. Zimbardo even admitted he began thinking of himself as a police superintendent rather than a psychologist. The study confirmed that people will conform to the social roles they’re expected to play, especially overly stereotyped ones such as prison guards.
“We realized how ordinary people could be readily transformed from the good Dr. Jekyll to the evil Mr. Hyde,” Zimbardo wrote.
The Asch Conformity Study, 1951
Solomon Asch, a Polish-American social psychologist, was determined to see whether an individual would conform to a group’s decision, even if the individual knew it was incorrect. Conformity is defined by the American Psychological Association as the adjustment of a person’s opinions or thoughts so that they fall closer in line with those of other people or the normative standards of a social group or situation.
In his experiment , Asch selected 50 male college students to participate in a “vision test.” Individuals would have to determine which line on a card was longer. However, the individuals at the center of the experiment did not know that the other people taking the test were actors following scripts, and at times selected the wrong answer on purpose. Asch found that, on average over 12 trials, nearly one-third of the naive participants conformed with the incorrect majority, and only 25 percent never conformed to the incorrect majority. In the control group that featured only the participants and no actors, less than one percent of participants ever chose the wrong answer.
Asch’s experiment showed that people will conform to groups to fit in (normative influence) because of the belief that the group was better informed than the individual. This explains why some people change behaviors or beliefs when in a new group or social setting, even when it goes against past behaviors or beliefs.
The Bobo Doll Experiment, 1961, 1963
Stanford University professor Albert Bandura wanted to put the social learning theory into action. Social learning theory suggests that people can acquire new behaviors “through direct experience or by observing the behavior of others.” Using a Bobo doll , which is a blow-up toy in the shape of a life-size bowling pin, Bandura and his team tested whether children witnessing acts of aggression would copy them.
Bandura and two colleagues selected 36 boys and 36 girls between the ages of 3 and 6 from the Stanford University nursery and split them into three groups of 24. One group watched adults behaving aggressively toward the Bobo doll. In some cases, the adult subjects hit the doll with a hammer or threw it in the air. Another group was shown an adult playing with the Bobo doll in a non-aggressive manner, and the last group was not shown a model at all, just the Bobo doll.
After each session, children were taken to a room with toys and studied to see how their play patterns changed. In a room with aggressive toys (a mallet, dart guns, and a Bobo doll) and non-aggressive toys (a tea set, crayons, and plastic farm animals), Bandura and his colleagues observed that children who watched the aggressive adults were more likely to imitate the aggressive responses.
Unexpectedly, Bandura found that female children acted more physically aggressive after watching a male subject and more verbally aggressive after watching a female subject. The results of the study highlight how children learn behaviors from observing others.
The Learned Helplessness Experiment, 1965
Martin Seligman wanted to research a different angle related to Dr. Watson’s study of classical conditioning. In studying conditioning with dogs, Seligman made an astute observation : the subjects, which had already been conditioned to expect a light electric shock if they heard a bell, would sometimes give up after another negative outcome, rather than searching for the positive outcome.
Under normal circumstances, animals will always try to get away from negative outcomes. When Seligman tested his experiment on animals who hadn’t been previously conditioned, the animals attempted to find a positive outcome. Oppositely, the dogs who had been already conditioned to expect a negative response assumed there would be another negative response waiting for them, even in a different situation.
The conditioned dogs’ behavior became known as learned helplessness, the idea that some subjects won’t try to get out of a negative situation because past experiences have forced them to believe they are helpless. The study’s findings shed light on depression and its symptoms in humans.
Is a Psychology Degree Right for You?
Develop you strength in psychology, communication, critical thinking, research, writing, and more.
The Milgram Experiment, 1963
In the wake of the horrific atrocities carried out by Nazi Germany during World War II, Stanley Milgram wanted to test the levels of obedience to authority. The Yale University professor wanted to study if people would obey commands, even when it conflicted with the person’s conscience.
Participants of the condensed study , 40 males between the ages of 20 and 50, were split into learners and teachers. Though it seemed random, actors were always chosen as the learners, and unsuspecting participants were always the teachers. A learner was strapped to a chair with electrodes in one room while the experimenter äóñ another actor äóñ and a teacher went into another.
The teacher and learner went over a list of word pairs that the learner was told to memorize. When the learner incorrectly paired a set of words together, the teacher would shock the learner. The teacher believed the shocks ranged from mild all the way to life-threatening. In reality, the learner, who intentionally made mistakes, was not being shocked.
As the voltage of the shocks increased and the teachers became aware of the believed pain caused by them, some refused to continue the experiment. After prodding by the experimenter, 65 percent resumed. From the study, Milgram devised the agency theory , which suggests that people allow others to direct their actions because they believe the authority figure is qualified and will accept responsibility for the outcomes. Milgram’s findings help explain how people can make decisions against their own conscience, such as when participating in a war or genocide.
The Halo Effect Experiment, 1977
University of Michigan professors Richard Nisbett and Timothy Wilson were interested in following up a study from 50 years earlier on a concept known as the halo effect . In the 1920s, American psychologist Edward Thorndike researched a phenomenon in the U.S. military that showed cognitive bias. This is an error in how we think that affects how we perceive people and make judgements and decisions based on those perceptions.
In 1977, Nisbett and Wilson tested the halo effect using 118 college students (62 males, 56 females). Students were divided into two groups and were asked to evaluate a male Belgian teacher who spoke English with a heavy accent. Participants were shown one of two videotaped interviews with the teacher on a television monitor. The first interview showed the teacher interacting cordially with students, and the second interview showed the teacher behaving inhospitably. The subjects were then asked to rate the teacher’s physical appearance, mannerisms, and accent on an eight-point scale from appealing to irritating.
Nisbett and Wilson found that on physical appearance alone, 70 percent of the subjects rated the teacher as appealing when he was being respectful and irritating when he was cold. When the teacher was rude, 80 percent of the subjects rated his accent as irritating, as compared to nearly 50 percent when he was being kind.
The updated study on the halo effect shows that cognitive bias isn’t exclusive to a military environment. Cognitive bias can get in the way of making the correct decision, whether it’s during a job interview or deciding whether to buy a product that’s been endorsed by a celebrity we admire.
How Experiments Have Impacted Psychology Today
Contemporary psychologists have built on the findings of these studies to better understand human behaviors, mental illnesses, and the link between the mind and body. For their contributions to psychology, Watson, Bandura, Nisbett and Zimbardo were all awarded Gold Medals for Life Achievement from the American Psychological Foundation. Become part of the next generation of influential psychologists with King University’s online bachelor’s in psychology . Take advantage of King University’s flexible online schedule and complete the major coursework of your degree in as little as 16 months. Plus, as a psychology major, King University will prepare you for graduate school with original research on student projects as you pursue your goal of being a psychologist.
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
Ideas for Psychology Experiments
Inspiration for psychology experiments is all around if you know where to look
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Steven Gans, MD is board-certified in psychiatry and is an active supervisor, teacher, and mentor at Massachusetts General Hospital.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/steven-gans-1000-51582b7f23b6462f8713961deb74959f.jpg)
Psychology experiments can run the gamut from simple to complex. Students are often expected to design—and sometimes perform—their own experiments, but finding great experiment ideas can be a little challenging. Fortunately, inspiration is all around if you know where to look—from your textbooks to the questions that you have about your own life.
Always discuss your idea with your instructor before beginning your experiment—particularly if your research involves human participants. (Note: You'll probably need to submit a proposal and get approval from your school's institutional review board.)
At a Glance
If you are looking for an idea for psychology experiments, start your search early and make sure you have the time you need. Doing background research, choosing an experimental design, and actually performing your experiment can be quite the process. Keep reading to find some great psychology experiment ideas that can serve as inspiration. You can then find ways to adapt these ideas for your own assignments.
15 Ideas for Psychology Experiments
Most of these experiments can be performed easily at home or at school. That said, you will need to find out if you have to get approval from your teacher or from an institutional review board before getting started.
The following are some questions you could attempt to answer as part of a psychological experiment:
- Are people really able to "feel like someone is watching" them ? Have some participants sit alone in a room and have them note when they feel as if they are being watched. Then, see how those results line up to your own record of when participants were actually being observed.
- Can certain colors improve learning ? You may have heard teachers or students claim that printing text on green paper helps students read better, or that yellow paper helps students perform better on math exams. Design an experiment to see whether using a specific color of paper helps improve students' scores on math exams.
- Can color cause physiological reactions ? Perform an experiment to determine whether certain colors cause a participant's blood pressure to rise or fall.
- Can different types of music lead to different physiological responses ? Measure the heart rates of participants in response to various types of music to see if there is a difference.
- Can smelling one thing while tasting another impact a person's ability to detect what the food really is ? Have participants engage in a blind taste test where the smell and the food they eat are mismatched. Ask the participants to identify the food they are trying and note how accurate their guesses are.
- Could a person's taste in music offer hints about their personality ? Previous research has suggested that people who prefer certain styles of music tend to exhibit similar personality traits. Administer a personality assessment and survey participants about their musical preferences and examine your results.
- Do action films cause people to eat more popcorn and candy during a movie ? Have one group of participants watch an action movie, and another group watch a slow-paced drama. Compare how much popcorn is consumed by each group.
- Do colors really impact moods ? Investigate to see if the color blue makes people feel calm, or if the color red leaves them feeling agitated.
- Do creative people see optical illusions differently than more analytical people ? Have participants complete an assessment to measure their level of creative thinking. Then ask participants to look at optical illusions and note what they perceive.
- Do people rate individuals with perfectly symmetrical faces as more beautiful than those with asymmetrical faces ? Create sample cards with both symmetrical and asymmetrical faces and ask participants to rate the attractiveness of each picture.
- Do people who use social media exhibit signs of addiction ? Have participants complete an assessment of their social media habits, then have them complete an addiction questionnaire.
- Does eating breakfast help students do better in school ? According to some, eating breakfast can have a beneficial influence on school performance. For your experiment, you could compare the test scores of students who ate breakfast to those who did not.
- Does sex influence short-term memory ? You could arrange an experiment that tests whether men or women are better at remembering specific types of information.
- How likely are people to conform in groups ? Try this experiment to see what percentage of people are likely to conform . Enlist confederates to give the wrong response to a math problem and then see if the participants defy or conform to the rest of the group.
- How much information can people store in short-term memory ? Have participants study a word list and then test their memory. Try different versions of the experiment to see which memorization strategies, like chunking or mnemonics, are most effective.
Once you have an idea, the next step is to learn more about how to conduct a psychology experiment .
Psychology Experiments on Your Interests
If none of the ideas in the list above grabbed your attention, there are other ways to find inspiration for your psychology experiments.
How do you come up with good psychology experiments? One of the most effective approaches is to look at the various problems, situations, and questions that you are facing in your own life.
You can also think about the things that interest you. Start by considering the topics you've studied in class thus far that have really piqued your interest. Then, whittle the list down to two or three major areas within psychology that seem to interest you the most.
From there, make a list of questions you have related to the topic. Any of these questions could potentially serve as an experiment idea.
Use Textbooks for Inspiration for Psychology Experiments
Your psychology textbooks are another excellent source you can turn to for experiment ideas. Choose the chapters or sections that you find particularly interesting—perhaps it's a chapter on social psychology or a section on child development.
Start by browsing the experiments discussed in your book. Then think of how you could devise an experiment related to some of the questions your text asks. The reference section at the back of your textbook can also serve as a great source for additional reference material.

Discuss Psychology Experiments with Other Students
It can be helpful to brainstorm with your classmates to gather outside ideas and perspectives. Get together with a group of students and make a list of interesting ideas, subjects, or questions you have.
The information from your brainstorming session can serve as a basis for your experiment topic. It's also a great way to get feedback on your own ideas and to determine if they are worth exploring in greater depth.
Study Classic Psychology Experiments
Taking a closer look at a classic psychology experiment can be an excellent way to trigger some unique and thoughtful ideas of your own. To start, you could try conducting your own version of a famous experiment or even updating a classic experiment to assess a slightly different question.
Famous Psychology Experiments
Examples of famous psychology experiments that might be a source of further questions you'd like to explore include:
- Marshmallow test experiments
- Little Albert experiment
- Hawthorne effect experiments
- Bystander effect experiments
- Robbers Cave experiments
- Halo effect experiments
- Piano stairs experiment
- Cognitive dissonance experiments
- False memory experiments
You might not be able to replicate an experiment exactly (lots of classic psychology experiments have ethical issues that would preclude conducting them today), but you can use well-known studies as a basis for inspiration.
Review the Literature on Psychology Experiments
If you have a general idea about what topic you'd like to experiment, you might want to spend a little time doing a brief literature review before you start designing. In other words, do your homework before you invest too much time on an idea.
Visit your university library and find some of the best books and articles that cover the particular topic you are interested in. What research has already been done in this area? Are there any major questions that still need to be answered? What were the findings of previous psychology experiments?
Tackling this step early will make the later process of writing the introduction to your lab report or research paper much easier.
Ask Your Instructor About Ideas for Psychology Experiments
If you have made a good effort to come up with an idea on your own but you're still feeling stumped, it might help to talk to your instructor. Ask for pointers on finding a good experiment topic for the specific assignment. You can also ask them to suggest some other ways you could generate ideas or inspiration.
While it can feel intimidating to ask for help, your instructor should be more than happy to provide some guidance. Plus, they might offer insights that you wouldn't have gathered on your own. Your instructor probably has lots of ideas for psychology experiments that would be worth exploring.
If you need to design or conduct psychology experiments, there are plenty of great ideas (both old and new) for you to explore. Consider an idea from the list above or turn some of your own questions about the human mind and behavior into an experiment.
Before you dive in, make sure that you are observing the guidelines provided by your instructor and always obtain the appropriate permission before conducting any research with human or animal subjects.
Frequently Asked Questions
Finding a topic for a research paper is much like finding an idea for an experiment. Start by considering your own interests, or browse though your textbooks for inspiration. You might also consider looking at online news stories or journal articles as a source of inspiration.
Three of the most classic social psychology experiments are:
- The Asch Conformity Experiment : This experiment involved seeing if people would conform to group pressure when rating the length of a line.
- The Milgram Obedience Experiment : This experiment involved ordering participants to deliver what they thought was a painful shock to another person.
- The Stanford Prison Experiment : This experiment involved students replicating a prison environment to see how it would affect participant behavior.
Jakovljević T, Janković MM, Savić AM, et al. The effect of colour on reading performance in children, measured by a sensor hub: From the perspective of gender . PLoS One . 2021;16(6):e0252622. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0252622
Greenberg DM, et al. Musical preferences are linked to cognitive styles . PLoS One. 2015;10(7). doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0131151
Kurt S, Osueke KK. The effects of color on the moods of college students . Sage. 2014;4(1). doi:10.1177/2158244014525423
Hartline-Grafton H, Levin M. Breakfast and School-Related Outcomes in Children and Adolescents in the US: A Literature Review and its Implications for School Nutrition Policy . Curr Nutr Rep . 2022;11(4):653-664. doi:10.1007/s13668-022-00434-z
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."

The 11 Most Influential Psychological Experiments in History
The history of psychology is marked by groundbreaking experiments that transformed our understanding of the human mind. These 11 Most Influential Psychological Experiments in History stand out as pivotal, offering profound insights into behaviour, cognition, and the complexities of human nature.
In this PsychologyOrg article, we’ll explain these key experiments, exploring their impact on our understanding of human behaviour and the intricate workings of the mind.
Table of Contents
Experimental psychology.
Experimental psychology is a branch of psychology that uses scientific methods to study human behaviour and mental processes. Researchers in this field design experiments to test hypotheses about topics such as perception, learning, memory, emotion, and motivation.
They use a variety of techniques to measure and analyze behaviour and mental processes, including behavioural observations, self-report measures, physiological recordings, and computer simulations. The findings of experimental psychology studies can have important implications for a wide range of fields, including education, healthcare, and public policy.
Experimental Psychology, Psychologists have long tried to gain insight into how we perceive the world, to understand what motivates our behavior. They have made great strides in lifting that veil of mystery. In addition to providing us with food for stimulating party conversations, some of the most famous psychological experiments of the last century reveal surprising and universal truths about nature.

Throughout the history of psychology, revolutionary experiments have reshaped our comprehension of the human mind. These 11 experiments are pivotal, providing deep insights into human behaviour, cognition, and the intricate facets of human nature.
1. Kohler and the Chimpanzee experiment
Wolfgang Kohler studied the insight process by observing the behaviour of chimpanzees in a problem situation. In the experimental situation, the animals were placed in a cage outside of which food, for example, a banana, was stored. There were other objects in the cage, such as sticks or boxes. The animals participating in the experiment were hungry, so they needed to get to the food. At first, the chimpanzee used sticks mainly for playful activities; but suddenly, in the mind of the hungry chimpanzee, a relationship between sticks and food developed.
The cane, from an object to play with, became an instrument through which it was possible to reach the banana placed outside the cage. There has been a restructuring of the perceptual field: Kohler stressed that the appearance of the new behaviour was not the result of random attempts according to a process of trial and error. It is one of the first experiments on the intelligence of chimpanzees.
2. Harlow’s experiment on attachment with monkeys
In a scientific paper (1959), Harry F. Harlow described how he had separated baby rhesus monkeys from their mothers at birth, and raised them with the help of “puppet mothers”: in a series of experiments he compared the behavior of monkeys in two situations:
Little monkeys with a puppet mother without a bottle, but covered in a soft, fluffy, and furry fabric. Little monkeys with a “puppet” mother that supplied food, but was covered in wire. The little monkeys showed a clear preference for the “furry” mother, spending an average of fifteen hours a day attached to her, even though they were exclusively fed by the “suckling” puppet mother. conclusions of the Harlow experiment: all the experiments showed that the pleasure of contact elicited attachment behaviours, but the food did not.
3. The Strange Situation by Mary Ainsworth
Building on Bowlby’s attachment theory, Mary Ainsworth and colleagues (1978) have developed an experimental method called the Strange Situation, to assess individual differences in attachment security. The Strange Situation includes a series of short laboratory episodes in a comfortable environment and the child’s behaviors are observed.
Ainsworth and colleagues have paid special attention to the child’s behaviour at the time of reunion with the caregiver after a brief separation, thus identifying three different attachment patterns or styles, so called from that moment on. kinds of attachment according to Mary Ainsworth:
Secure attachment (63% of the dyads examined) Anxious-resistant or ambivalent (16%) Avoidant (21%) The Strange Situation by Mary Ainsworth
In a famous 1971 experiment, known as the Stanford Prison, Zimbardo and a team of collaborators reproduced a prison in the garages of Stanford University to study the behaviour of subjects in a context of very particular and complex dynamics. Let’s see how it went and the thoughts on the Stanford prison experiment. The participants (24 students) were randomly divided into two groups:
“ Prisoners “. The latter were locked up in three cells in the basement of a University building for six days; they were required to wear a white robe with a paper over it and a chain on the right ankle. “ Guards “. The students who had the role of prison guards had to watch the basement, choose the most appropriate methods to maintain order, and make the “prisoners” perform various tasks; they were asked to wear dark glasses and uniforms, and never to be violent towards the participants of the opposite role. However, the situation deteriorated dramatically: the fake police officers very soon began to seriously mistreat and humiliate the “detainees”, so it was decided to discontinue the experiment.
4. Jane Elliot’s Blue Eyes Experiment
On April 5, 1968, in a small school in Riceville, Iowa, Professor Jane Elliot decided to give a practical lesson on racism to 28 children of about eight years of age through the blue eyes brown eyes experiment.
“Children with brown eyes are the best,” the instructor began. “They are more beautiful and intelligent.” She wrote the word “melanin” on the board and explained that it was a substance that made people intelligent. Dark-eyed children have more, so they are more intelligent, while blue-eyed children “go hand in hand.”
In a very short time, the brown-eyed children began to treat their blue-eyed classmates with superiority, who in turn lost their self-confidence. A very good girl started making mistakes during arithmetic class, and at recess, she was approached by three little friends with brown eyes “You have to apologize because you get in their way and because we are the best,” said one of them. The girl hastened to apologize. This is one of the psychosocial experiments demonstrating how beliefs and prejudices play a role.
5. The Bobo de Bbandura doll
Albert Bandura gained great fame for the Bobo doll experiment on child imitation aggression, where:
A group of children took as an example, by visual capacity, the adults in a room, without their behaviour being commented on, hit the Bobo doll. Other contemporaries, on the other hand, saw adults sitting, always in absolute silence, next to Bobo.
Finally, all these children were brought to a room full of toys, including a doll like Bobo. Of the 10 children who hit the doll, 8 were those who had seen it done before by an adult. This explains how if a model that we follow performs a certain action, we are tempted to imitate it and this happens especially in children who still do not have the experience to understand for themselves if that behaviour is correct or not.
6. Milgram’s experiment
The Milgram experiment was first carried out in 1961 by psychologist Stanley Milgram, as an investigation into the degree of our deference to authority. A subject is invited to give an electric shock to an individual playing the role of the student, positioned behind a screen when he does not answer a question correctly. An authorized person then tells the subject to gradually increase the intensity of the shock until the student screams in pain and begs to stop.
No justification is given, except for the fact that the authorized person tells the subject to obey. In reality, it was staged: there was absolutely no electric shock given, but in the experiment two-thirds of the subjects were influenced by what they thought was a 450-volt shock, simply because a person in authority told them they would not be responsible for it. nothing.
7. little Albert
We see little Albert’s experiment on unconditioned stimulus, which must be the most famous psychological study. John Watson and Rosalie Raynor showed a white laboratory rat to a nine-month-old boy, little Albert. At first, the boy showed no fear, but then Watson jumped up from behind and made him flinch with a sudden noise by hitting a metal bar with a hammer. Of course, the noise frightened little Albert, who began to cry.
Every time the rat was brought out, Watson and Raynor would rattle the bar with their hammer to scare the poor boy away. Soon the mere sight of the rat was enough to reduce little Albert to a trembling bundle of nerves: he had learned to fear the sight of a rat, and soon afterwards began to fear a series of similar objects shown to him.
8. Pavlov’s dog
Ivan Pavlov’s sheepdog became famous for his experiments that led him to discover what we call “classical conditioning” or “Pavlovian reflex” and is still a very famous psychological experiment today. Hardly any other psychological experiment is cited so often and with such gusto as Pavlov’s theory expounded in 1905: the Russian physiologist had been impressed by the fact that his dogs did not begin to drool at the sight of food, but rather when they heard it. to the laboratory employees who took it away.
He researched it and ordered a buzzer to ring every time it was mealtime. Very soon the sound of the doorbell was enough for the dogs to start drooling: they had connected the signal to the arrival of food.
9. Asch’s experiment
It is about a social psychology experiment carried out in 1951 by the Polish psychologist Solomon Asch on the influence of the majority and social conformity.
The experiment is based on the idea that being part of a group is a sufficient condition to change a person’s actions, judgments, and visual perceptions. The very simple experiment consisted of asking the subjects involved to associate line 1 drawn on a white sheet with the corresponding one, choosing between three different lines A, B, and C present on another sheet. Only one was identical to the other, while the other two were longer or shorter.
The experimentation was carried out in three phases. As soon as one of the subjects, Asch’s accomplice gave a wrong answer associating line 1 with the wrong one, the other members of the group also made the same mistake, even though the correct answer was more than obvious. The participants questioned the reason for this choice and responded that aware of the correct answer, they had decided to conform to the group, adapting to those who had preceded them.
psychotherapy definition types and techniques | Psychotherapy vs therapy Psychologyorg.com
10. Rosenbaum’s experiment
Among the most interesting investigations in this field, an experiment carried out by David Rosenhan (1923) to document the low validity of psychiatric diagnoses stands out. Rosenhan admitted eight assistants to various psychiatric hospitals claiming psychotic symptoms, but once they entered the hospital they behaved as usual.
Despite this, they were held on average for 19 days, with all but one being diagnosed as “psychotic”. One of the reasons why the staff is not aware of the “normality” of the subjects, is, according to Rosenhan, the very little contact between the staff and the patients.
11. Bystander Effect (1968)
The Bystander Effect studied in 1968 after the tragic case of Kitty Genovese, explores how individuals are less likely to intervene in emergencies when others are present. The original research by John Darley and Bibb Latané involved staged scenarios where participants believed they were part of a discussion via intercom.
In the experiment, participants were led to believe they were communicating with others about personal problems. Unknown to them, the discussions were staged, and at a certain point, a participant (confederate) pretended to have a seizure or needed help.
The results were startling. When participants believed they were the sole witness to the emergency, they responded quickly and sought help. However, when they thought others were also present (but were confederates instructed to not intervene), the likelihood of any individual offering help significantly decreased. This phenomenon became known as the Bystander Effect.
The diffusion of responsibility, where individuals assume others will take action, contributes to this effect. The presence of others creates a diffusion of responsibility among bystanders, leading to a decreased likelihood of any single individual taking action.
This experiment highlighted the social and psychological factors influencing intervention during emergencies and emphasized the importance of understanding bystander behaviour in critical situations.
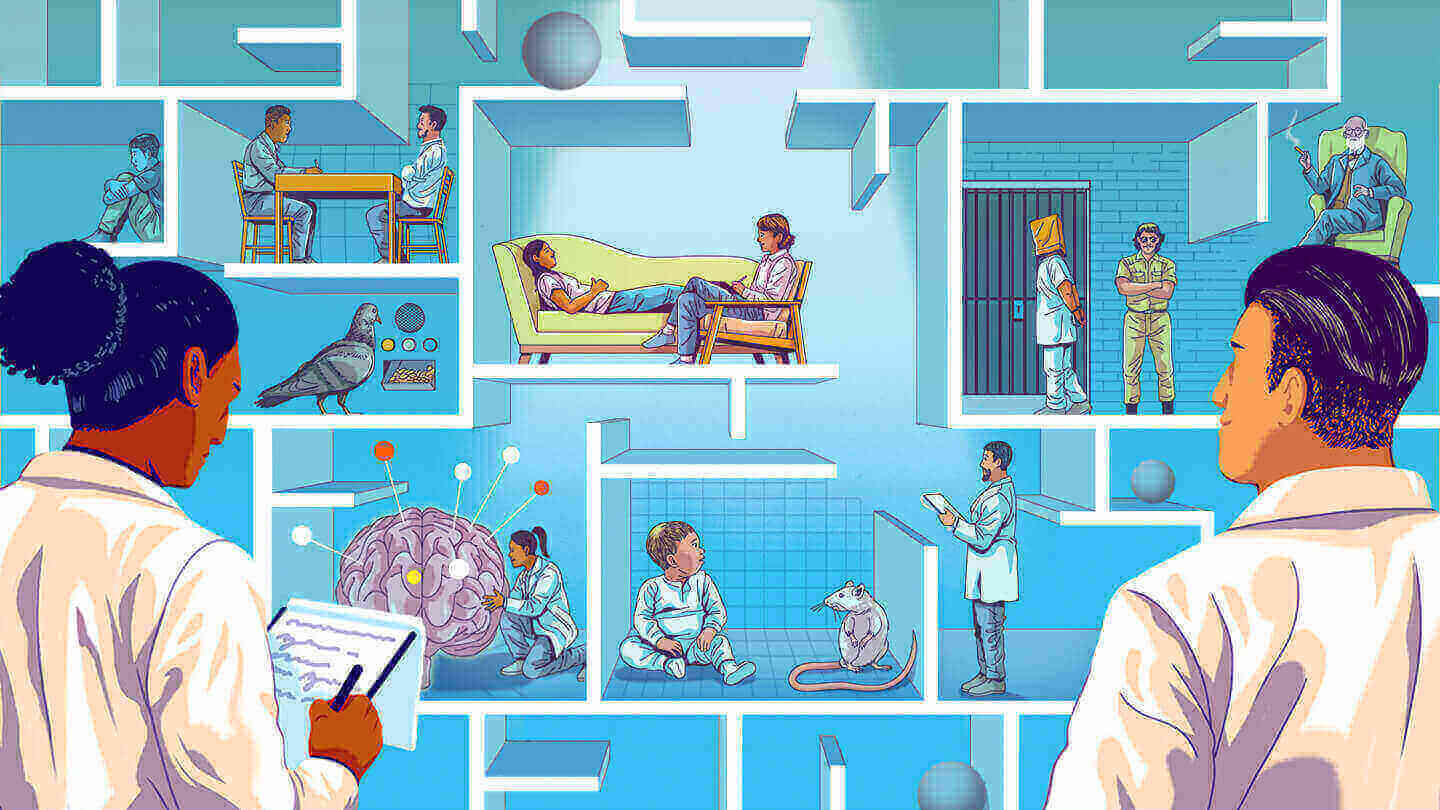
The journey through the “11 Most Influential Psychological Experiments in History” illuminates the profound impact these studies have had on our understanding of human behaviour, cognition, and social dynamics.
Each experiment stands as a testament to the dedication of pioneering psychologists who dared to delve into the complexities of the human mind. From Milgram’s obedience studies to Zimbardo’s Stanford Prison Experiment, these trials have shaped not only the field of psychology but also our societal perceptions and ethical considerations in research.
They serve as timeless benchmarks, reminding us of the ethical responsibilities and the far-reaching implications of delving into the human psyche. The enduring legacy of these experiments lies not only in their scientific contributions but also in the ethical reflections they provoke, urging us to navigate the boundaries of knowledge with caution, empathy, and an unwavering commitment to understanding the intricacies of our humanity.
What is the most famous experiment in the history of psychology?
One of the most famous experiments is the Milgram Experiment, conducted by Stanley Milgram in the 1960s. It investigated obedience to authority figures and remains influential in understanding human behaviour.
Who wrote the 25 most influential psychological experiments in history?
The book “The 25 Most Influential Psychological Experiments in History” was written by Michael Shermer, a science writer and historian of science.
What is the history of experimental psychology?
Experimental psychology traces back to Wilhelm Wundt, often considered the father of experimental psychology. He established the first psychology laboratory in 1879 at the University of Leipzig, marking the formal beginning of experimental psychology as a distinct field.
What was the psychological experiment in the 1960s?
Many significant psychological experiments were conducted in the 1960s. One notable example is the Stanford Prison Experiment led by Philip Zimbardo, which examined the effects of situational roles on behaviour.
Who was the first experimental psychologist?
Wilhelm Wundt is often regarded as the first experimental psychologist due to his establishment of the first psychology laboratory and his emphasis on empirical research methods in psychology.
If you want to read more articles similar to The 11 Most Influential Psychological Experiments in History , we recommend that you enter our Psychology category.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
0, text: error()">
0, text: error(), css: errorCssClass">
Reset your password
Enter your email address or username and we’ll send you a link to reset your password
Check your inbox
An email with a link to reset your password was sent to the email address associated with your account
Provide email
Please enter your email to complete registration
Activate to continue
Your account isn't active yet. We've emailed you an activation link. Please check your inbox and click the link to activate your account
0, text: error" style="display: none;">
0, text: success" style="display: none;">

- Relationships
The Bored Panda iOS app is live! Fight boredom with iPhones and iPads here .
- Partnership
- Success stories
- --> -->