
Advantages and disadvantages of literature review
This comprehensive article explores some of the advantages and disadvantages of literature review in research. Reviewing relevant literature is a key area in research, and indeed, it is a research activity in itself. It helps researchers investigate a particular topic in detail. However, it has some limitations as well.
What is literature review?
In order to understand the advantages and disadvantages of literature review, it is important to understand what a literature review is and how it differs from other methods of research. According to Jones and Gratton (2009) a literature review essentially consists of critically reading, evaluating, and organising existing literature on a topic to assess the state of knowledge in the area. It is sometimes called critical review.
A literature review is a select analysis of existing research which is relevant to a researcher’s selected topic, showing how it relates to their investigation. It explains and justifies how their investigation may help answer some of the questions or gaps in the chosen area of study (University of Reading, 2022).
A literature review is a term used in the field of research to describe a systematic and methodical investigation of the relevant literature on a particular topic. In other words, it is an analysis of existing research on a topic in order to identify any relevant studies and draw conclusions about the topic.
A literature review is not the same as a bibliography or a database search. Rather than simply listing references to sources of information, a literature review involves critically evaluating and summarizing existing research on a topic. As such, it is a much more detailed and complex process than simply searching databases and websites, and it requires a lot of effort and skills.
Advantages of literature review
Information synthesis
A literature review is a very thorough and methodical exercise. It can be used to synthesize information and draw conclusions about a particular topic. Through a careful evaluation and critical summarization, researchers can draw a clear and comprehensive picture of the chosen topic.
Familiarity with the current knowledge
According to the University of Illinois (2022), literature reviews allow researchers to gain familiarity with the existing knowledge in their selected field, as well as the boundaries and limitations of that field.
Creation of new body of knowledge
One of the key advantages of literature review is that it creates new body of knowledge. Through careful evaluation and critical summarisation, researchers can create a new body of knowledge and enrich the field of study.
Answers to a range of questions
Literature reviews help researchers analyse the existing body of knowledge to determine the answers to a range of questions concerning a particular subject.
Disadvantages of literature review
Time consuming
As a literature review involves collecting and evaluating research and summarizing the findings, it requires a significant amount of time. To conduct a comprehensive review, researchers need to read many different articles and analyse a lot of data. This means that their review will take a long time to complete.
Lack of quality sources
Researchers are expected to use a wide variety of sources of information to present a comprehensive review. However, it may sometimes be challenging for them to identify the quality sources because of the availability of huge numbers in their chosen field. It may also happen because of the lack of past empirical work, particularly if the selected topic is an unpopular one.
Descriptive writing
One of the major disadvantages of literature review is that instead of critical appreciation, some researchers end up developing reviews that are mostly descriptive. Their reviews are often more like summaries of the work of other writers and lack in criticality. It is worth noting that they must go beyond describing the literature.
Key features of literature review
Clear organisation
A literature review is typically a very critical and thorough process. Universities usually recommend students a particular structure to develop their reviews. Like all other academic writings, a review starts with an introduction and ends with a conclusion. Between the beginning and the end, researchers present the main body of the review containing the critical discussion of sources.
No obvious bias
A key feature of a literature review is that it should be very unbiased and objective. However, it should be mentioned that researchers may sometimes be influenced by their own opinions of the world.
Proper citation
One of the key features of literature review is that it must be properly cited. Researchers should include all the sources that they have used for information. They must do citations and provide a reference list by the end in line with a recognized referencing system such as Harvard.
To conclude this article, it can be said that a literature review is a type of research that seeks to examine and summarise existing research on a particular topic. It is an essential part of a dissertation/thesis. However, it is not an easy thing to handle by an inexperienced person. It also requires a lot of time and patience.
Hope you like this ‘Advantages and disadvantages of literature review’. Please share this with others to support our research work.
Other useful articles:
How to evaluate website content
Advantages and disadvantages of primary and secondary research
Advantages and disadvantages of simple random sampling
Last update: 08 May 2022
References:
Jones, I., & Gratton, C. (2009) Research Methods for Sports Shttps://www.howandwhat.net/new/evaluate-website-content/tudies, 2 nd edition, London: Routledge
University of Illinois (2022) Literature review, available at: https://www.uis.edu/learning-hub/writing-resources/handouts/learning-hub/literature-review (accessed 08 May 2022)
University of Reading (2022) Literature reviews, available at: https://libguides.reading.ac.uk/literaturereview/starting (accessed 07 May 2022)

Author: M Rahman
M Rahman writes extensively online and offline with an emphasis on business management, marketing, and tourism. He is a lecturer in Management and Marketing. He holds an MSc in Tourism & Hospitality from the University of Sunderland. Also, graduated from Leeds Metropolitan University with a BA in Business & Management Studies and completed a DTLLS (Diploma in Teaching in the Life-Long Learning Sector) from London South Bank University.
Related Posts
How to be a good team player, competitive advantage for tourist destinations, advantages and disadvantages of snowball sampling.

- About the LSE Impact Blog
- Comments Policy
- Popular Posts
- Recent Posts
- Subscribe to the Impact Blog
- Write for us
- LSE comment
Neal Haddaway
October 19th, 2020, 8 common problems with literature reviews and how to fix them.
3 comments | 326 shares
Estimated reading time: 5 minutes
Literature reviews are an integral part of the process and communication of scientific research. Whilst systematic reviews have become regarded as the highest standard of evidence synthesis, many literature reviews fall short of these standards and may end up presenting biased or incorrect conclusions. In this post, Neal Haddaway highlights 8 common problems with literature review methods, provides examples for each and provides practical solutions for ways to mitigate them.
Enjoying this blogpost? 📨 Sign up to our mailing list and receive all the latest LSE Impact Blog news direct to your inbox.
Researchers regularly review the literature – it’s an integral part of day-to-day research: finding relevant research, reading and digesting the main findings, summarising across papers, and making conclusions about the evidence base as a whole. However, there is a fundamental difference between brief, narrative approaches to summarising a selection of studies and attempting to reliably and comprehensively summarise an evidence base to support decision-making in policy and practice.
So-called ‘evidence-informed decision-making’ (EIDM) relies on rigorous systematic approaches to synthesising the evidence. Systematic review has become the highest standard of evidence synthesis and is well established in the pipeline from research to practice in the field of health . Systematic reviews must include a suite of specifically designed methods for the conduct and reporting of all synthesis activities (planning, searching, screening, appraising, extracting data, qualitative/quantitative/mixed methods synthesis, writing; e.g. see the Cochrane Handbook ). The method has been widely adapted into other fields, including environment (the Collaboration for Environmental Evidence ) and social policy (the Campbell Collaboration ).

Despite the growing interest in systematic reviews, traditional approaches to reviewing the literature continue to persist in contemporary publications across disciplines. These reviews, some of which are incorrectly referred to as ‘systematic’ reviews, may be susceptible to bias and as a result, may end up providing incorrect conclusions. This is of particular concern when reviews address key policy- and practice- relevant questions, such as the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic or climate change.
These limitations with traditional literature review approaches could be improved relatively easily with a few key procedures; some of them not prohibitively costly in terms of skill, time or resources.
In our recent paper in Nature Ecology and Evolution , we highlight 8 common problems with traditional literature review methods, provide examples for each from the field of environmental management and ecology, and provide practical solutions for ways to mitigate them.
There is a lack of awareness and appreciation of the methods needed to ensure systematic reviews are as free from bias and as reliable as possible: demonstrated by recent, flawed, high-profile reviews. We call on review authors to conduct more rigorous reviews, on editors and peer-reviewers to gate-keep more strictly, and the community of methodologists to better support the broader research community. Only by working together can we build and maintain a strong system of rigorous, evidence-informed decision-making in conservation and environmental management.
Note: This article gives the views of the authors, and not the position of the LSE Impact Blog, nor of the London School of Economics. Please review our comments policy if you have any concerns on posting a comment below
Image credit: Jaeyoung Geoffrey Kang via unsplash

About the author

Neal Haddaway is a Senior Research Fellow at the Stockholm Environment Institute, a Humboldt Research Fellow at the Mercator Research Institute on Global Commons and Climate Change, and a Research Associate at the Africa Centre for Evidence. He researches evidence synthesis methodology and conducts systematic reviews and maps in the field of sustainability and environmental science. His main research interests focus on improving the transparency, efficiency and reliability of evidence synthesis as a methodology and supporting evidence synthesis in resource constrained contexts. He co-founded and coordinates the Evidence Synthesis Hackathon (www.eshackathon.org) and is the leader of the Collaboration for Environmental Evidence centre at SEI. @nealhaddaway
Why is mission creep a problem and not a legitimate response to an unexpected finding in the literature? Surely the crucial points are that the review’s scope is stated clearly and implemented rigorously, not when the scope was finalised.
- Pingback: Quick, but not dirty – Can rapid evidence reviews reliably inform policy? | Impact of Social Sciences
#9. Most of them are terribly boring. Which is why I teach students how to make them engaging…and useful.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Notify me of follow-up comments by email.
Related Posts

“But I’m not ready!” Common barriers to writing and how to overcome them
November 16th, 2020.

“Remember a condition of academic writing is that we expose ourselves to critique” – 15 steps to revising journal articles
January 18th, 2017.

A simple guide to ethical co-authorship
March 29th, 2021.

How common is academic plagiarism?
February 8th, 2024.

Visit our sister blog LSE Review of Books
Pros and Cons of Literature Review
Table of Contents
Understanding the Purpose of a Literature Review in Research
A literature review is a comprehensive overview of existing research and scholarly articles on a particular topic. Its primary purpose is to synthesize and evaluate the current state of knowledge, identifying central themes, methodologies, and findings from various sources. This process helps researchers contextualize their work within the broader academic conversation, ensuring that their contributions are relevant and informed. According to the American Psychological Association (APA), a well-crafted literature review provides a framework for understanding previous research that can guide further inquiry.
Moreover, literature reviews serve as foundational elements in various types of research, including dissertations, theses, and grant proposals. They outline what is already known, highlight the importance of the topic, and justify the necessity for further research. By doing so, literature reviews not only support the researcher’s arguments but also help establish credibility and authority in their chosen field. This engagement with existing scholarship demonstrates a thorough understanding of the topic, which is crucial for any academic endeavor.
The literature review process also fosters critical thinking and analytical skills, as researchers must assess the quality and relevance of various sources. This intellectual rigor encourages scholars to engage with a diverse array of perspectives, leading to a more nuanced understanding of the subject matter. Ultimately, the purpose of a literature review is multifaceted: it contextualizes research, identifies gaps, and enhances the overall integrity of academic work.
Advantages of Conducting a Thorough Literature Review
One of the primary advantages of conducting a thorough literature review is the ability to gain a comprehensive understanding of a particular field or topic. By reviewing a wide range of sources, researchers can identify trends, patterns, and notable developments in their area of interest. This rich context not only informs their research but also exposes them to a variety of methodologies and theoretical frameworks. According to a study published in the journal Research Studies , researchers who engage in extensive literature reviews often produce higher-quality work, as they can draw on a wealth of existing knowledge.
Furthermore, a literature review allows researchers to discover key authors and seminal works that have shaped their field. By understanding which studies are most frequently cited, researchers can pinpoint influential theories and debates, thus enriching their own contributions. This awareness fosters a sense of belonging within the academic community and encourages constructive dialogue among scholars. In fact, a literature review can help facilitate collaborations, as researchers share common interests and expertise.
Lastly, conducting a thorough literature review enhances the likelihood of funding for research projects. Granting agencies often require applicants to demonstrate a comprehensive understanding of existing research, as this showcases the project’s relevance and significance. A well-researched literature review can thus serve as a persuasive argument for why the proposed research is necessary, making it an essential component of successful grant applications.
Identifying Gaps in Existing Research: A Key Benefit
One of the most critical benefits of conducting a literature review is the ability to identify gaps in existing research. By systematically reviewing the literature, researchers can pinpoint areas that have been overlooked, underexplored, or lack consensus. This process leads to the formulation of new research questions that can significantly advance the field. According to a survey conducted by the American Educational Research Association , nearly 70% of researchers indicated that identifying gaps in literature was a primary motivation for their work.
Identifying these gaps not only contributes to the advancement of knowledge in a specific area but also opens doors for innovative research opportunities. By addressing these unexplored areas, researchers can make meaningful contributions that challenge established norms or introduce novel perspectives. This can lead to groundbreaking findings that reshape the understanding of a particular field and inspire future inquiries.
Moreover, recognizing gaps in the literature can assist researchers in justifying the need for their studies. When researchers can demonstrate that existing literature lacks sufficient exploration of certain topics, it strengthens their case for why their research is not only relevant but necessary. This alignment with the broader academic discourse enhances the overall impact of the research and can result in more significant citations and attention from fellow scholars.
The Time-Consuming Nature of Literature Reviews
Despite the many advantages of literature reviews, one significant drawback is that they can be extremely time-consuming. Researchers may spend weeks or even months sifting through articles, books, and other sources to ensure they are well-informed about their topic. According to a study by the National Institutes of Health, an average literature review can take 22 hours per week over several months, resulting in a substantial time investment that can detract from other critical aspects of the research process.
Additionally, the sheer volume of published literature can be overwhelming. With thousands of articles published annually in various academic fields, narrowing down the relevant materials requires considerable effort. Researchers must develop effective search strategies and utilize databases efficiently to manage this information overload. This process can lead to frustration and exhaustion, particularly for early-career researchers who may not yet have mastered these skills.
Finally, the time spent on literature reviews may delay the actual research process. Researchers may find themselves so engrossed in reviewing existing literature that they struggle to move forward with their original research questions. This prolonged phase of exploration can hinder productivity and may even lead to missed deadlines or extended research timelines, ultimately affecting the quality and timeliness of their work.
Potential for Bias in Literature Review Selection Process
Another important challenge associated with literature reviews is the potential for bias in the selection process. Researchers may unintentionally favor certain studies or perspectives, influenced by their own beliefs, experiences, or institutional affiliations. This bias can lead to an incomplete or skewed representation of the existing body of literature, ultimately compromising the integrity of the review. According to a study published in PLOS ONE , biases in literature selection can significantly affect research outcomes and interpretations.
Moreover, the tendency to rely on easily accessible or more recently published studies can further exacerbate this issue. Researchers may overlook older but relevant works or fail to include marginalized voices in the academic discourse. This narrow approach can perpetuate existing power dynamics within scholarly fields and limit the diversity of viewpoints presented in literature reviews. It is crucial for researchers to actively seek out a variety of sources and perspectives to present a balanced viewpoint.
To mitigate bias, scholars can employ systematic review methodologies, which provide structured guidelines for identifying and selecting literature. By following these rigorous protocols, researchers can enhance the transparency and reliability of their literature reviews. However, even with these strategies, complete objectivity is challenging to achieve, and a critical awareness of potential biases remains essential for maintaining the credibility of the review process.
How Literature Reviews Enhance Research Credibility
Conducting a well-structured literature review significantly enhances the credibility of a research study. By showcasing a thorough understanding of the existing body of knowledge, researchers can demonstrate their expertise and commitment to the field. A literature review provides a backdrop against which the new research can be compared and evaluated, situating the study within the broader academic context. This contextualization is vital for establishing the research’s relevance and significance, which can ultimately lead to greater trust from readers and peers.
Additionally, literature reviews help to substantiate hypotheses and research questions by providing empirical support from previously published studies. Citing reputable sources lends weight to the research arguments and findings, reinforcing their validity. According to the Journal of Research Practice , studies that include comprehensive literature reviews are cited 45% more often than those that do not, indicating a strong correlation between literature reviews and research impact.
Moreover, the process of conducting a literature review encourages transparency in the research process. By documenting the sources consulted, methodologies employed, and the rationale behind the selection of literature, researchers allow others to trace their intellectual journey. This transparency enhances accountability and fosters a culture of open inquiry, increasing the overall credibility of the research itself.
Limitations of Literature Reviews in Providing New Insights
While literature reviews play an essential role in synthesizing existing knowledge, they often have limitations in providing new insights. A literature review primarily focuses on summarizing and analyzing existing studies, which can lead to redundancy in findings. Researchers may find that many publications reiterate similar conclusions, which can stifle innovation and creative thinking. A meta-analysis conducted by Research Trends revealed that up to 60% of literature reviews in certain disciplines merely confirm prior research without offering fresh perspectives.
Additionally, literature reviews may struggle to address rapidly evolving fields, where new studies emerge frequently. In such cases, a literature review may become outdated quickly, limiting its applicability to current research needs. For example, in fields such as technology and medicine, new findings can significantly reshape existing knowledge, rendering earlier literature reviews less relevant. Researchers must constantly assess and update their literature reviews to keep pace with advancements, a process that can be resource-intensive.
Moreover, literature reviews often lack the ability to generate novel hypotheses, as they primarily summarize existing knowledge rather than proposing new theories or models. This limitation is particularly pronounced in fields where empirical testing is essential for theoretical advancements. Researchers must balance the insights gleaned from literature reviews with original research to drive innovation and contribute new knowledge to their respective fields.
Balancing the Pros and Cons for Effective Research Outcomes
In conclusion, while literature reviews present several advantages, including the identification of research gaps and the enhancement of credibility, they also come with notable drawbacks, such as the potential for bias and the time-consuming nature of the process. To achieve effective research outcomes, scholars must be mindful of both the pros and cons associated with literature reviews. Striking the right balance entails harnessing the strengths of literature reviews while mitigating their limitations.
To optimize the literature review process, researchers can employ systematic approaches that promote inclusivity and diversity in source selection. By actively seeking out various perspectives and methodologies, scholars can create a more comprehensive and balanced overview of the existing literature. Furthermore, researchers should regularly update their literature reviews, ensuring that they remain relevant and reflective of the current state of knowledge in their fields.
Ultimately, a well-executed literature review can serve as a powerful tool for advancing research and fostering academic dialogue. By acknowledging the pros and cons and striving for a balanced approach, researchers can leverage literature reviews to enhance their research endeavors and contribute meaningful insights to the academic community.
Related posts:
- Types of Literature Reviews Explained
- Pros and Cons of Systematic Review
- Pros and Cons of Scientific Peer Review
- Pros and Cons of Peer Review
Jordon Layne
- 10 Best Vanilla Buttercream Frosting Recipes
- 10 Best Trail Mix Recipes
- 10 Best Sliders Recipes
- 10 Best Spicy Meatloaf Recipes
- 10 Best Smoked Meatloaf Recipes
- 10 Best Pumpkin Bar Recipes
- 10 Best Pineapple Cheese Ball Recipes
- 10 Best Jambalaya Recipes
- 10 Best Herbalife Tea Recipes With Defense
- 10 Best Ham And Beans Crockpot Recipes
Eight problems with literature reviews and how to fix them
Affiliations.
- 1 Mercator Research Institute on Climate Change and Global Commons, Berlin, Germany. [email protected].
- 2 Stockholm Environment Institute, Stockholm, Sweden. [email protected].
- 3 Africa Centre for Evidence, University of Johannesburg, Johannesburg, South Africa. [email protected].
- 4 College of Medicine and Health, Exeter University, Exeter, UK.
- 5 Department of Zoology, University of Cambridge, Cambridge, UK.
- 6 School of Biological Sciences, University of East Anglia, Norwich, UK.
- 7 Department of Biological Sciences, Royal Holloway University of London, Egham, UK.
- 8 Stockholm Environment Institute, Stockholm, Sweden.
- 9 Department of Zoology, University of Oxford, Oxford, UK.
- 10 Collaboration for Environmental Evidence, UK Centre, School of Natural Sciences, Bangor University, Bangor, UK.
- 11 Liljus ltd, London, UK.
- 12 Department of Forest Sciences, University of Helsinki, Helsinki, Finland.
- 13 Evidence Synthesis Lab, School of Natural and Environmental Sciences, University of Newcastle, Newcastle-upon-Tyne, UK.
- PMID: 33046871
- DOI: 10.1038/s41559-020-01295-x
Traditional approaches to reviewing literature may be susceptible to bias and result in incorrect decisions. This is of particular concern when reviews address policy- and practice-relevant questions. Systematic reviews have been introduced as a more rigorous approach to synthesizing evidence across studies; they rely on a suite of evidence-based methods aimed at maximizing rigour and minimizing susceptibility to bias. Despite the increasing popularity of systematic reviews in the environmental field, evidence synthesis methods continue to be poorly applied in practice, resulting in the publication of syntheses that are highly susceptible to bias. Recognizing the constraints that researchers can sometimes feel when attempting to plan, conduct and publish rigorous and comprehensive evidence syntheses, we aim here to identify major pitfalls in the conduct and reporting of systematic reviews, making use of recent examples from across the field. Adopting a 'critical friend' role in supporting would-be systematic reviews and avoiding individual responses to police use of the 'systematic review' label, we go on to identify methodological solutions to mitigate these pitfalls. We then highlight existing support available to avoid these issues and call on the entire community, including systematic review specialists, to work towards better evidence syntheses for better evidence and better decisions.
- Environment
- Research Design
- Systematic Reviews as Topic*
Eight common problems with science literature reviews and how to fix them
Research Fellow, Africa Centre for Evidence, University of Johannesburg
Disclosure statement
Neal Robert Haddaway works for the Stockholm Environment Institute and the Mercator Research Institute on Global Commons and Climate Change. He receives funding from the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation, Mistra, Formas, and Vinnova. He is also an honorary Research Associate at the Africa Centre for Evidence at the University of Johannesburg.
University of Johannesburg provides support as an endorsing partner of The Conversation AFRICA.
View all partners

Researchers regularly review the literature that’s generated by others in their field. This is an integral part of day-to-day research: finding relevant research, reading and digesting the main findings, summarising across papers, and making conclusions about the evidence base as a whole.
However, there is a fundamental difference between brief, narrative approaches to summarising a selection of studies and attempting to reliably, comprehensively summarise an evidence base to support decision-making in policy and practice.
So-called “evidence-informed decision-making” relies on rigorous systematic approaches to synthesising the evidence. Systematic review has become the highest standard of evidence synthesis. It is well established in the pipeline from research to practice in several fields including health , the environment and social policy . Rigorous systematic reviews are vital for decision-making because they help to provide the strongest evidence that a policy is likely to work (or not). They also help to avoid expensive or dangerous mistakes in the choice of policies.
But systematic review has not yet entirely replaced traditional methods of literature review. These traditional reviews may be susceptible to bias and so may end up providing incorrect conclusions. This is especially worrying when reviews address key policy and practice questions.
The good news is that the limitations of traditional literature review approaches could be improved relatively easily with a few key procedures. Some of these are not prohibitively costly in terms of skill, time or resources. That’s particularly important in African contexts, where resource constraints are a daily reality, but should not compromise the continent’s need for rigorous, systematic and transparent evidence to inform policy.
In our recent paper in Nature Ecology and Evolution , we highlighted eight common problems with traditional literature review methods. We gave examples for each problem, drawing from the field of environmental management and ecology. Finally, we outlined practical solutions.
These are the eight problems we identified in our paper .
First, traditional literature reviews can lack relevance. This is because limited stakeholder engagement can lead to a review that is of limited practical use to decision-makers.
Second, reviews that don’t publish their methods in an a priori (meaning that it is published before the review work begins) protocol may suffer from mission creep. In our paper we give the example of a 2019 review that initially stated it was looking at all population trends among insects. Instead, it ended up focusing only on studies that showed insect population declines. This could have been prevented by publishing and sticking to methods outlined in a protocol.
Third, a lack of transparency and replicability in the review methods may mean that the review cannot be replicated . Replicability is a central tenet of the scientific method.
Selection bias is another common problem. Here, the studies that are included in a literature review are not representative of the evidence base. A lack of comprehensiveness, stemming from an inappropriate search method, can also mean that reviews end up with the wrong evidence for the question at hand.
Traditional reviews may also exclude grey literature . This is defined as any document
produced on all levels of government, academics, business and industry in print and electronic formats, but which is not controlled by commercial publishers, i.e., where publishing is not the primary activity of the producing body.
It includes organisational reports and unpublished theses or other studies . Traditional reviews may also fail to test for evidence of publication bias; both these issues can result in incorrect or misleading conclusions. Another common error is to treat all evidence as equally valid. The reality is that some research studies are more valid than others. This needs to be accounted for in the synthesis.
Inappropriate synthesis is another common issue. This involves methods like vote-counting, which refers to tallying studies based on their statistical significance. Finally, a lack of consistency and error checking (as would happen when a reviewer works alone) can introduce errors and biases if a single reviewer makes decisions without consensus .
All of these common problems can be solved, though. Here’s how.
Stakeholders can be identified, mapped and contacted for feedback and inclusion without the need for extensive budgets. Best-practice guidelines for this process already exist .
Researchers can carefully design and publish an a priori protocol that outlines planned methods for searching, screening, data extraction, critical appraisal and synthesis in detail. Organisations like the Collaboration for Environmental Evidence have existing protocols from which people can draw.
Researchers also need to be explicit and use high-quality guidance and standards for review conduct and reporting . Several such standards already exist .
Another useful approach is to carefully design a search strategy with an info specialist; to trial the search strategy against a benchmark list; and to use multiple bibliographic databases, languages and sources of grey literature. Researchers should then publish their search methods in an a priori protocol for peer review.
Researchers should consider carefully planning and trialling a critical appraisal tool before starting the process in full, learning from existing robust critical appraisal tools . Critical appraisal is the carefully planned assessment of all possible risks of bias and possible confounders in a research study. Researchers should select their synthesis method carefully, based on the data analysed. Vote-counting should never be used instead of meta-analysis. Formal methods for narrative synthesis should be used to summarise and describe the evidence base.
Finally, at least two reviewers should screen a subset of the evidence base to ensure consistency and shared understanding of the methods before proceeding. Ideally, reviewers should conduct all decisions separately and then consolidate.
Collaboration
Collaboration is crucial to address the problems with traditional review processes. Authors need to conduct more rigorous reviews. Editors and peer reviewers need to gate-keep more strictly. The community of methodologists needs to better support the broader research community.
Working together, the academic and research community can build and maintain a strong system of rigorous, evidence-informed decision-making in conservation and environmental management – and, ultimately, in other disciplines.
- Systematic reviews
- Evidence based policy
- Academic research

Head of IT Operations

Research Fellow, Agricultural Sustainability

ARDC Project Management Office Manager

Lecturer / Senior Lecturer in Indigenous Knowledges

Professor in Physiotherapy

Strengths and Weaknesses of Systematic Reviews

Automate every stage of your literature review to produce evidence-based research faster and more accurately.
Systematic reviews are considered credible sources since they are comprehensive, reproducible, and precise in stating the outcomes. The type of review system used and the approach taken depend on the goals and objectives of the research. To choose the best-suited review system, researchers must be aware of the strengths and weaknesses of each one.
Let us now look at the strengths and limitations of systematic reviews.
Strengths Of Systematic Reviews
Systematic reviews have become increasingly popular owing to their transparency, accuracy, replicability, and reduced risk of bias. Some of the main benefits of systematic reviews are;
Specificity
Researchers can answer specific research questions of high importance. For example, the efficacy of a particular drug in the treatment of an illness.

Explicit Methodology
A systematic review requires rigorous planning. Each stage of the review is predefined to the last detail. The research question is formulated using the PICO (population, intervention, comparison, and outcome) approach. A strict eligibility criteria is then established for inclusion and exclusion criteria for selecting the primary studies for the review. Every stage of the systematic review methodology is pre-specified to the last detail and made publicly available, even before starting the review process. This makes all the stages in the methodology transparent and reproducible.
Reliable And Accurate Results
The results of a systematic review are either analyzed qualitatively and presented as a textual narrative or quantitatively using statistical methods such as meta-analyses and numeric effect estimates. The quality of evidence or the confidence in effect estimates is calculated using the standardized GRADE approach.
Comprehensive And Exhaustive
A systematic review involves a thorough search of all the available data on a certain topic. It is exhaustive and considers every bit of evidence in synthesizing the outcome. Primary sources for the review are collected from databases and multiple sources, such as blogs from pharmaceutical companies, unpublished research directly from researchers, government reports, and conference proceedings. These are referred to as grey literature. The search criteria and keywords used in sourcing are specific and predefined.
Reproducible
Learn more about distillersr.
(Article continues below)
Weaknesses Of Systematic Reviews
Although systematic reviews are robust tools in scientific research they are not immune to errors. They can be misleading, or even harmful if the data is inappropriately handled or if they are biased. Some of the limitations of systematic reviews include:
Mass Production
Due to the popularity systematic reviews have gained, they tend to be used more than required. The growth rate of systematic reviews has outpaced the growth rate of studies overall. This results in redundancy. For example, a survey published in the BMJ[1], included 73 randomly selected meta-analyses published in 2010 found that for two-thirds of these studies, there was at least one, and sometimes as many as 13, additional meta-analyses published on the same topic by early 2013.
Risk of Bias
Although systematic reviews have many advantages, they are also more susceptible to certain types of biases. A bias is a systematic or methodological error that causes misrepresentation of the study outcomes. As bias can appear at any stage, authors should be aware of the specific risks at each stage of the review process. Most of the known errors in systematic reviews arise in the selection and publication stages. The eligibility criterion in a systematic review helps to avoid selection bias. Poor study design and execution can also result in a biased outcome. It’s important to learn about the types of bias in systematic reviews .
Expressing Strong Opinions by Stealth
Selective outcome reporting is a major threat to a systematic review. The author or reviewer may decide to only report a selection of the statistically significant outcomes that suit his interest. The possibility of unfair or misleading interpretation of evidence outcomes in a systematic review can have serious implications.
Like any review system, systematic reviews have their advantages and disadvantages. Understanding them is essential to making a choice of which review system to use.
Overlapping meta-analyses on the same topic: survey of published studies. BMJ 2013; 347:f4501
3 Reasons to Connect


Dissertations - Skills Guide
- Where to start
- Research Proposal
- Ethics Form
- Primary Research
Literature Review
- Methodology
- Downloadable Resources
- Further Reading
What is it?
Literature reviews involve collecting information from literature that is already available, similar to a long essay. It is a written argument that builds a case from previous research (Machi and McEvoy, 2012). Every dissertation should include a literature review, but a dissertation as a whole can be a literature review. In this section we discuss literature reviews for the whole dissertation.
What are the benefits of a literature review?
There are advantages and disadvantages to any approach. The advantages of conducting a literature review include accessibility, deeper understanding of your chosen topic, identifying experts and current research within that area, and answering key questions about current research. The disadvantages might include not providing new information on the subject and, depending on the subject area, you may have to include information that is out of date.
How do I write it?
A literature review is often split into chapters, you can choose if these chapters have titles that represent the information within them, or call them chapter 1, chapter 2, ect. A regular format for a literature review is:
Introduction (including methodology)
This particular example is split into 6 sections, however it may be more or less depending on your topic.
Literature Reviews Further Reading
- << Previous: Primary Research
- Next: Methodology >>
- Last Updated: Oct 18, 2023 9:32 AM
- URL: https://libguides.derby.ac.uk/c.php?g=690330

🚀 Work With Us
Private Coaching
Language Editing
Qualitative Coding
✨ Free Resources
Templates & Tools
Short Courses
Articles & Videos
Writing A Literature Review
By: David Phair (PhD) | Reviewed By: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | June 2021

C rafting a high-quality literature review is critical to earning marks and developing a strong dissertation, thesis or research project. But, it’s no simple task. Here at Grad Coach, we’ve reviewed thousands of literature reviews and seen a recurring set of mistakes and issues that drag students down.
In this post, we’ll unpack 7 common literature review mistakes , so that you can avoid these pitfalls and submit a literature review that impresses.
Overview: 7 Literature Review Killers
- Over-reliance on low-quality sources
- A lack of landmark/seminal literature
- A lack of current literature
- Description instead of integration and synthesis
- Irrelevant or unfocused content
- Poor chapter structure and layout
- Plagiarism and poor referencing
Mistake #1: Over-reliance on low-quality sources
One of the most common issues we see in literature reviews is an over-reliance on low-quality sources . This includes a broad collection of non-academic sources like blog posts, opinion pieces, publications by advocacy groups and daily news articles.
Of course, just because a piece of content takes the form of a blog post doesn’t automatically mean it is low-quality . However, it’s (generally) unlikely to be as academically sound (i.e., well-researched, objective and scientific) as a journal article, so you need to be a lot more sceptical when considering this content and make sure that it has a strong, well-reasoned foundation. As a rule of thumb, your literature review shouldn’t rely heavily on these types of content – they should be used sparingly.
Ideally, your literature review should be built on a strong base of journal articles , ideally from well-recognised, peer-reviewed journals with a high H index . You can also draw on books written by well-established subject matter experts. When considering books, try to focus on those that are published by academic publishers , for example, Cambridge University Press, Oxford University Press and Routledge. You can also draw on government websites, provided they have a strong reputation for objectivity and data quality. As with any other source, be wary of any government website that seems to be pushing an agenda.

Source: UCCS
As I mentioned, this doesn’t mean that your literature review can’t include the occasional blog post or news article. These types of content have their place , especially when setting the context for your study. For example, you may want to cite a collection of newspaper articles to demonstrate the emergence of a recent trend. However, your core arguments and theoretical foundations shouldn’t rely on these. Build your foundation on credible academic literature to ensure that your study stands on the proverbial shoulders of giants.

Mistake #2: A lack of landmark/seminal literature
Another issue we see in weaker literature reviews is an absence of landmark literature for the research topic . Landmark literature (sometimes also referred to as seminal or pivotal work) refers to the articles that initially presented an idea of great importance or influence within a particular discipline. In other words, the articles that put the specific area of research “on the map”, so to speak.
The reason for the absence of landmark literature in poor literature reviews is most commonly that either the student isn’t aware of the literature (because they haven’t sufficiently immersed themselves in the existing research), or that they feel that they should only present the most up to date studies. Whatever the cause, it’s a problem, as a good literature review should always acknowledge the seminal writing in the field.
But, how do you find landmark literature?
Well, you can usually spot these by searching for the topic in Google Scholar and identifying the handful of articles with high citation counts. They’ll also be the studies most commonly cited in textbooks and, of course, Wikipedia (but please don’t use Wikipedia as a source!).
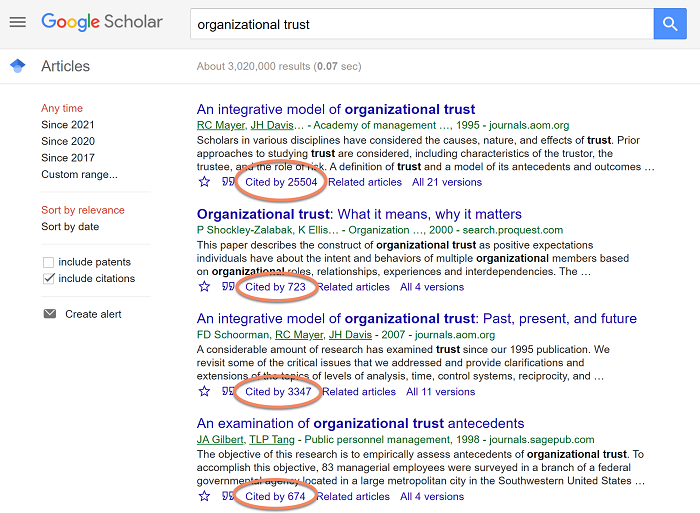
So, when you’re piecing your literature review together, remember to pay homage to the classics , even if only briefly. Seminal works are the theoretical foundation of a strong literature review.
Mistake #3: A lack of current literature
As I mentioned, it’s incredibly important to acknowledge the landmark studies and research in your literature review. However, a strong literature review should also incorporate the current literature . It should, ideally, compare and contrast the “classics” with the more up to date research, and briefly comment on the evolution.
Of course, you don’t want to burn precious word count providing an in-depth history lesson regarding the evolution of the topic (unless that’s one of your research aims, of course), but you should at least acknowledge any key differences between the old and the new.
But, how do you find current literature?
To find current literature in your research area, you can once again use Google Scholar by simply selecting the “Since…” link on the left-hand side. Depending on your area of study, recent may mean the last year or two, or a fair deal longer.

So, as you develop your catalogue of literature, remember to incorporate both the classics and the more up to date research. By doing this, you’ll achieve a comprehensive literature base that is both well-rooted in tried and tested theory and current.
Mistake #4: Description instead of integration and synthesis
This one is a big one. And, unfortunately, it’s a very common one. In fact, it’s probably the most common issue we encounter in literature reviews.
All too often, students think that a literature review is simply a summary of what each researcher has said. A lengthy, detailed “he said, she said”. This is incorrect . A good literature review needs to go beyond just describing all the relevant literature. It needs to integrate the existing research to show how it all fits together.
A good literature review should also highlight what areas don’t fit together , and which pieces are missing . In other words, what do researchers disagree on and why might that be. It’s seldom the case that everyone agrees on everything because the “truth” is typically very nuanced and intricate in reality. A strong literature review is a balanced one , with a mix of different perspectives and findings that give the reader a clear view of the current state of knowledge.
A good analogy is that of a jigsaw puzzle. The various findings and arguments from each piece of literature form the individual puzzle pieces, and you then put these together to develop a picture of the current state of knowledge . Importantly, that puzzle will in all likelihood have pieces that don’t fit well together, and pieces that are missing. It’s seldom a pretty puzzle!
By the end of this process of critical review and synthesis of the existing literature , it should be clear what’s missing – in other words, the gaps that exist in the current research . These gaps then form the foundation for your proposed study. In other words, your study will attempt to contribute a missing puzzle piece (or get two pieces to fit together).
So, when you’re crafting your literature review chapter, remember that this chapter needs to go well beyond a basic description of the existing research – it needs to synthesise it (bring it all together) and form the foundation for your study.

Mistake #5: Irrelevant or unfocused content
Another common mistake we see in literature review chapters is quite simply the inclusion of irrelevant content . Some chapters can waffle on for pages and pages and leave the reader thinking, “so what?”
So, how do you decide what’s relevant?
Well, to ensure you stay on-topic and focus, you need to revisit your research aims, objectives and research questions . Remember, the purpose of the literature review is to build the theoretical foundation that will help you achieve your research aims and objectives, and answer your research questions . Therefore, relevant content is the relatively narrow body of content that relates directly to those three components .
Let’s look at an example.
If your research aims to identify factors that cultivate employee loyalty and commitment, your literature review needs to focus on existing research that identifies such factors. Simple enough, right? Well, during your review process, you will invariably come across plenty of research relating to employee loyalty and commitment, including things like:
- The benefits of high employee commitment
- The different types of commitment
- The impact of commitment on corporate culture
- The links between commitment and productivity
While all of these relate to employee commitment, they’re not focused on the research aims , objectives and questions, as they’re not identifying factors that foster employee commitment. Of course, they may still be useful in helping you justify your topic, so they’ll likely have a place somewhere in your dissertation or thesis. However, for your literature review, you need to keep things focused.
So, as you work through your literature review, always circle back to your research aims, objective and research questions and use them as a litmus test for article relevance.
Need a helping hand?
Mistake #6: Poor chapter structure and layout
Even the best content can fail to earn marks when the literature review chapter is poorly structured . Unfortunately, this is a fairly common issue, resulting in disjointed, poorly-flowing arguments that are difficult for the reader (the marker…) to follow.
The most common reason that students land up with a poor structure is that they start writing their literature review chapter without a plan or structure . Of course, as we’ve discussed before, writing is a form of thinking , so you don’t need to plan out every detail before you start writing. However, you should at least have an outline structure penned down before you hit the keyboard.
So, how should you structure your literature review?
We’ve covered literature review structure in detail previously , so I won’t go into it here. However, as a quick overview, your literature review should consist of three core sections :
- The introduction section – where you outline your topic, introduce any definitions and jargon and define the scope of your literature review.
- The body section – where you sink your teeth into the existing research. This can be arranged in various ways (e.g. thematically, chronologically or methodologically).
- The conclusion section – where you present the key takeaways and highlight the research gap (or gaps), which lays the foundation for your study.
Another reason that students land up with a poor structure is that they start writing their literature chapter prematurely . In other words, they start writing before they’ve finished digesting the literature. This is a costly mistake, as it always results in extensive rewriting , which takes a lot longer than just doing it one step at a time. Again, it’s completely natural to do a little extra reading as thoughts crop up during the writing process, but you should complete your core reading before you start writing.
Long story short – don’t start writing your literature review without some sort of structural plan. This structure can (and likely will) evolve as you write, but you need some sort of outline as a starting point. Pro tip – check out our free literature review template to fast-track your structural outline.

Mistake #7: Plagiarism and poor referencing
This one is by far the most unforgivable literature review mistake, as it carries one of the heaviest penalties , while it is so easily avoidable .
All too often, we encounter literature reviews that, at first glance, look pretty good. However, a quick run through a plagiarism checker and it quickly becomes apparent that the student has failed to fully digest the literature they’ve reviewed and put it into their own words.
“But, the original author said it perfectly…”
I get it – sometimes the way an author phrased something is “just perfect” and you can’t find a better way to say it. In those (pretty rare) cases, you can use direct quotes (and a citation, of course). However, for the vast majority of your literature review, you need to put things into your own words .
The good news is that if you focus on integrating and synthesising the literature (as I mentioned in point 3), you shouldn’t run into this issue too often, as you’ll naturally be writing about the relationships between studies , not just about the studies themselves. Remember, if you can’t explain something simply (in your own words), you don’t really understand it.
A related issue that we see quite often is plain old-fashioned poor referencing . This can include citation and reference formatting issues (for example, Harvard or APA style errors), or just a straight out lack of references . In academic writing, if you fail to reference a source, you are effectively claiming the work as your own, which equates to plagiarism. This might seem harmless, but plagiarism is a serious form of academic misconduct and could cost you a lot more than just a few marks.
So, when you’re writing up your literature review, remember that you need to digest the content and put everything into your own words. You also need to reference the sources of any and all ideas, theories, frameworks and models you draw on.
Recap: 7 Literature Review Mistakes
We’ve covered a lot of ground in this post. Let’s quickly recap on the 7 most common literature review mistakes.
Now that you’re aware of these common mistakes, be sure to also check out our literature review walkthrough video , where to dissect an actual literature review chapter . This will give you a clear picture of what a high-quality literature review looks like and hopefully provide some inspiration for your own.
If you have any questions about these literature review mistakes, leave a comment below and we’ll do our best to answer. If you’re interested in private coaching, book an initial consultation with a friendly coach to discuss how we can move you forward.

Watch More Podcasts:

How To Review & Understand Academic Literature Quickly
Learn how to fast-track your literature review by reading with intention and clarity. Dr E and Amy Murdock explain how.

Dissertation Writing Services: Far Worse Than You Think
Thinking about using a dissertation or thesis writing service? You might want to reconsider that move. Here’s what you need to know.
The Harsh Truths Of Academic Research
Dr. Ethar Al-Saraf and Dr. Amy Murdock dive into the darker truths of academic research, so that you’re well prepared for reality.

Dissertation Paralysis: How To Get Unstuck
In this episode of the podcast, Dr. Ethar and Dr. Amy Murdock dive into how to get unstuck when you’re facing dissertation paralysis

Viva Voce Victory: How To Defend Your Thesis
Suffering from writer’s block while working on your dissertation or thesis? Learn three powerful techniques that will move you forward.
📄 FREE TEMPLATES
Research Topic Ideation
Proposal Writing
Literature Review
Methodology & Analysis
Academic Writing
Referencing & Citing
Apps, Tools & Tricks
The Grad Coach Podcast
10 Comments
Dear GradCoach,
Thank you for making our uni student lives better. Could you kindly do a video on how to use your literature review excel template? I am sure a lot of students would appreciate that.
Thank you so much for this inlightment concerning the mistakes that should be avoided while writing a literature review chapter. It is concise and precise. You have mentioned that this chapter include three main parts; introduction, body, and conclusion. Is the theoritical frameworke considered a part of the literature review chapter, or it should be written in a seperate chapter? If it is included in the literature review, should it take place at the beginning, the middle or at the end of the chapter? Thank you one again for “unpacking” things for us.
Hi I would enjoy the video on lit review. You mentioned cataloging references, I would like the template for excel. Would you please sent me this template.
on the plagiarism and referencing what is the correct way to cite the words said by the author . What are the different methods you can use
its clear, precise and understandable many thanks affectionately yours’ Godfrey
Thanks for this wonderful resource! I am final year student and will be commencing my dissertation work soon. This course has significantly improved my understanding of dissertation and has greater value in terms of its practical applicability compared to other literature works and articles out there on the internet. I will advice my colleague students more especially first time thesis writers to make good use of this course. It’s explained in simple, plain grammar and you will greatly appreciate it.
Thanks. A lot. This was excellent. I really enjoyed it. Again thank you.
The information in this article is very useful for students and very interesting I really like your article thanks for sharing this post!
Thank you for putting more knowledge in us. Thank you for using simple you’re bless.
This article is really useful. Thanks a lot for sharing this knowledge. Please continue the journey of sharing and facilitating the young researchers.
Trackbacks/Pingbacks
- Reply to Danette - Allessaysexpert - […] Jansen, D. (2021, June). Writing a literature review: 7 common (and costly) mistakes to avoid. https://gradcoach.com/literature-review-mistakes/ […]
- Reply to Danette - Academia Essays - […] Jansen, D. (2021, June). Writing a literature review: 7 common (and costly) mistakes to avoid. https://gradcoach.com/literature-review-mistakes/ […]
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Submit Comment
- Print Friendly

IMAGES
COMMENTS
One of the major disadvantages of literature review is that instead of critical appreciation, some researchers end up developing reviews that are mostly descriptive. Their reviews are often more like summaries of the work of other writers and lack in criticality.
In this post, Neal Haddaway highlights 8 common problems with literature review methods, provides examples for each and provides practical solutions for ways to mitigate them.
Despite the many advantages of literature reviews, one significant drawback is that they can be extremely time-consuming. Researchers may spend weeks or even months sifting through articles, books, and other sources to ensure they are well-informed about their topic.
Recognizing the constraints that researchers can sometimes feel when attempting to plan, conduct and publish rigorous and comprehensive evidence syntheses, we aim here to identify major pitfalls in the conduct and reporting of systematic reviews, making use of recent examples from across the field.
These are the eight problems we identified in our paper. First, traditional literature reviews can lack relevance. This is because limited stakeholder engagement can lead to a review that...
Although systematic reviews are robust tools in scientific research they are not immune to errors. They can be misleading, or even harmful if the data is inappropriately handled or if they are biased. Some of the limitations of systematic reviews include: Due to the popularity systematic reviews have gained, they tend to be used more than required.
Systematic reviews use a retrospective, observational research design, and as such are subject to systematic and random error. 4 A recent article by Doleman et al. 13 offers a detailed explanation about these limitations.
There are advantages and disadvantages to any approach. The advantages of conducting a literature review include accessibility, deeper understanding of your chosen topic, identifying experts and current research within that area, and answering key questions about current research.
In this post, we’ll unpack 7 common literature review mistakes, so that you can avoid these pitfalls and submit a literature review that impresses. One of the most common issues we see in literature reviews is an over-reliance on low-quality sources.
This paper discusses literature review as a methodology for conducting research and offers an overview of different types of reviews, as well as some guidelines to how to both conduct and evaluate a literature review paper.