Looking for AI in local government? See our newest product, Madison AI.

More Like this
What is the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan.
It is not uncommon that the terms ‘strategic plan’ and ‘business plan’ get confused in the business world. While a strategic plan is a type of business plan, there are several important distinctions between the two types that are worth noting. Before beginning your strategic planning process or strategy implementation, look at the article below to learn the key difference between a business vs strategic plan and how each are important to your organization.
Definition of a business plan vs. a strategic plan
A strategic plan is essential for already established organizations looking for a way to manage and implement their strategic direction and future growth. Strategic planning is future-focused and serves as a roadmap to outline where the organization is going over the next 3-5 years (or more) and the steps it will take to get there.
Get the Free Guide for Setting OKRs that Work (with 100 examples!)
A strategic plan serves 6 functions for an organization that is striving to reach the next level of their growth:.
- Defines the purpose of the organization.
- Builds on an organization’s competitive advantages.
- Communicates the strategy to the staff.
- Prioritizes the financial needs of the organization.
- Directs the team to move from plan to action.
- Creates long-term sustainability and growth impact
Alternatively, a business plan is used by new businesses or organizations trying to get off the ground. The fundamentals of a business plan focus on setting the foundation for the business or organization. While it looks towards the future, the focus is set more on the immediate future (>1 year). Some of the functions of a business plan may overlap with a strategic plan. However, the focus and intentions diverge in a few key areas.
A business plan for new businesses, projects, or organizations serves these 5 functions:
- Simplifies or explains the objectives and goals of your organization.
- Coordinates human resource management and determines operational requirements.
- Secures funding for your organization.
- Evaluates potential business prospects.
- Creates a framework for conceptualizing ideas.
In other words, a strategic plan is utilized to direct the momentum and growth of an established company or organization. In contrast, a business plan is meant to set the foundation of a newly (or not quite) developed company by setting up its operational teams, strategizing ways to enter a new market, and obtaining funding.
A strategic plan focuses on long-term growth and the organization’s impact on the market and its customers. Meanwhile, a business plan must focus more on the short-term, day-to-day operational functions. Often, new businesses don’t have the capacity or resources to create a strategic plan, though developing a business plan with strategy elements is never a bad idea.
Business and strategic plans ultimately differ in several key areas–timeframe, target audience, focus, resource allocation, nature, and scalability.
While both a strategic and business plan is forward-facing and focused on future success, a business plan is focused on the more immediate future. A business plan normally looks ahead no further than one year. A business plan is set up to measure success within a 3- to 12-month timeframe and determines what steps a business owner needs to take now to succeed.
A strategic plan generally covers the organizational plan over 3 to 5+ years. It is set with future expansion and development in mind and sets up roadmaps for how the organization will reach its desired future state.
Pro Tip: While a vision statement could benefit a business plan, it is essential to a strategic plan.
Target Audience
A strategic plan is for established companies, businesses, organizations, and owners serious about growing their organizations. A strategic plan communicates the organization’s direction to the staff and stakeholders. The strategic plan is communicated to the essential change makers in the organization who will have a hand in making the progress happen.
A business plan could be for new businesses and entrepreneurs who are start-ups. The target audience for the business plan could also be stakeholders, partners, or investors. However, a business plan generally presents the entrepreneur’s ideas to a bank. It is meant to get the necessary people onboard to obtain the funding needed for the project.
A strategic plan provides focus, direction, and action to move the organization from where they are now to where they want to go. A strategic plan may consist of several months of studies, analyses, and other processes to gauge an organization’s current state. The strategy officers may conduct an internal and external analysis, determine competitive advantages, and create a strategy roadmap. They may take the time to redefine their mission, vision, and values statements.
Alternatively, a business plan provides a structure for ideas to define the business initially. It maps out the more tactical beginning stages of the plan.
Pro Tip: A mission statement is useful for business and strategic plans as it helps further define the enterprise’s value and purpose. If an organization never set its mission statement at the beginning stages of its business plan, it can create one for its strategic plan.
A strategic plan is critical to prioritizing resources (time, money, and people) to grow the revenue and increase the return on investment. The strategic plan may start with reallocating current financial resources already being utilized more strategically.
A business plan will focus on the resources the business still needs to obtain, such as vendors, investors, staff, and funding. A business plan is critical if new companies seek funding from banks or investors. It will add accountability and transparency for the organization and tell the funding channels how they plan to grow their business operations and ROI in the first year of the business.
The scalability of a business plan vs. strategic plan
Another way to grasp the difference is by understanding the difference in ‘scale’ between strategic and business plans. Larger organizations with multiple business units and a wide variety of products frequently start their annual planning process with a corporate-driven strategic plan. It is often followed by departmental and marketing plans that work from the Strategic Plan.
Smaller and start-up companies typically use only a business plan to develop all aspects of operations of the business on paper, obtain funding and then start the business.
Why understanding the differences between a business plan vs a strategic plan matters
It is important to know the key differences between the two terms, despite often being used interchangeably. But here’s a simple final explanation:
A business plan explains how a new business will get off the ground. A strategic plan answers where an established organization is going in the future and how they intend to reach that future state.
A strategic plan also focuses on building a sustainable competitive advantage and is futuristic. A business plan is used to assess the viability of a business opportunity and is more tactical.
10 Comments
I agree with your analysis about small companies, but they should do a strategic plan. Just check out how many of the INC 500 companies have an active strategic planning process and they started small. Its about 78%,
Strategic management is a key role of any organization even if belong to small business. it help in growth and also to steam line your values. im agree with kristin.
I agree with what you said, without strategic planning no organization can survive whether it is big or small. Without a clear strategic plan, it is like walking in the darkness.. Best Regards..
Vision, Mission in Business Plan VS Strategic Plan ?
you made a good analysis on strategic plan and Business plan the difference is quite clear now. But on the other hand, it seems that strategic plan and strategic management are similar which I think not correct. Please can you tell us the difference between these two?. Thanks
Thank you. I get points to work on it
super answer Thanking you
Hi. I went through all the discussions, comments and replies. Thanks! I got a very preliminary idea about functions and necessity of Strategic Planning in Business. But currently I am looking for a brief nice, flowery, juicy definition of “Business Strategic Planning” as a whole, which will give anyone a fun and interesting way to understand. Can anyone help me out please? Awaiting replies…… 🙂
that was easy to understand,
Developing a strategic plan either big or small company or organization mostly can’t achieve its goal. A strategic plan or formulation is the first stage of the strategic management plan, therefore, we should be encouraged to develop a strategic management plan. We can develop the best strategic plan but without a clear plan of implementation and evaluation, it will be difficult to achieve goals.
Comments Cancel
Join 60,000 other leaders engaged in transforming their organizations., subscribe to get the latest agile strategy best practices, free guides, case studies, and videos in your inbox every week..

Leading strategy? Join our FREE community.
Become a member of the chief strategy officer collaborative..
Free monthly sessions and exclusive content.
Do you want to 2x your impact.
AI ASSISTANTS
Upmetrics AI Your go-to AI-powered business assistant
AI Writing Assist Write, translate, and refine your text with AI
AI Financial Assist Automated forecasts and AI recommendations
AI Research Assist Your go-to AI-powered research assistant
TOP FEATURES
AI Business Plan Generator Create business plans faster with AI
Financial Forecasting Make accurate financial forecasts faster
INTEGRATIONS
QuickBooks Sync and compare with your QuickBooks data
Strategic Planning Develop actionable strategic plans on-the-go
AI Pitch Deck Generator Use AI to generate your investor deck
Xero Sync and compare with your Xero data
See how easy it is to plan your business with Upmetrics: Take a Tour →
AI-powered business planning software
Very useful business plan software connected to AI. Saved a lot of time, money and energy. Their team is highly skilled and always here to help.
- Julien López
BY USE CASE
Secure Funding, Loans, Grants Create plans that get you funded
Starting & Launching a Business Plan your business for launch and success
Validate Your Business Idea Discover the potential of your business idea
E2 Visa Business Plan Create a business plan to support your E2 - Visa
Business Consultant & Advisors Plan with your team members and clients
Incubators & Accelerators Empowering startups for growth
Business Schools & Educators Simplify business plan education for students
Students & Learners Your e-tutor for business planning
- Sample Plans
Plan Writing & Consulting We create a business plan for you
Business Plan Review Get constructive feedback on your plan
Financial Forecasting We create financial projections for you
SBA Lending Assistance We help secure SBA loans for your business
WHY UPMETRICS?
Reviews See why customers love Upmetrics
Blogs Latest business planning tips and strategies
Strategic Planning Templates Ready-to-use strategic plan templates
Business Plan Course A step-by-step business planning course
Customer Success Stories Read our customer success stories
Help Center Help & guides to plan your business
Ebooks & Guides A free resource hub on business planning
Business Tools Free business tools to help you grow
Business Plan Vs Strategic Plan: What’s the Difference?

Business Plan Template
- May 6, 2024

Strategic and business plans are both different sides of the same coin! Some entrepreneurs use it interchangeably but they have a significant difference.
Now the question might arise, when to use which, and what is the difference, right?
Worry not—we’re here to guide you through it all. In this article, we’ll learn the differences between a business and a strategic plan, understand their meanings, and know how to use them effectively.
So, let’s kick-start this journey by exploring a business plan vs. strategic plan . Get ready to unlock everything about both!
What is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a written document that outlines a company’s goals, timeline, finances, and strategies for achieving them. It provides a roadmap for the future of your business.
Generally, it includes sections such as an executive summary, company description, market analysis, products & services, financial plan, and much more. Your business plan is a must-have document when it comes to securing funds for your business.
Okay! And what about the strategic plan?
What is a Strategic Plan?
A strategic plan is a document that communicates an organization’s vision, mission, and core values. It focuses more on specifics about how a business will operate and generate profits.
Strategic plans are typically long-term documents, covering a period of three to five years or more, and are used to guide decision-making and resource allocation within the organization.
Key Difference Between a Business Plan and Strategic Plan
It was all about the basic definition of business and strategic plan. Now, let’s compare them side-by-side to understand their use case, and how they are distinct from each other:
Level of detail
A business plan is usually considered a granular and in-depth document. It outlines the tactics and actions necessary to achieve operational objectives. Business plans are usually 15-30 pages long .
A strategic plan typically provides a high-level overview of the organization’s goals and the strategies to achieve them without going deep into the business operations. Strategic plans are generally 10-15 pages long, but the length depends on various factors of the business.
Time horizon
A business plan focuses on a shorter time frame, often one to three years, and is more operational. It focuses on things like product development, marketing strategies, financial projections, etc.
A strategic plan answers the questions related to a longer time frame, usually five or more years. It sets the direction of the company for the future by mentioning the mission, vision, and objectives.
Audience and use
A business plan is primarily used to attract investors, bankers, or partners for securing funding or partnership.
Whereas, internal members, such as senior management or a board of directors, use a strategic plan to guide decision-making.
A business plan explains all the sections like market analysis, products & services, management team, target market, sales & marketing strategies, financial projections, and more.
While a strategic plan has a vision statement, mission statement, core values, action plans, and more. Some of the strategic planning models are SWOT analysis , PESTLE (political, economic, social, technological, legal, and environmental) analysis, Porter’s five forces, and more.
Entrepreneurs and startups use business plans to create a strategy to build a successful business. It is used for assessing how marketable a business idea is and also helps them gauge how they can get the funding to turn this idea into reality.
Established companies use the strategic plan to give them a clear direction for where they want the company to change or develop.
For instance, decisions like changing the products they provide or moving into a nonprofit can be made with the help of a strategic plan.
Create winning business and strategic plans with our
AI Business Plan Generator
Plans starting from $7/month

Now that we know the key differences between strategic and business planning, let us understand the common pitfalls.
Common Pitfalls in Execution
Despite the benefits of business planning as well as the strategic planning process , organizations often face many challenges in their strategy implementation. Here are some common pitfalls:
Disparity between strategy and execution: Without effective execution, even the strategic plan that is the most well-crafted may fail to give results.
Lack of alignment: Failure to align the business plan with strategic objectives often results in missed opportunities and misallocation of resources.
Inadequate marketing analysis: Insufficient analysis of external factors leads to missed opportunities or strategic blind spots that can cause more harm to a company.
To overcome these challenges, organizations need to foster a culture of communication, continuous improvement, and collaboration.
The Bottom Line
There is no one-fits-all solution when it comes to this decision! Choosing between a business and a strategic plan solely depends on the needs & objectives of your business.
Moreover, know this planning is not a one-time process! As your business evolves and external factors change, you will need to revise your plans accordingly.
A business and a strategic plan are crucial for guiding any organization to success. By using both methods effectively, businesses can navigate uncertainties, achieve steady growth, and grab opportunities in a constantly changing business world.
Build your Business Plan Faster
with step-by-step Guidance & AI Assistance.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which comes first, strategy or business plan.
Before making a business plan, you should create a strategic plan. A business should know all its long-term growth goals before actually defining how to reach them.
So, first, create a strategic plan, then a business plan, and then edit both of them when needed according to the circumstances.
Can a business plan be used for a strategic plan?
No, both are different. While a business plan details the operational and financial aspects of a business, a strategic plan defines goals and the strategies to achieve them. Therefore, serving different purposes, a business plan can not be used to make a strategic plan.
Is there a sample business plan or strategic plan template available online?
Yes, there are many sample business plans and strategic plan templates available online. You can find such templates on:
- Upmetrics – An AI-powered business plan software
- Small Business Administration Website
- SCORE business plans
Do I need both a business and strategic plan?
Yes, both a business plan and a strategic plan are essential for a company’s growth. A business plan focuses on the initial stages of a business, aiming to get it started. In contrast, a strategic plan focuses on the business’s distant goals and strategies to achieve them.
About the Author
Upmetrics Team
Upmetrics is the #1 business planning software that helps entrepreneurs and business owners create investment-ready business plans using AI. We regularly share business planning insights on our blog. Check out the Upmetrics blog for such interesting reads. Read more
Get started with Upmetrics Al
- 400+ sample business plans
- Al-powered financial planning
- Collaborative workspace
Reach Your Goals with Accurate Planning

- Certifications
- Associate Business Strategy Professional
- Senior Business Strategy Professional
- Examination
- Partnership
- For Academic Affiliation
- For Training Companies
- For Corporates
- Help Center
- Associate Business Strategy Professional (ABSP™)
- Senior Business Strategy Professional (SBSP™)
- Certification Process
- TSI Certification Examination
- Get your Institution TSI Affiliated
- Become a Corporate Education Partner
- Become a Strategy Educator
- Frequently Asked Questions
What is Business Strategy? Definition, Importance, Levels, and Examples

Business strategy is the battle plan for a better future. - Patrick Dixon
Scaling up a business without a clear strategy is like captaining a ship without a rudder. The success of any business depends on the strategy that one follows. The business strategy establishes the needs of the business. Business strategy plays an important role for businesses of all sizes and entrepreneurs. It sets the direction of the organization and helps to create goals to aim towards.
What is Business Strategy?
Business strategy is defined as the course of action or set of decisions that support entrepreneurs in achieving certain business goals. It is a master plan that outlines the direction the organization intends to make, the actions it will undertake, and the resources it will give to attain certain competitive benefits and drive sustainable growth. It involves a combination of decisions, actions, and resource allocation that positions an organization in its industry or market.
Why is a Business Strategy important?
Business Strategy plays a crucial role in guiding a firm’s growth, competitiveness, and success. It offers a roadmap for decision-making, resource providing, and adaptation to transforming circumstances, ensuring that the firm stays agile, focused, and well-prepared to achieve its goals successfully. It is carefully planned and flexibly designed with the purpose of:
- Achieving effectiveness
- Perceiving and utilizing opportunities
- Mobilizing resources
- Securing an advantageous position
- Meeting the challenges and threats
- Directing efforts, behavior and
- Gaining command over the situation
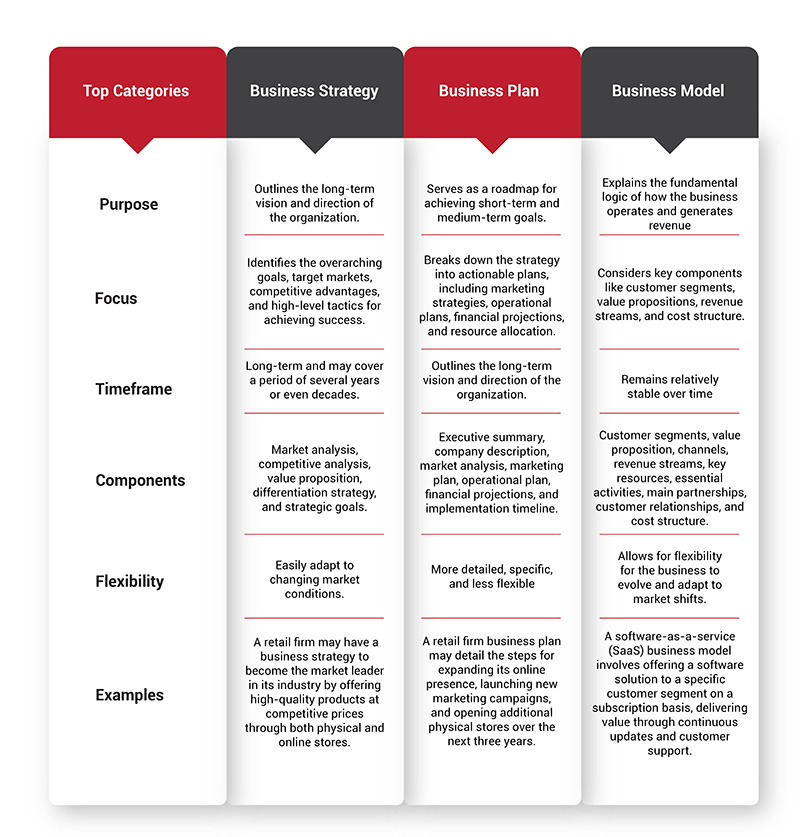
What is the Difference between Business Strategy & Business Plan & Business Model
Business Strategy, Business Plan, and Business Model are three distinct elements that offer various purposes in the world of business. They are vital for the success and sustainability of a business, and they are interconnected, with slight changes which are often confused by several aspiring business strategists , especially during their interviews. Here's a breakdown of the important differences between these:
Levels of Business Strategy
Effective strategic management consists of coordination and alignment across various levels of strategy to achieve the organization's long-term goals and competitive advantage. Business strategy can be categorized into different levels depending on its scope, focus, and the organizational hierarchy at which it functions.
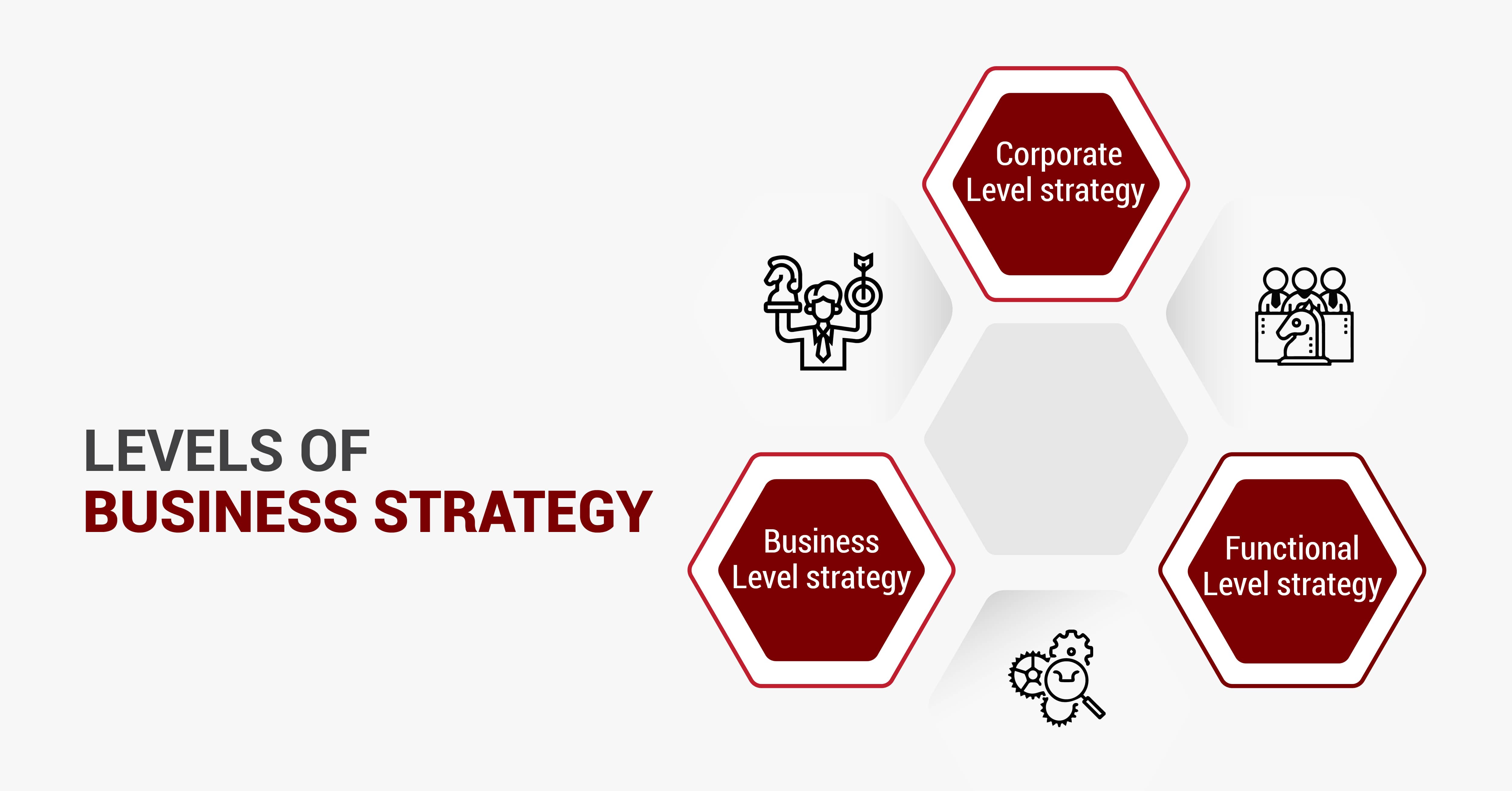
The three primary levels of business strategy are:
- Corporate level strategy Corporate level strategy is a long-range, action-oriented, integrated, and comprehensive plan, which is formulated by the top management of a company. It is very helpful to ascertain business lines, expansion, growth, takeovers and mergers, diversification , integration, and the latest fields for investment.
- Business level strategy The strategies that relate to a specific business are known as business-level strategies. It is developed by the general managers, who convert mission and vision into concrete, clear, and result-driven strategies. It acts like a blueprint for the total business.
- Functional level strategy Developed by the first-line managers or supervisors, the functional level strategy involves decision-making at the operational level concerning functional areas such as marketing, production, human resources, research and development, finance, and so on.
How to Implement a Successful Business Strategy?
A business strategist feels that it is tough to ideate any plan in a few hours. It requires a step-by-step procedure to be associated with completing a SWOT analysis . Here are the top steps that can be considered to build the best business strategies and execute them with precision:
- Understand the targets One of the clearest challenges for growth is poor targeting. Clear target markets offer an organization the ability to create an integrated sales and marketing approach, where marketing enables sales productivity. Sales and marketing business plan gets executed more efficiently if the targets are fixed in a proper way.
- Outline the tactics A successful business strategy is made up of several various tactics, including both online and offline options. The goals, target audience, and industry factor into this decision. For instance, if the target audience is young, focusing on social media is more beneficial as this is primarily where this group consumes content. If the industry is product-based (for instance, jewelry designing), then using a more visual platform would better showcase the products. To be most effective, one must choose which methods are right for the business. Once the selection of tactics is done, list them in the plan and determine how they’ll help to reach the goals.
- Think long term In the scope of constant change, planning the horizons is usually shorter than it can be. However, only thinking quarter to quarter is a trap that may rob organizations of their ability to see around the bend. Best-in-class organizations create processes designed for a series of financial and non-financial metrics to treat strategy as an annual cycle rather than a one-time, static event.
- Create a timeline Time is precious mainly when it is about the business. Based on the goals and objectives one can set for the business. Creating a timeline that will define what tasks can be completed and when they can be completed. It is highly advisable to allocate extra time for unexpected events that may delay some of the goals.
- Focus on growth A thriving organization is a growing organization. It is only through growth that the firms can afford to invest in aspects such as technology, the best staff, and the latest tools. The business strategy should identify the segments where an organization will grow and in what proportion.
- Have a budget plan Creating a budget for the business strategy can inform the efforts by determining what can be done and cannot be. Choosing the most cost-effective options for the business ensures the success of the overall business strategy. This doesn’t have to limit the options. Paid advertising on social media and search engines gives access to manage budgets well.
- Make fact-based decisions Several executives often complain about a lack of fruitful data, but they consistently find information that is useful in the formation of business strategy. The business has a set of values that guides it. Making fact-based decisions will outline the values and ensure that the people who interact with the business are aware of them. It will also ease the message that reflects on the brand honestly so it can actively demonstrate the values outlined in the mission statement through the interactions with clients.
- Invest in pre-work Always allocate time to do proper pre-work so that one can be up to date. It is better to conduct proper end-to-end research and prepare relevant information in advance of the business strategy meetings. The goals and needs will change over time. Ideally, it is important to revisit the business plan every annum to make adjustments as needed. Follow industry news and trends that can add to the existing strategy.
- Execute well and measure results Measuring the effectiveness of the business strategy will inform the current plan and future efforts. Always be sure to track and measure the business so these measurements are effective. Set up a corporate calendar to enhance the productive meetings, and also to form a performance management cycle. One should write the marketing plan with this growth in mind so they can measure it. The execution of strategic planning needs discipline, and it must be taken care of by the senior executives to promote processes that keep the team focused.
Examples of Business Strategy
Hubspot developed and executed a perfect business strategy where it created a market that didn’t even exist – inbound marketing. It created an online resource guide explaining the limitations of interruption marketing and informing about the advantages of inbound marketing. The organizations even offered free courses to help the target audience understand its offering better.
Apple Inc. differentiated its Smartphone operating system iOS by making it simple as compared to Android. This differentiated it and built its followership. The organization has been following a similar business strategy for its other products as well.

Wrapping up
Establishing the business strategy keeps the business goals organized and focused, saving valuable time and money. With the increase in the competition, the demand for business strategy is becoming apparent and there is a tremendous increase in the types of business strategies used by the businesses.

Recent Posts

How Data Analytics Can Revolutionize Your Business - A Strategist's Guide
Download this Strategist's Guide to empower yourself with resourceful insights:
- Roadblocks to Data Usage
- Advantages that Data Analytics offer for businesses
- Elements of a Data Analytics Strategy
- Top reasons why businesses must adopt a Data Analytics Strategy
- Case studies, Scenarios, and more

CredBadge™ is a proprietary, secure, digital badging platform that provides for seamless authentication and verification of credentials across digital media worldwide.
CredBadge™ powered credentials ensure that professionals can showcase and verify their qualifications and credentials across all digital platforms, and at any time, across the planet.

Verify A Credential
Please enter the License Number/Unique Credential Code of the certificant. Results will be displayed if the person holds an active credential from TSI.
Stay Informed!
Keep yourself informed on the latest updates and information about business strategy by subscribing to our newsletter.
Start Your Journey with The Strategy Institute by Creating Your myTSI Account Today.
- Manage your professional profile conveniently.
- Manage your credentials anytime.
- Share your experiences and ideas with The Strategy Institute.
Account Login
- Remember Password
- Forgot Password?
Forgot Password
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is a Business Plan?
Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one.
Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, How To Create One
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One CURRENT ARTICLE
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros & Cons, and Differences From an LLC
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types
- What is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined
- Corporation: What It Is and How to Form One
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide
A business plan is a document that outlines a company's goals and the strategies to achieve them. It's valuable for both startups and established companies. For startups, a well-crafted business plan is crucial for attracting potential lenders and investors. Established businesses use business plans to stay on track and aligned with their growth objectives. This article will explain the key components of an effective business plan and guidance on how to write one.
Key Takeaways
- A business plan is a document detailing a company's business activities and strategies for achieving its goals.
- Startup companies use business plans to launch their venture and to attract outside investors.
- For established companies, a business plan helps keep the executive team focused on short- and long-term objectives.
- There's no single required format for a business plan, but certain key elements are essential for most companies.
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley
Any new business should have a business plan in place before beginning operations. Banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before considering making a loan or providing capital to new businesses.
Even if a company doesn't need additional funding, having a business plan helps it stay focused on its goals. Research from the University of Oregon shows that businesses with a plan are significantly more likely to secure funding than those without one. Moreover, companies with a business plan grow 30% faster than those that don't plan. According to a Harvard Business Review article, entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than those who don't.
A business plan should ideally be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect achieved goals or changes in direction. An established business moving in a new direction might even create an entirely new plan.
There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. It allows for careful consideration of ideas before significant investment, highlights potential obstacles to success, and provides a tool for seeking objective feedback from trusted outsiders. A business plan may also help ensure that a company’s executive team remains aligned on strategic action items and priorities.
While business plans vary widely, even among competitors in the same industry, they often share basic elements detailed below.
A well-crafted business plan is essential for attracting investors and guiding a company's strategic growth. It should address market needs and investor requirements and provide clear financial projections.
While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business.
Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company.
The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, gathering the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document is best. Any additional crucial elements, such as patent applications, can be referenced in the main document and included as appendices.
Common elements in many business plans include:
- Executive summary : This section introduces the company and includes its mission statement along with relevant information about the company's leadership, employees, operations, and locations.
- Products and services : Describe the products and services the company offers or plans to introduce. Include details on pricing, product lifespan, and unique consumer benefits. Mention production and manufacturing processes, relevant patents , proprietary technology , and research and development (R&D) information.
- Market analysis : Explain the current state of the industry and the competition. Detail where the company fits in, the types of customers it plans to target, and how it plans to capture market share from competitors.
- Marketing strategy : Outline the company's plans to attract and retain customers, including anticipated advertising and marketing campaigns. Describe the distribution channels that will be used to deliver products or services to consumers.
- Financial plans and projections : Established businesses should include financial statements, balance sheets, and other relevant financial information. New businesses should provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years. This section may also include any funding requests.
Investors want to see a clear exit strategy, expected returns, and a timeline for cashing out. It's likely a good idea to provide five-year profitability forecasts and realistic financial estimates.
2 Types of Business Plans
Business plans can vary in format, often categorized into traditional and lean startup plans. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
- Traditional business plans : These are detailed and lengthy, requiring more effort to create but offering comprehensive information that can be persuasive to potential investors.
- Lean startup business plans : These are concise, sometimes just one page, and focus on key elements. While they save time, companies should be ready to provide additional details if requested by investors or lenders.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?
A business plan isn't a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections. Markets and the economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All this calls for building flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed.
How Often Should a Business Plan Be Updated?
How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on its nature. Updating your business plan is crucial due to changes in external factors (market trends, competition, and regulations) and internal developments (like employee growth and new products). While a well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary, a new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly.
What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?
The lean startup business plan is ideal for quickly explaining a business, especially for new companies that don't have much information yet. Key sections may include a value proposition , major activities and advantages, resources (staff, intellectual property, and capital), partnerships, customer segments, and revenue sources.
A well-crafted business plan is crucial for any company, whether it's a startup looking for investment or an established business wanting to stay on course. It outlines goals and strategies, boosting a company's chances of securing funding and achieving growth.
As your business and the market change, update your business plan regularly. This keeps it relevant and aligned with your current goals and conditions. Think of your business plan as a living document that evolves with your company, not something carved in stone.
University of Oregon Department of Economics. " Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Business Planning Using Palo Alto's Business Plan Pro ." Eason Ding & Tim Hursey.
Bplans. " Do You Need a Business Plan? Scientific Research Says Yes ."
Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ."
Harvard Business Review. " How to Write a Winning Business Plan ."
U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ."
SCORE. " When and Why Should You Review Your Business Plan? "
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/business-test-5bfc2da446e0fb0083c0d8aa.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
- Business Essentials
- Leadership & Management
- Credential of Leadership, Impact, and Management in Business (CLIMB)
- Entrepreneurship & Innovation
- Digital Transformation
- Finance & Accounting
- Business in Society
- For Organizations
- Support Portal
- Media Coverage
- Founding Donors
- Leadership Team

- Harvard Business School →
- HBS Online →
- Business Insights →
Business Insights
Harvard Business School Online's Business Insights Blog provides the career insights you need to achieve your goals and gain confidence in your business skills.
- Career Development
- Communication
- Decision-Making
- Earning Your MBA
- Negotiation
- News & Events
- Productivity
- Staff Spotlight
- Student Profiles
- Work-Life Balance
- AI Essentials for Business
- Alternative Investments
- Business Analytics
- Business Strategy
- Business and Climate Change
- Creating Brand Value
- Design Thinking and Innovation
- Digital Marketing Strategy
- Disruptive Strategy
- Economics for Managers
- Entrepreneurial Marketing
- Entrepreneurship Essentials
- Financial Accounting
- Global Business
- Launching Tech Ventures
- Leadership Principles
- Leadership, Ethics, and Corporate Accountability
- Leading Change and Organizational Renewal
- Leading with Finance
- Management Essentials
- Negotiation Mastery
- Organizational Leadership
- Power and Influence for Positive Impact
- Strategic Financial Analysis
- Strategy Execution
- Sustainable Business Strategy
- Sustainable Investing
- Winning with Digital Platforms
How to Develop a Business Strategy: 6 Steps

- 25 Oct 2022
Business strategy can seem daunting, and for good reason: It can make or break an organization. Yet, developing a strong strategy doesn’t need to be overwhelming.
In the online course Business Strategy , Harvard Business School Professor Felix Oberholzer-Gee posits that strategy is simple. His secret? Focus on your organization’s value creation.
“Strategy often sounds like a lofty concept that only the most senior executives can develop,” Oberholzer-Gee says. “But actually, anyone can think and act strategically. It doesn’t need to be difficult; all you need is a proven framework.”
Here’s a breakdown of why business strategy is important, the basics of value-based strategy, and six steps for developing your own.
Why Do You Need a Business Strategy?
Business strategy is the development, alignment, and integration of an organization’s strategic initiatives to give it a competitive edge in the market. Devising a business strategy can ensure you have a clear plan for reaching organizational goals and continue to survive and thrive.
According to a study by Bridges Business Consultancy , 48 percent of organizations fail to meet half of their strategic targets and 85 percent fail to meet two-thirds, highlighting why dedication to the business strategy process is crucial.
One type of business strategy is called value-based strategy, which simplifies the process by leveraging the value stick framework to focus on the advantage your business creates.
Access your free e-book today.
What Is Value-Based Strategy?
Value-based strategy , also called value-based pricing, is a pricing method in which an organization relies on the perceived value of its goods and services to determine its pricing structure and resource allocation.
The value stick framework can be used to visualize how various factors impact each other and determine which initiatives to pursue to increase value for all parties.

The value stick has four factors:
- Willingness to pay (WTP) : The highest price a customer is willing to pay for your product or service
- Price : The amount customers have to pay for goods or services
- Cost : The amount a company spends on producing goods or services
- Willingness to sell (WTS) : The lowest amount suppliers are willing to accept for the materials required to produce goods or services
To determine how to best create value, you can toggle each factor on the value stick to see how the others are affected. For instance, lowering price increases customer delight.
"As strategists, we really ask three questions,” Oberholzer-Gee says in Business Strategy. “How can my business best create value for customers? How can my business create value for employees? And how can my business create value by collaborating with suppliers? Think of a company's strategy as an answer to these three questions."
Related: 4 Business Strategy Skills Every Business Leader Needs
6 Steps to Develop a Value-Based Business Strategy
1. define your purpose.
When approaching business strategy, defining your organization’s purpose can be a useful starting point.
This is vital in creating customer and employee value, especially if your organization’s purpose is linked to a cause such as environmental protection or alleviating specific social issues.
A recent survey conducted by clean energy company Swytch found that nearly 75 percent of millennials would take a decrease in salary if it meant working for an environmentally responsible company. Nearly 40 percent selected one job over another because of an organization’s sustainability practices.
Additionally, research in the Harvard Business Review shows that consumers’ motivation to buy from sustainable brands is on the rise. Sales of products marked as sustainable grew more than five times faster than those that weren’t.
By starting with purpose, your organization can create more value down the line.
2. Assess Market Opportunity
Next, understand your market’s competitive landscape. Which companies own shares of the market? What differentiates your competitors’ products from yours? Are there any unmet needs your organization could take advantage of?
Conducting this research before planning a strategy is critical in identifying how your organization provides unique customer value and opportunities to create even more.
3. Create Value for Customers
With an understanding of the market and your company’s purpose, you can determine how your organization provides unique or greater value and strategize ways to improve.
On the value stick, the value captured by customers is called “customer delight.” It can be increased by raising their willingness to pay and decreasing the product’s price. If lowering the price isn’t an option, brainstorm how you could make the product more valuable to customers, thus increasing their willingness to pay.
Some ways to create customer value include:
- Lowering the product’s price
- Increasing the product’s physical quality and longevity
- Providing quick, high-quality customer service and a smooth shopping experience
- Leveraging network effects , if applicable, to create a community of users
- Incorporating an environmental or social cause into processes, packaging, and branding
4. Create Value for Suppliers
In addition to creating value for customers, you also need to provide value for suppliers. Suppliers can include any company that provides raw materials, labor, and transportation to help your organization produce goods or deliver services.
Supplier surplus, also called supplier delight, is created when the cost of materials increases or their willingness to sell decreases. The relationship between a firm and its suppliers can be contentious, given that both want to increase their margins. Yet, there are ways to create value for both parties.
Some ways to create value for suppliers include:
- Agreeing to pay more for higher quality materials : While this increases the supplier surplus, it may also increase customer delight by raising willingness to pay, or increase the firm’s margin by allowing you to raise prices.
- Working with the supplier to increase efficiency : This strategy can increase supplier surplus by lowering the overall cost of the supplier’s labor and their willingness to sell.

5. Create Value for Employees
Creating value for employees is a critical part of an effective business strategy and can be assessed using the value stick. Think of your employees as the “supplier” of labor and the supplier margin as employee satisfaction.
Employee satisfaction can be increased by raising wages or lowering the minimum salary they’re willing to receive by delivering value in other ways. Satisfied employees may provide a better customer experience, resulting in increased customer delight.
The value you provide employees ensures they’re motivated to do their best work, develop their skills, and stay with your company long-term.
Some examples of ways to create value for your employees include:
- Offering competitive salaries and bonuses
- Offering benefits like ample paid vacation and sick days, generous parental leave, and wellness budgets
- Providing flexibility of work location, whether your team is fully remote or hybrid
- Aiding in professional development
- Creating a workplace rich with a diversity of experiences, identities, and ideas
- Fostering a supportive organizational culture
One example from Business Strategy is that of a call center for a diagnostics company. The employees were being paid minimum wage and expressed that the analytical nature of their phone calls with customers warranted higher pay. They also expressed pain points about cumbersome tasks and work conditions.
When a pay increase was implemented for all employees, along with operational changes to make processes smoother, employee productivity increased to the point that it balanced out the higher cost of salaries.
Because the employees’ satisfaction increased, they also began providing better experiences on the phone with customers. This increased the customers’ willingness to pay, directly impacting customer delight.
6. Map Strategy to Actionable Tasks and KPIs
Amidst creating value for each of the three groups, don’t forget the fourth party that needs value: your company. By creating value for employees, suppliers, and customers, you’re creating value for your firm, too.
To ensure you’re tracking to goals, determine your key performance indicators, what metrics constitute success, and how you’ll report results over time. Then, break each of the above value-creation goals into action items. For instance, what steps can you take to increase your employees’ compensation? Who will be responsible for each task?
Having actionable assignments and clear metrics for success will allow for a smooth transition from strategy formulation to execution.

Building Your Strategic Skill Set
By leveraging the value stick, you can create a business strategy that provides value to employees, customers, suppliers, and your firm.
To develop your strategies further and dig deeper into how to navigate value creation, consider taking an online course like Business Strategy . Professor Oberholzer-Gee walks through real-world examples of business challenges, prompts you to consider how you’d create value, and then reveals what those business leaders did and how you can apply the lessons to your organization.
Want to learn more about how to craft a successful strategy for your organization? Explore Business Strategy , one of our online strategy courses , to learn how to create organizational value. Not sure which course is the right fit? Download our free flowchart .

About the Author
🎧 Real entrepreneurs. Real stories.
Subscribe to The Hurdle podcast today!
Business Plan Vs Strategic Plan Vs Operational Plan—Differences Explained

Noah Parsons
5 min. read
Updated October 27, 2023

Many business owners know and understand the value of a business plan. The business plan is a key component of the startup and fundraising process and serves as a foundation for your organization. However, it only tells part of the story. To get the whole picture and have a framework on which to build your business you also need a strategic plan and an operational plan.
- What is a business plan?
In its simplest format, a business plan describes the “who” and the “what” of your business. It lays out who is running the business and what the business does. It describes the products and services that your business sells and who the customers are.
- What is a strategic plan?
A strategic plan looks beyond the basics of a business plan to explain the “how”. It explains the long-term goals of the business and how it expects to achieve those goals over the long term. A strategic plan explores future products and services that your business might offer and target markets that you might expand into. The plan explains your strategy for long-term growth and expansion.
- What is an operational plan?
An operation plan zooms into the details of your business to explain how you are going to achieve your short-term goals . It is the “when” and “where” of your planning process. The operational plan covers the details of marketing campaigns, short-term product development, and more immediate goals and projects that will happen within the next year.
- What is the difference between a strategic plan and a business plan?
First, let’s look at the difference between a business and a strategic plan. For review:
A business plan covers the “who” and “what” of the business. The strategic plan gives us long-term goals and explains “how” the business will get there, providing a long-term view.
In broader terms, the business plan tells us who by showing us:
- Who is running the business? What makes them qualified? What do they bring to the table that adds value?
- Who is the competition? What do they offer and what makes you different?
- Who is your customer? How big is the market? Where are they? What do they want and how will you give it to them? Also, how will you connect with your market?
The business plan answers the “what” by telling us:
- What the business provides and how it’s provided.
- Product, services, and operations are all explained so that readers understand how customer needs are met.
The strategic plan, on the other hand, outlines long term goals and the “how”, focusing on the following:
- Where will the business be in 3, 5, or even 10 years?
- How will you expand to offer different products and services over time?
- Will your market and industry change over time and how will your business react to those changes?
- How will you grow your market and reach new customers?
- What needs to happen so you can achieve your goals? What resources do you need to get there?
- How will you measure success? What metrics matter and how will you track them?
So, your business plan explains what you are doing right now. Your strategic plan explains long-term aspirations and how you plan to transition your business from where it is today to where you want it to be in the future. The strategic plan helps you look more deeply into the future and explains the key moves you have to make to achieve your vision.
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
- What is the difference between strategic planning and operational planning?
While strategic planning looks at the long term and explains your broad strategies for growth, an operational plan looks at the short term. It explains the details of what your business is going to do and when it’s going to do it over the next twelve months or so. An operational plan covers details like:
- What activities need to happen to achieve your business goals?
- When will each activity take place, who will do it, and when do you need to reach specific milestones?
- How will your business operate? What suppliers will you work with? When do you need to have them in place?
- What marketing campaigns will you run and what will they cost?
- What investments will you make in your products and services this year?
The bottom line, your operational plan is the short-term action plan for your business. It’s the tasks, milestones, and steps needed to drive your business forward. Typically an operational plan provides details for a 1-year period, while a strategic plan looks at a 3-5 year timeline , and sometimes even longer. The operational plan is essentially the roadmap for how you will execute your strategic plan.
- How to use your business plan for strategic development and operations
A great business plan can encompass both the basic plans for the business, the long-term strategic plan, and the near-term operational plan. Using a lean planning method, you can tackle all three phases of planning and make the process easy to review and revise as your business grows, changes, and adapts.
Start with a simple plan
The lean planning methodology starts with a simple, 30-minute business plan that outlines the fundamentals of your business: who you are, what you are doing, and who your customers are. It’s a great way to provide a brief overview of your business.
Expand your plan
From there, you can expand your plan to include your longer-term strategy. Adding greater detail to elements of the plan to explain long-term goals, milestones, and how your products and services will change and expand over time to meet changing market conditions.
Finally, your lean plan will cover financial forecasts that include monthly details about the short-term revenue and expenses, as well as longer-term annual summaries of your financial goals, including profitability and potential future loans and investments.
- Use your business plan to manage your business
Regardless of the type of plan, you are working on, you need a team of players on hand to help you plan, develop, and execute both the operational and strategic plans. Remember, your business needs both to give it a clear foundation and a sense of direction. As well as to assist you with identifying the detailed work that has to happen to help you reach your long-term goals.
Learn how LivePlan can help you develop a business plan that defines your business, outlines strategic steps, and tracks ongoing operations. You can easily share it with your team and all of the right stakeholders, explore scenarios and update your plan based on real-world results. Everything you need to turn your business plan into a tool for growth.
Noah is the COO at Palo Alto Software, makers of the online business plan app LivePlan. He started his career at Yahoo! and then helped start the user review site Epinions.com. From there he started a software distribution business in the UK before coming to Palo Alto Software to run the marketing and product teams.
Table of Contents
Related Articles

11 Min. Read
Use This Simple Business Plan Outline Example to Organize Your Plan

7 Min. Read
5 Consequences of Skipping a Business Plan

3 Min. Read
11 Key Components of a Business Plan

6 Min. Read
Business Plan vs Business Model Canvas Explained
The LivePlan Newsletter
Become a smarter, more strategic entrepreneur.
Your first monthly newsetter will be delivered soon..
Unsubscribe anytime. Privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
While both a strategic and business plan is forward-facing and focused on future success, a business plan is focused on the more immediate future. A business plan normally looks ahead no further than one year. A business plan is set up to measure success within a 3- to 12-month timeframe and determines what steps a business owner needs to take ...
A strategic plan typically provides a high-level overview of the organization's goals and the strategies to achieve them without going deep into the business operations. Strategic plans are generally 10-15 pages long, but the length depends on various factors of the business.
The strategic plan and business plan also offer different uses and benefits as well. Benefits of using a strategic plan One of the primary benefits of a strategic plan is that it helps a company to increase its profitability, allowing for greater flexibility in how it can allocate funds for components like buying newer technologies and hiring ...
A business plan is exactly what the name suggests— a plan to start and run a business or a new entity of an existing business; usually either an expansion in a newer region or a diversification into a new market. Business plans are mainly created for internal reference purposes or external funding purposes, with the latter being the common usage.
Business strategy is the battle plan for a better future. - Patrick Dixon . Scaling up a business without a clear strategy is like captaining a ship without a rudder. The success of any business depends on the strategy that one follows. The business strategy establishes the needs of the business.
Strategy Implementation. Crafting a business strategy is just the first step in the process. Implementation takes a strategy from formulation to execution.Successful implementation includes the following steps:. Establish clear goals and key performance indicators (KPIs); Set expectations and ensure employees are aware of their roles and responsibilities
A business plan is a document detailing a company's business activities and strategies for achieving its goals. Startup companies use business plans to launch their venture and to attract outside ...
Related: 4 Business Strategy Skills Every Business Leader Needs. 6 Steps to Develop a Value-Based Business Strategy 1. Define Your Purpose. When approaching business strategy, defining your organization's purpose can be a useful starting point. This is vital in creating customer and employee value, especially if your organization's purpose ...
A great business plan can encompass both the basic plans for the business, the long-term strategic plan, and the near-term operational plan. Using a lean planning method, you can tackle all three phases of planning and make the process easy to review and revise as your business grows, changes, and adapts.
"A business plan describes the foundations of a company, its owners, its capabilities, the industry and market(s) in which it operates, how it generates revenues and its financial projections," says Jérôme Côté, a Business Advisor with BDC's Advisory Services who counsels companies on strategic planning.