
- Games & Quizzes
- History & Society
- Science & Tech
- Biographies
- Animals & Nature
- Geography & Travel
- Arts & Culture
- On This Day
- One Good Fact
- New Articles
- Lifestyles & Social Issues
- Philosophy & Religion
- Politics, Law & Government
- World History
- Health & Medicine
- Browse Biographies
- Birds, Reptiles & Other Vertebrates
- Bugs, Mollusks & Other Invertebrates
- Environment
- Fossils & Geologic Time
- Entertainment & Pop Culture
- Sports & Recreation
- Visual Arts
- Demystified
- Image Galleries
- Infographics
- Top Questions
- Britannica Kids
- Saving Earth
- Space Next 50
- Student Center
- Introduction & Top Questions

Early life and training
- Screen memories
- The interpretation of dreams
- Further theoretical development
- Sexuality and development
- Toward a general theory
- Religion, civilization, and discontents

Where was Sigmund Freud educated?
What did sigmund freud die of, why is sigmund freud famous.

Sigmund Freud
Our editors will review what you’ve submitted and determine whether to revise the article.
- Simply Psychology - Sigmund Freud's Theories
- British Psychological Society - Sigmund Freud and penis envy – a failure of courage?
- Good Therapy - Sigmund Freud
- Famous Scientists - Sigmund Freud
- Institute of Psychoanalysis - Sigmund Freud
- Public Broadcasting Service - People and Discoveries - Biography of Sigmund Freud
- Social Science LibreTexts - A Brief Biography of Sigmund Freud, M.D.
- Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy - Biography of Sigmund Freud
- Sigmund Freud - Children's Encyclopedia (Ages 8-11)
- Sigmund Freud - Student Encyclopedia (Ages 11 and up)
- Table Of Contents

After graduating (1873) from secondary school in Vienna, Sigmund Freud entered the medical school of the University of Vienna , concentrating on physiology and neurology ; he obtained a medical degree in 1881. He trained (1882–85) as a clinical assistant at the General Hospital in Vienna and studied (1885–86) in Paris under neurologist Jean-Martin Charcot .
Sigmund Freud died of a lethal dose of morphine administered at his request by his friend and physician Max Schur. Freud had been suffering agonizing pain caused by an inoperable cancerous tumour in his eye socket and cheek. The cancer had begun as a lesion in his mouth that he discovered in 1923.
What did Sigmund Freud write?
Sigmund Freud’s voluminous writings included The Interpretation of Dreams (1899/1900), The Psychopathology of Everyday Life (1904), Totem and Taboo (1913), and Civilization and Its Discontents (1930).
Freud is famous for inventing and developing the technique of psychoanalysis ; for articulating the psychoanalytic theory of motivation, mental illness , and the structure of the subconscious ; and for influencing scientific and popular conceptions of human nature by positing that both normal and abnormal thought and behaviour are guided by irrational and largely hidden forces.
Recent News
Trusted Britannica articles, summarized using artificial intelligence, to provide a quicker and simpler reading experience. This is a beta feature. Please verify important information in our full article.
This summary was created from our Britannica article using AI. Please verify important information in our full article.
Sigmund Freud (born May 6, 1856, Freiberg, Moravia , Austrian Empire [now Příbor, Czech Republic]—died September 23, 1939, London , England) was an Austrian neurologist and the founder of psychoanalysis .
(Read Sigmund Freud’s 1926 Britannica essay on psychoanalysis.)
Freud may justly be called the most influential intellectual legislator of his age. His creation of psychoanalysis was at once a theory of the human psyche, a therapy for the relief of its ills, and an optic for the interpretation of culture and society. Despite repeated criticisms , attempted refutations, and qualifications of Freud’s work, its spell remained powerful well after his death and in fields far removed from psychology as it is narrowly defined. If, as American sociologist Philip Rieff once contended, “psychological man” replaced such earlier notions as political, religious, or economic man as the 20th century’s dominant self-image, it is in no small measure due to the power of Freud’s vision and the seeming inexhaustibility of the intellectual legacy he left behind.
Freud’s father, Jakob, was a Jewish wool merchant who had been married once before he wed the boy’s mother, Amalie Nathansohn. The father, 40 years old at Freud’s birth , seems to have been a relatively remote and authoritarian figure, while his mother appears to have been more nurturant and emotionally available. Although Freud had two older half-brothers, his strongest if also most ambivalent attachment seems to have been to a nephew, John, one year his senior, who provided the model of intimate friend and hated rival that Freud reproduced often at later stages of his life.
In 1859 the Freud family was compelled for economic reasons to move to Leipzig and then a year after to Vienna , where Freud remained until the Nazi annexation of Austria 78 years later. Despite Freud’s dislike of the imperial city , in part because of its citizens’ frequent anti-Semitism , psychoanalysis reflected in significant ways the cultural and political context out of which it emerged. For example, Freud’s sensitivity to the vulnerability of paternal authority within the psyche may well have been stimulated by the decline in power suffered by his father’s generation, often liberal rationalists, in the Habsburg empire. So too his interest in the theme of the seduction of daughters was rooted in complicated ways in the context of Viennese attitudes toward female sexuality .
In 1873 Freud was graduated from the Sperl Gymnasium and, apparently inspired by a public reading of an essay by Goethe on nature, turned to medicine as a career. At the University of Vienna he worked with one of the leading physiologists of his day, Ernst von Brücke , an exponent of the materialist, antivitalist science of Hermann von Helmholtz . In 1882 he entered the General Hospital in Vienna as a clinical assistant to train with the psychiatrist Theodor Meynert and the professor of internal medicine Hermann Nothnagel. In 1885 Freud was appointed lecturer in neuropathology, having concluded important research on the brain ’s medulla . At this time he also developed an interest in the pharmaceutical benefits of cocaine , which he pursued for several years. Although some beneficial results were found in eye surgery, which have been credited to Freud’s friend Carl Koller , the general outcome was disastrous. Not only did Freud’s advocacy lead to a mortal addiction in another close friend, Ernst Fleischl von Marxow, but it also tarnished his medical reputation for a time. Whether or not one interprets this episode in terms that call into question Freud’s prudence as a scientist, it was of a piece with his lifelong willingness to attempt bold solutions to relieve human suffering.
Freud’s scientific training remained of cardinal importance in his work, or at least in his own conception of it. In such writings as his “Entwurf einer Psychologie” (written 1895, published 1950; “Project for a Scientific Psychology”) he affirmed his intention to find a physiological and materialist basis for his theories of the psyche. Here a mechanistic neurophysiological model vied with a more organismic, phylogenetic one in ways that demonstrate Freud’s complicated debt to the science of his day.
In late 1885 Freud left Vienna to continue his studies of neuropathology at the Salpêtrière clinic in Paris, where he worked under the guidance of Jean-Martin Charcot . His 19 weeks in the French capital proved a turning point in his career, for Charcot’s work with patients classified as “ hysterics ” introduced Freud to the possibility that psychological disorders might have their source in the mind rather than the brain. Charcot’s demonstration of a link between hysterical symptoms, such as paralysis of a limb, and hypnotic suggestion implied the power of mental states rather than nerves in the etiology of disease . Although Freud was soon to abandon his faith in hypnosis , he returned to Vienna in February 1886 with the seed of his revolutionary psychological method implanted.
Several months after his return Freud married Martha Bernays, the daughter of a prominent Jewish family whose ancestors included a chief rabbi of Hamburg and Heinrich Heine . She was to bear six children, one of whom, Anna Freud , was to become a distinguished psychoanalyst in her own right. Although the glowing picture of their marriage painted by Ernest Jones in his study The Life and Works of Sigmund Freud (1953–57) has been nuanced by later scholars, it is clear that Martha Bernays Freud was a deeply sustaining presence during her husband’s tumultuous career.
Shortly after getting married Freud began his closest friendship, with the Berlin physician Wilhelm Fliess, whose role in the development of psychoanalysis has occasioned widespread debate. Throughout the 15 years of their intimacy Fliess provided Freud an invaluable interlocutor for his most daring ideas. Freud’s belief in human bisexuality , his idea of erotogenic zones on the body, and perhaps even his imputation of sexuality to infants may well have been stimulated by their friendship.
A somewhat less controversial influence arose from the partnership Freud began with the physician Josef Breuer after his return from Paris. Freud turned to a clinical practice in neuropsychology , and the office he established at Berggasse 19 was to remain his consulting room for almost half a century. Before their collaboration began, during the early 1880s, Breuer had treated a patient named Bertha Pappenheim —or “Anna O.,” as she became known in the literature—who was suffering from a variety of hysterical symptoms. Rather than using hypnotic suggestion, as had Charcot, Breuer allowed her to lapse into a state resembling autohypnosis, in which she would talk about the initial manifestations of her symptoms. To Breuer’s surprise, the very act of verbalization seemed to provide some relief from their hold over her (although later scholarship has cast doubt on its permanence). “The talking cure” or “chimney sweeping,” as Breuer and Anna O., respectively, called it, seemed to act cathartically to produce an abreaction, or discharge, of the pent-up emotional blockage at the root of the pathological behaviour.
Sigmund Freud
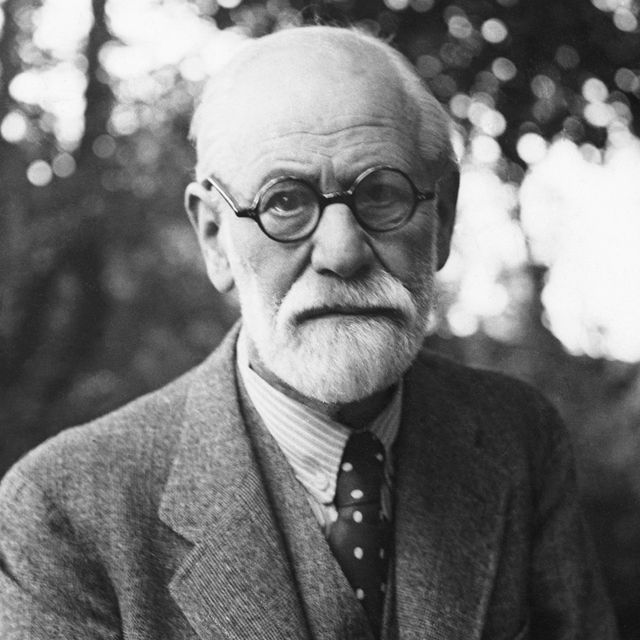

(1856-1939)
Who Was Sigmund Freud?
Sigmund Freud was an Austrian neurologist who developed psychoanalysis, a method through which an analyst unpacks unconscious conflicts based on the free associations, dreams and fantasies of the patient. His theories on child sexuality, libido and the ego, among other topics, were some of the most influential academic concepts of the 20th century.
Early Life, Education and Career
Freud was born in the Austrian town of Freiberg, now known as the Czech Republic, on May 6, 1856. When he was four years old, Freud’s family moved to Vienna, the town where he would live and work for most of the remainder of his life. He received his medical degree in 1881. As a medical student and young researcher, Freud’s research focused on neurobiology, exploring the biology of brains and nervous tissue of humans and animals.
After graduation, Freud promptly set up a private practice and began treating various psychological disorders. Considering himself first and foremost a scientist, rather than a doctor, he endeavored to understand the journey of human knowledge and experience.
Early in his career, Freud became greatly influenced by the work of his friend and Viennese colleague, Josef Breuer, who had discovered that when he encouraged a hysterical patient to talk uninhibitedly about the earliest occurrences of the symptoms, the symptoms sometimes gradually abated.
After much work together, Breuer ended the relationship, feeling that Freud placed too much emphasis on the sexual origins of a patient's neuroses and was completely unwilling to consider other viewpoints. Meanwhile, Freud continued to refine his own argument.
Freud's psychoanalytic theory, inspired by his colleague Josef Breuer, posited that neuroses had their origins in deeply traumatic experiences that had occurred in the patient's past. He believed that the original occurrences had been forgotten and hidden from consciousness. His treatment was to empower his patients to recall the experience and bring it to consciousness, and in doing so, confront it both intellectually and emotionally. He believed one could then discharge it and rid oneself of the neurotic symptoms. Some of Freud’s most discussed theories included:
- Id, ego and superego: These are the three essential parts of the human personality. The id is the primitive, impulsive and irrational unconscious that operates solely on the outcome of pleasure or pain and is responsible for instincts to sex and aggression. The ego is the “I” people perceive that evaluates the outside physical and social world and makes plans accordingly. And the superego is the moral voice and conscience that guides the ego; violating it results in feelings of guilt and anxiety. Freud believed the superego was mostly formed within the first five years of life based on the moral standards of a person’s parents; it continued to be influenced into adolescence by other role models.
- Psychic energy: Freud postulated that the id was the basic source of psychic energy or the force that drives all mental processes. In particular, he believed that libido, or sexual urges, was a psychic energy that drives all human actions; the libido was countered by Thanatos, the death instinct that drives destructive behavior.
- Oedipus complex: Between the ages of three and five, Freud suggested that as a normal part of the development process all kids are sexually attracted to the parent of the opposite sex and in competition with the parent of the same sex. The theory is named after the Greek legend of Oedipus, who killed his father so he could marry his mother.
- Dream analysis: In his book The Interpretation of Dreams , Freud believed that people dreamed for a reason: to cope with problems the mind is struggling with subconsciously and can’t deal with consciously. Dreams were fueled by a person’s wishes. Freud believed that by analyzing our dreams and memories, we can understand them, which can subconsciously influence our current behavior and feelings.
The great reverence that was later given to Freud's theories was not in evidence for some years. Most of his contemporaries felt that his emphasis on sexuality was either scandalous or overplayed. In 1909, he was invited to give a series of lectures in the United States; it was only after the ensuing publication of his book Five Lectures on Psycho-Analysis (1916) that his fame grew exponentially.
Freud has published a number of important works on psychoanalysis. Some of the most influential include:
'Studies in Hysteria' (1895)
Freud and Breuer published their theories and findings in this book, which discussed their theories that by confronting trauma from a patient’s past, a psychoanalyst can help a patient rid him or herself of neuroses.
'The Interpretation of Dreams' (1900)
In 1900, after a serious period of self-analysis, Freud published what has become his most important and defining work, which posits that dream analysis can give insight into the workings of the unconscious mind. The book was and remains controversial, producing such topics as the Oedipus complex. Many psychologists say this work gave birth to modern scientific thinking about the mind and the fields of psychology, psychiatry and psychoanalysis.
'The Psychopathology of Everyday Life' (1901)
This book gave birth to the so-called “Freudian slip” — the psychological meaning behind the misuse of words in everyday writing and speech and the forgetting of names and words. These slips, he explained through a series of examples, revealed our inner desires, anxieties and fantasies.
'Three Essays on the Theory of Sexuality' (1905)
While no one person will die without sex, the whole of humanity would without it — so sex drives human instincts, Freud believed. In this work, he explores sexual development and the relationship between sex and social behavior without applying his controversial Oedipal complex.
Wife and Kids
In 1882, Freud became engaged to marry Martha Bernays. The couple had six children — the youngest of whom, Anna Freud, went on to become a distinguished psychoanalyst herself.
Freud fled Austria to escape the Nazis in 1938 and died in England on September 23, 1939, at age 83 by suicide. He had requested a lethal dose of morphine from his doctor, following a long and painful battle with oral cancer.
Watch "Sigmund Freud: Analysis of a Mind" on HISTORY Vault

QUICK FACTS
- Name: Sigmund Freud
- Birth Year: 1856
- Birth date: May 6, 1856
- Birth City: Freiberg, Moravia, Austrian Empire
- Gender: Male
- Best Known For: Sigmund Freud was an Austrian neurologist best known for developing the theories and techniques of psychoanalysis.
- Writing and Publishing
- World War II
- Education and Academia
- Science and Medicine
- Astrological Sign: Taurus
- University of Vienna
- Nacionalities
- Interesting Facts
- Freud's book, 'The Interpretation of Dreams,' is said to have given birth to modern scientific thinking about the mind and the fields of psychology, psychiatry and psychoanalysis.
- Death Year: 1939
- Death date: September 23, 1939
- Death City: London
- Death Country: England
We strive for accuracy and fairness.If you see something that doesn't look right, contact us !
CITATION INFORMATION
- Article Title: Sigmund Freud Biography
- Author: Biography.com Editors
- Website Name: The Biography.com website
- Url: https://www.biography.com/scientists/sigmund-freud
- Access Date:
- Publisher: A&E; Television Networks
- Last Updated: May 3, 2021
- Original Published Date: April 3, 2014
- Religion is an illusion and it derives its strength from the fact that it falls in with our instinctual desires.
- Where id is, there shall ego be.
- Sometimes a cigar is just a cigar.
Famous Scientists
The Solar Eclipse That Made Albert Einstein a Star

Jane Goodall

Marie Curie

Howard Carter, King Tut's Tomb, and a Deadly Curse

Benjamin Banneker

Neil deGrasse Tyson

Daniel Hale Williams

Patricia Bath

Mae Jemison

George Washington Carver

Albert Einstein’s Role in the Atomic Bomb
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
Sigmund Freud's Life, Theories, and Influence
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Cara Lustik is a fact-checker and copywriter.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Cara-Lustik-1000-77abe13cf6c14a34a58c2a0ffb7297da.jpg)
Keystone / Hulton Archive / Getty Images
Psychoanalysis
- Major Works
- Perspectives
- Thinkers Influenced by Freud
- Contributions
Frequently Asked Questions
Psychology's most famous figure is also one of the most influential and controversial thinkers of the 20th century. Sigmund Freud, an Austrian neurologist born in 1856, is often referred to as the "father of modern psychology."
Freud revolutionized how we think about and treat mental health conditions. Freud founded psychoanalysis as a way of listening to patients and better understanding how their minds work. Psychoanalysis continues to have an enormous influence on modern psychology and psychiatry.
Sigmund Freud's theories and work helped shape current views of dreams, childhood, personality, memory, sexuality, and therapy. Freud's work also laid the foundation for many other theorists to formulate ideas, while others developed new theories in opposition to his ideas.
Sigmund Freud Biography
To understand Freud's legacy, it is important to begin with a look at his life. His experiences informed many of his theories, so learning more about his life and the times in which he lived can lead to a deeper understanding of where his theories came from.
Freud was born in 1856 in a town called Freiberg in Moravia—in what is now known as the Czech Republic. He was the oldest of eight children. His family moved to Vienna several years after he was born, and he lived most of his life there.
Freud earned a medical degree and began practicing as a doctor in Vienna. He was appointed Lecturer on Nervous Diseases at the University of Vienna in 1885.
After spending time in Paris and attending lectures given by the French neurologist Jean-Martin Charcot, Freud became more interested in theories explaining the human mind (which would later relate to his work in psychoanalysis).
Freud eventually withdrew from academia after the Viennese medical community rejected the types of ideas he brought back from Paris (specifically on what was then called hysteria ). Freud went on to publish influential works in neurology, including "On Aphasia: A Critical Study," in which he coined the term agnosia , meaning the inability to interpret sensations.
In later years, Freud and his colleague Josef Breuer published "Preliminary Report" and "Studies on Hysteria." When their friendship ended, Freud continued to publish his own works on psychoanalysis.
Freud and his family left Vienna due to discrimination against Jewish people. He moved to England in 1938 and died in 1939.
Sigmund Freud’s Theories
Freud's theories were enormously influential but subject to considerable criticism both now and during his life. However, his ideas have become interwoven into the fabric of our culture, with terms such as " Freudian slip ," "repression," and "denial" appearing regularly in everyday language.
Freud's theories include:
- Unconscious mind : This is one of his most enduring ideas, which is that the mind is a reservoir of thoughts, memories, and emotions that lie outside the awareness of the conscious mind.
- Personality : Freud proposed that personality was made up of three key elements: the id, the ego, and the superego . The ego is the conscious state, the id is the unconscious, and the superego is the moral or ethical framework that regulates how the ego operates.
- Life and death instincts : Freud claimed that two classes of instincts, life and death, dictated human behavior. Life instincts include sexual procreation, survival and pleasure; death instincts include aggression, self-harm, and destruction.
- Psychosexual development : Freud's theory of psychosexual development posits that there are five stages of growth in which people's personalities and sexual selves evolve. These phases are the oral stage, anal stage, phallic stage, latent stage, and genital stage.
- Mechanisms of defense : Freud suggested that people use defense mechanisms to avoid anxiety. These mechanisms include displacement, repression, sublimation, and regression.
Sigmund Freud and Psychoanalysis
Freud's ideas had such a strong impact on psychology that an entire school of thought emerged from his work: psychoanalysis. Psychoanalysis has had a lasting impact on both the study of psychology and the practice of psychotherapy.
Psychoanalysis sought to bring unconscious information into conscious awareness in order to induce catharsis . Catharsis is an emotional release that may bring about relief from psychological distress.
Research has found that psychoanalysis can be an effective treatment for a number of mental health conditions. The self-examination that is involved in the therapy process can help people achieve long-term growth and improvement.
Sigmund Freud's Patients
Freud based his ideas on case studies of his own patients and those of his colleagues. These patients helped shape his theories and many have become well known. Some of these individuals included:
- Anna O. (aka Bertha Pappenheim)
- Little Hans (Herbert Graf)
- Dora (Ida Bauer)
- Rat Man (Ernst Lanzer)
- Wolf Man (Sergei Pankejeff)
- Sabina Spielrein
Anna O. was never actually a patient of Freud's. She was a patient of Freud's colleague Josef Breuer. The two men corresponded often about Anna O's symptoms, eventually publishing the book, "Studies on Hysteria" on her case. It was through their work and correspondence that the technique known as talk therapy emerged.
Major Works by Freud
Freud's writings detail many of his major theories and ideas. His personal favorite was "The Interpretation of Dreams ." Of it, he wrote: "[It] contains...the most valuable of all the discoveries it has been my good fortune to make. Insight such as this falls to one's lot but once in a lifetime."
Some of Freud's major books include:
- " The Interpretation of Dreams "
- "The Psychopathology of Everyday Life"
- "Totem and Taboo"
- "Civilization and Its Discontents"
- "The Future of an Illusion"
Freud's Perspectives
Outside of the field of psychology, Freud wrote and theorized about a broad range of subjects. He also wrote about and developed theories related to topics including sex, dreams, religion, women, and culture.
Views on Women
Both during his life and after, Freud was criticized for his views of women , femininity, and female sexuality. One of his most famous critics was the psychologist Karen Horney , who rejected his view that women suffered from "penis envy."
Penis envy, according to Freud, was a phenomenon that women experienced upon witnessing a naked male body, because they felt they themselves must be "castrated boys" and wished for their own penis.
Horney instead argued that men experience "womb envy" and are left with feelings of inferiority because they are unable to bear children.
Views on Religion
Freud was born and raised Jewish but described himself as an atheist in adulthood. "The whole thing is so patently infantile, so foreign to reality, that to anyone with a friendly attitude to humanity it is painful to think that the great majority of mortals will never be able to rise above this view of life," he wrote of religion.
He continued to have a keen interest in the topics of religion and spirituality and wrote a number of books focused on the subject.
Psychologists Influenced by Freud
In addition to his grand and far-reaching theories of human psychology, Freud also left his mark on a number of individuals who went on to become some of psychology's greatest thinkers. Some of the eminent psychologists who were influenced by Sigmund Freud include:
- Alfred Adler
- Erik Erikson
- Melanie Klein
- Ernst Jones
While Freud's work is often dismissed today as non-scientific, there is no question that he had a tremendous influence not only on psychology but on the larger culture as well.
Many of Freud's ideas have become so steeped in public awareness that we oftentimes forget that they have their origins in his psychoanalytic tradition.
Freud's Contributions to Psychology
Freud's theories are highly controversial today. For instance, he has been criticized for his lack of knowledge about women and for sexist notions in his theories about sexual development, hysteria, and penis envy.
People are skeptical about the legitimacy of Freud's theories because they lack the scientific evidence that psychological theories have today.
However, it remains true that Freud had a significant and lasting influence on the field of psychology. He provided a foundation for many concepts that psychologists used and continue to use to make new discoveries.
Perhaps Freud's most important contribution to the field of psychology was the development of talk therapy as an approach to treating mental health problems.
In addition to serving as the basis for psychoanalysis, talk therapy is now part of many psychotherapeutic interventions designed to help people overcome psychological distress and behavioral problems.
The Unconscious
Prior to the works of Freud, many people believed that behavior was inexplicable. He developed the idea of the unconscious as being the hidden motivation behind what we do. For instance, his work on dream interpretation suggested that our real feelings and desires lie underneath the surface of conscious life.
Childhood Influence
Freud believed that childhood experiences impact adulthood—specifically, traumatic experiences that we have as children can manifest as mental health issues when we're adults.
While childhood experiences aren't the only contributing factors to mental health during adulthood, Freud laid the foundation for a person's childhood to be taken into consideration during therapy and when diagnosing.
Literary Theory
Literary scholars and students alike often analyze texts through a Freudian lens. Freud's theories created an opportunity to understand fictional characters and even their authors based on what's written or what a reader can interpret from the text on topics such as dreams, sexuality, and personality.
Sigmund Freud was an Austrian neurologist who founded psychoanalysis. Also known as the father of modern psychology, he was born in 1856 and died in 1939.
While Freud theorized that childhood experiences shaped personality, the neo-Freudians (including Carl Jung, Alfred Adler, and Karen Horney) believed that social and cultural influences played an important role. Freud believed that sex was a primary human motivator, whereas neo-Freudians did not.
Sigmund Freud founded psychoanalysis and published many influential works such as "The Interpretation of Dreams." His theories about personality and sexuality were and continue to be extremely influential in the fields of psychology and psychiatry.
Sigmund Freud was born in a town called Freiberg in Moravia, which is now the Czech Republic.
It's likely that Freud died by natural means. However, he did have oral cancer at the time of his death and was administered a dose of morphine that some believed was a method of physician-assisted suicide.
Freud used psychoanalysis, also known as talk therapy, in order to get his patients to uncover their own unconscious thoughts and bring them into consciousness. Freud believed this would help his patients change their maladaptive behaviors.
Freud was the founder of psychoanalysis and introduced influential theories such as: his ideas of the conscious and unconscious; the id, ego, and superego; dream interpretation; and psychosexual development.
A Word From Verywell
While Freud's theories have been the subject of considerable controversy and debate, his impact on psychology, therapy, and culture is undeniable. As W.H. Auden wrote in his 1939 poem, "In Memory of Sigmund Freud":
"...if often he was wrong and, at times, absurd, to us he is no more a person now but a whole climate of opinion."
Grzybowski A, Żołnierz J. Sigmund Freud (1856-1939) . J Neurol . 2021;268(6):2299-2300. doi:10.1007/s00415-020-09972-4
Bargh JA. The modern unconscious . World Psychiatry . 2019;18(2):225-226. doi:10.1002/wps.20625
Boag S. Ego, drives, and the dynamics of internal objects . Front Psychol . 2014;5:666. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2014.00666
Meissner WW. The question of drive vs. motive in psychoanalysis: A modest proposal . J Am Psychoanal Assoc . 2009;57(4):807-845. doi:10.1177/0003065109342572
APA Dictionary of Psychology. Psychosexual development . American Psychological Association.
Waqas A, Rehman A, Malik A, Muhammad U, Khan S, Mahmood N. Association of ego defense mechanisms with academic performance, anxiety and depression in medical students: A mixed methods study . Cureus . 2015;7(9):e337. doi:10.7759/cureus.337
Shedler J. The efficacy of psychodynamic psychotherapy . Am Psychol . 2010;65(2):98-109. doi:10.1037/a0018378
Bogousslavsky J, Dieguez S. Sigmund Freud and hysteria: The etiology of psychoanalysis . In: Bogousslavsky J, ed. Frontiers of Neurology and Neuroscience . S Karger AG. 2014;35:109-125. doi:10.1159/000360244
Grubin D. Young Dr. Freud . Public Broadcasting Service.
Gersick S. Penis envy . In: Zeigler-Hill V, Shackelford T, eds. Encyclopedia of Personality and Individual Differences . Springer, Cham. 2017. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-28099-8_616-1
Bayne E. Womb envy: The cause of misogyny and even male achievement? . Womens Stud Int Forum. 2011;34(2):151-160. doi:10.1016/j.wsif.2011.01.007
Freud S. Civilization and Its Discontents . Norton.
Yeung AWK. Is the influence of Freud declining in psychology and psychiatry? A bibliometric analysis . Front Psychol. 2021;12. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2021.631516
Giordano G. The contribution of Freud’s theories to the literary analysis of two Victorian novels: Wuthering Heights and Jane Eyre . Int J Engl Lit. 2020;11(2):29-34. doi:10.5897/IJEL2019.1312
APA Dictionary of Psychology. Neo-Freudian . American Psychological Association.
Hoffman L. Un homme manque: Freud's engagement with Alfred Adler's masculine protest: Commentary on Balsam . J Am Psychoanal Assoc . 2017;65(1):99-108. doi:10.1177/0003065117690351
Macleod ADS. Was Sigmund Freud's death hastened? . Intern Med J. 2017;47(8):966-969. doi:10.1111/imj.13504
Kernberg OF. The four basic components of psychoanalytic technique and derived psychoanalytic psychotherapies . World Psychiatry . 2016;15(3):287-288. doi:10.1002/wps.20368
Yale University. In Memory of Sigmund Freud .
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
Sigmund Freud’s Theories & Contribution to Psychology
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:

Sigmund Freud (1856 to 1939) was the founding father of psychoanalysis , a method for treating mental illness and a theory explaining human behavior.
Freud believed that events in our childhood have a great influence on our adult lives, shaping our personality. For example, anxiety originating from traumatic experiences in a person’s past is hidden from consciousness and may cause problems during adulthood (neuroses).
Thus, when we explain our behavior to ourselves or others (conscious mental activity), we rarely give a true account of our motivation. This is not because we are deliberately lying. While human beings are great deceivers of others; they are even more adept at self-deception.
Freud’s life work was dominated by his attempts to penetrate this often subtle and elaborate camouflage that obscures the hidden structure and processes of personality.
His lexicon has become embedded within the vocabulary of Western society. Words he introduced through his theories are now used by everyday people, such as anal (personality), libido, denial, repression, cathartic, Freudian slip , and neurotic.
Who is Sigmund Freud
Sigmund Freud, born on May 6, 1856, in what is now Příbor, Czech Republic (then part of the Austrian Empire), is hailed as the father of psychoanalysis. He was the eldest of eight children in a Jewish family.
Freud initially wanted to become a law professional but later developed an interest in medicine. He entered the University of Vienna in 1873, graduating with an MD in 1881. His primary interests included neurology and neuropathology. He was particularly interested in the condition of hysteria and its psychological causes.
In 1885, Freud received a grant to study with Jean-Martin Charcot, a renowned neurologist who used hypnosis to treat women suffering from what was then called “hysteria.” This experience sparked Freud’s interest in the unconscious mind, a theme that would recur throughout his career.
In 1886, Freud returned to Vienna, married Martha Bernays, and set up a private practice to treat nervous disorders. His work during this time led to his revolutionary concepts of the human mind and the development of the psychoanalytic method.
Freud introduced several influential concepts, including the Oedipus complex, dream analysis, and the structural model of the psyche divided into the id, ego, and superego. He published numerous works throughout his career, the most notable being “ The Interpretation of Dreams ” (1900), “ The Psychopathology of Everyday Life ” (1901), and “ Three Essays on the Theory of Sexuality ” (1905).
Despite controversy and opposition, Freud continued to develop his theories and expand the field of psychoanalysis. He was deeply affected by the outbreak of World War I and later by the rise of the Nazis in Germany. In 1938, due to the Nazi threat, he emigrated to London with his wife and youngest daughter.
Freud died in London on September 23, 1939, but his influence on psychology, literature, and culture remains profound and pervasive.
He radically changed our understanding of the human mind, emphasizing the power of unconscious processes and pioneering therapeutic techniques that continue to be used today.
Sigmund Freud’s Theories & Contributions
Psychoanalytic Theory : Freud is best known for developing psychoanalysis , a therapeutic technique for treating mental health disorders by exploring unconscious thoughts and feelings.
Unconscious Mind : Freud (1900, 1905) developed a topographical model of the mind, describing the features of the mind’s structure and function. Freud used the analogy of an iceberg to describe the three levels of the mind.

The id, ego, and superego have most commonly been conceptualized as three essential parts of the human personality.
Psychosexual Development : Freud’s controversial theory of psychosexual development suggests that early childhood experiences and stages (oral, anal, phallic, latency, and genital) shape our adult personality and behavior.
His theory of psychosexual stages of development is predicated by the concept that childhood experiences create the adult personality and that problems in early life would come back to haunt the individual as a mental illness.
Dream Analysis : Freud believed dreams were a window into the unconscious mind and developed methods for analyzing dream content for repressed thoughts and desires.
Dreams represent unfulfilled wishes from the id, trying to break through to the conscious. But because these desires are often unacceptable, they are disguised or censored using such defenses as symbolism.
Freud believed that by undoing the dreamwork , the analyst could study the manifest content (what they dreamt) and interpret the latent content ( what it meant) by understanding the symbols.
Defense Mechanisms : Freud proposed several defense mechanisms , like repression and projection, which the ego employs to handle the tension and conflicts among the id, superego, and the demands of reality.
Sigmund Freud’s Patients
Sigmund Freud’s clinical work with several patients led to major breakthroughs in psychoanalysis and a deeper understanding of the human mind. Here are summaries of some of his most notable cases:
Anna O. (Bertha Pappenheim) : Known as the ‘birth of psychoanalysis,’ Anna O . was a patient of Freud’s colleague Josef Breuer. However, her case heavily influenced Freud’s thinking.
She suffered from various symptoms, including hallucinations and paralysis, which Freud interpreted as signs of hysteria caused by repressed traumatic memories. The “talking cure” method with Anna O. would later evolve into Freudian psychoanalysis.
Dora (Ida Bauer) : Dora, a pseudonym Freud used, was a teenager suffering from what he diagnosed as hysteria. Her symptoms included aphonia (loss of voice) and a cough.
Freud suggested her issues were due to suppressed sexual desires, particularly those resulting from a complex series of relationships in her family. The Dora case is famous for the subject’s abrupt termination of therapy, and for the criticisms Freud received regarding his handling of the case.
Little Hans (Herbert Graf) : Little Hans , a five-year-old boy, feared horses. Freud never met Hans but used information from the boy’s father to diagnose him.
He proposed that Little Hans’ horse phobia was symbolic of a deeper fear related to the Oedipus Complex – unconscious feelings of affection for his mother and rivalry with his father. The case of Little Hans is often used as an example of Freud’s theory of the Oedipal Complex in children.
Rat Man (Ernst Lanzer) : Rat Man came to Freud suffering from obsessive thoughts and fears related to rats, a condition known as obsessional neurosis.
Freud connected his symptoms to suppressed guilt and repressed sexual desires. The treatment of Rat Man further expanded Freud’s work on understanding the role of internal conflicts and unconscious processes in mental health disorders.
Wolf Man (Sergei Pankejeff) : Wolf Man was a wealthy Russian aristocrat who came to Freud with various symptoms, including a recurring dream about wolves.
Freud’s analysis, focusing on childhood memories and dreams, led him to identify the presence of repressed memories and the influence of the Oedipus Complex . Wolf Man’s treatment is often considered one of Freud’s most significant and controversial cases.
In the highly repressive “Victorian” society in which Freud lived and worked, women, in particular, were forced to repress their sexual needs. In many cases, the result was some form of neurotic illness.
Freud sought to understand the nature and variety of these illnesses by retracing the sexual history of his patients. This was not primarily an investigation of sexual experiences as such. Far more important were the patient’s wishes and desires, their experience of love, hate, shame, guilt, and fear – and how they handled these powerful emotions.

Freud’s Followers
Freud attracted many followers, who formed a famous group in 1902 called the “Psychological Wednesday Society.” The group met every Wednesday in Freud’s waiting room.
As the organization grew, Freud established an inner circle of devoted followers, the so-called “Committee” (including Sàndor Ferenczi, and Hanns Sachs (standing) Otto Rank, Karl Abraham, Max Eitingon, and Ernest Jones).
At the beginning of 1908, the committee had 22 members and was renamed the Vienna Psychoanalytic Society.

Neo-Freudians
The term “neo-Freudians” refers to psychologists who were initially followers of Sigmund Freud (1856 to 1939) but later developed their own theories, often modifying or challenging Freud’s ideas.
Here are summaries of some of the most notable neo-Freudians:
Carl Jung : Jung (1875 – 1961) was a close associate of Freud but split due to theoretical disagreements. He developed the concept of analytical psychology, emphasizing the collective unconscious, which houses universal symbols or archetypes shared by all human beings. He also introduced the idea of introversion and extraversion.
Alfred Adler : Adler (1870 – 1937) was another early follower of Freud who broke away due to differing views. He developed the school of individual psychology, highlighting the role of feelings of inferiority and the striving for superiority or success in shaping human behavior. He also emphasized the importance of social context and community.
- Otto Rank : Rank (1884 – 1939) was an early collaborator with Freud and played a significant role in the development of psychoanalysis. He proposed the “trauma of birth” as a critical event influencing the psyche. Later, he shifted focus to the relationship between therapist and client, influencing the development of humanistic therapies.
Karen Horney : Horney (1885 – 1952) challenged Freud’s views on women, arguing against the concept of “penis envy.” She suggested that social and cultural factors significantly influence personality development and mental health. Her concept of ‘basic anxiety’ centered on feelings of helplessness and insecurity in childhood, shaping adult behavior.
- Harry Stack Sullivan : Sullivan (1892 – 1949) developed interpersonal psychoanalysis, emphasizing the role of interpersonal relationships and social experiences in personality development and mental disorders. He proposed the concept of the “self-system” formed through experiences of approval and disapproval during childhood.
Melanie Klein : Klein (1882 – 1960), a prominent psychoanalyst, is considered a neo-Freudian due to her development of object relations theory, which expanded on Freud’s ideas. She emphasized the significance of early childhood experiences and the role of the mother-child relationship in psychological development.
- Anna Freud : Freud’s youngest daughter significantly contributed to psychoanalysis, particularly in child psychology. Anna Freud (1895 – 1982) expanded on her father’s work, emphasizing the importance of ego defenses in managing conflict and preserving mental health.
Wilhelm Reich : Reich (1897 – 1957), once a student of Freud, diverged by focusing on bodily experiences and sexual repression, developing the theory of orgone energy. His emphasis on societal influence and body-oriented therapy made him a significant neo-Freudian figure.
- Erich Fromm : Fromm (1900-1980) was a German-American psychoanalyst associated with the Frankfurt School, who emphasized culture’s role in developing personality. He advocated psychoanalysis as a tool for curing cultural problems and thus reducing mental illness.
Erik Erikson : Erikson (1902 – 1994) extended Freud’s theory of psychosexual development by adding social and cultural aspects and proposing a lifespan development model. His theory of psychosocial development outlined eight stages, each marked by a specific crisis to resolve, that shape an individual’s identity and relationships.
Critical Evaluation
Does evidence support Freudian psychology? Freud’s theory is good at explaining but not predicting behavior (which is one of the goals of science ).
For this reason, Freud’s theory is unfalsifiable – it can neither be proved true or refuted. For example, the unconscious mind is difficult to test and measure objectively. Overall, Freud’s theory is highly unscientific.
Despite the skepticism of the unconscious mind, cognitive psychology has identified unconscious processes, such as procedural memory (Tulving, 1972), automatic processing (Bargh & Chartrand, 1999; Stroop, 1935), and social psychology has shown the importance of implicit processing (Greenwald & Banaji, 1995). Such empirical findings have demonstrated the role of unconscious processes in human behavior.
However, most evidence for Freud’s theories is from an unrepresentative sample. He mostly studied himself, his patients, and only one child (e.g., Little Hans ).
The main problem here is that the case studies are based on studying one person in detail, and regarding Freud, the individuals in question are most often middle-aged women from Vienna (i.e., his patients).
This makes generalizations to the wider population (e.g., the whole world) difficult. However, Freud thought this unimportant, believing in only a qualitative difference between people.
Freud may also have shown research bias in his interpretations – he may have only paid attention to information that supported his theories, and ignored information and other explanations that did not fit them.
However, Fisher & Greenberg (1996) argue that Freud’s theory should be evaluated in terms of specific hypotheses rather than a whole. They concluded that there is evidence to support Freud’s concepts of oral and anal personalities and some aspects of his ideas on depression and paranoia.
They found little evidence of the Oedipal conflict and no support for Freud’s views on women’s sexuality and how their development differs from men’.
Bargh, J. A., & Chartrand, T. L. (1999). The unbearable automaticity of being. American psychologist, 54 (7), 462.
Breuer, J., & Freud, S. (1895). Studies on hysteria . Standard Edition 2: London.
Fisher, S., & Greenberg, R. P. (1996). Freud scientifically reappraised: Testing the theories and therapy . John Wiley & Sons.
Freud, S. (1894). The neuro-psychoses of defence . SE, 3: 41-61.
Freud, S. (1896). Further remarks on the neuro-psychoses of defence . SE, 3: 157-185.
Freud, S. (1900). The interpretation of dreams . S.E., 4-5.
Freud, S. (1901). The psychopathology of everyday life. SE, 6. London: Hogarth .
Freud, S. (1905). Three essays on the theory of sexuality. Se , 7 , 125-243.
Freud, S. (1915). The unconscious . SE, 14: 159-204.
Freud, S. (1920) . Beyond the pleasure principle . SE, 18: 1-64.
Freud, S. (1923). The ego and the id . SE, 19: 1-66.
Freud, S. (1925). Negation. Standard edition , 19, 235-239.
Freud, S. (1961). The resistances to psycho-analysis. In T he Standard Edition of the Complete Psychological Works of Sigmund Freud, Volume XIX (1923-1925): The Ego and the Id and other works (pp. 211-224).
Greenwald, A. G., & Banaji, M. R. (1995). Implicit social cognition: attitudes, self-esteem, and stereotypes. Psychological review, 102 (1), 4.
Stroop, J. R. (1935). Studies of interference in serial verbal reactions. Journal of experimental psychology, 18 (6), 643.
Tulving, E. (1972). Episodic and semantic memory. In E. Tulving & W. Donaldson (Eds.), Organization of Memory , (pp. 381–403). New York: Academic Press.
What is Freud most famous for?
Why is freud so criticized, what did sigmund freud do.
His conceptualization of the mind’s structure (id, ego, superego), his theories of psychosexual development, and his exploration of defense mechanisms revolutionized our understanding of human psychology.
Despite controversies and criticisms, Freud’s theories have fundamentally shaped the field of psychology and the way we perceive the human mind.
What is the Freudian revolution’s impact on society?

Related Articles

Freudian Psychology
Attachment Theory and Psychoanalysis

Soft Determinism In Psychology

Branches of Psychology

Sigmund Freud Dream Theory

Anna O (Bertha Pappenheim): Life & Impact on Psychology

Freudian Psychology , Understanding Therapy
What Is Transference In Psychology?
Change Password
Your password must have 6 characters or more:.
- a lower case character,
- an upper case character,
- a special character
Password Changed Successfully
Your password has been changed
Create your account
Forget yout password.
Enter your email address below and we will send you the reset instructions
If the address matches an existing account you will receive an email with instructions to reset your password
Forgot your Username?
Enter your email address below and we will send you your username
If the address matches an existing account you will receive an email with instructions to retrieve your username

- July 01, 2024 | VOL. 181, NO. 7 CURRENT ISSUE pp.565-686
- June 01, 2024 | VOL. 181, NO. 6 pp.461-564
- May 01, 2024 | VOL. 181, NO. 5 pp.347-460
- April 01, 2024 | VOL. 181, NO. 4 pp.255-346
- March 01, 2024 | VOL. 181, NO. 3 pp.171-254
- February 01, 2024 | VOL. 181, NO. 2 pp.83-170
- January 01, 2024 | VOL. 181, NO. 1 pp.1-82
The American Psychiatric Association (APA) has updated its Privacy Policy and Terms of Use , including with new information specifically addressed to individuals in the European Economic Area. As described in the Privacy Policy and Terms of Use, this website utilizes cookies, including for the purpose of offering an optimal online experience and services tailored to your preferences.
Please read the entire Privacy Policy and Terms of Use. By closing this message, browsing this website, continuing the navigation, or otherwise continuing to use the APA's websites, you confirm that you understand and accept the terms of the Privacy Policy and Terms of Use, including the utilization of cookies.
Sigmund Freud, 1856–1939
- Glen O. Gabbard , M.D.
Search for more papers by this author
Sigmund Freud was born in 1856 in Moravia (now part of Czechoslovakia). Influenced by physiologist Hermann Helmholtz, he set out to apply the laws of physics to the human nervous system. His interest in neurology gradually gave way to pioneering efforts to understand unconscious influences on our behavior in illness and health. He studied with Brucke, Meynert, and Charcot, but Freud ultimately blazed a new trail of research and therapy that came to be known as psychoanalysis. When his efforts to retrieve the contents of the unconscious mind through hypnotically induced abreaction failed to produce lasting therapeutic results, Freud turned to the systematic analysis of the patient’s free associations to learn more about the unconscious factors that produced the symptoms of hysteria. This approach led him to replace the topographic model of making the unconscious conscious with the structural model of ego, id, and superego. Among his principal discoveries were transference, the displacement of past relationships onto figures in one’s current life, and resistance, the patient’s unconscious tendency to oppose the physician who is intent on helping. He was also instrumental in unlocking the mystery of dreamwork by identifying mechanisms such as condensation, displacement, symbolic representation, and secondary revision. Psychoanalysis and psychodynamic psychotherapy (derived from psychoanalysis) are now practiced throughout the world. Few thinkers have played so central a role in the last century’s intellectual and cultural life. While some of Freud’s ideas have required revision, modern neuroscience has confirmed many of his basic tenets. Freud predicted that psychoanalytic understanding would ultimately be wedded to breakthroughs in the study of brain mechanisms, and his dream is now coming to fruition.
Address reprint requests to Dr. Gabbard, Department of Psychiatry, Baylor College of Medicine, One Baylor Plaza, Houston, TX 77030; [email protected] (e-mail). Photo used with permission of the Kansas State Historical Society, Topeka, Kan.

Sigmund Freud Biography

Sigmund Freud was the man behind the concept and method of psychoanalysis, which was a means of delving into a person's inner conflicts that lie within the unconscious mind. This method is based on the understanding that people's fantasies and dreams say something about these problems that affect them in their daily lives. Freud also formed several theories that relate to the ego, libido and sexuality of the child, which are only a few of the other topics he studied and specialized on during his lifetime. Hence, Freud was regarded as one of the most influential and controversial personalities of the 20th century.
Sigmund Freud lived most of his years in Vienna, although Freiberg (a town in Austria) was his birthplace. When his family relocated to Vienna, Freud was only four years of age. It was in this city in Austria where he received a degree in the field of medicine, which was in 1881. A year after, he married and decided to practice his profession for a living. His main focus was on treating patients who suffered from psychological disorders, and this started his journey and preoccupation on studying human experience and instincts. He also worked with other scientists and scholars throughout his life, although he eventually formulated his own theories and developed a method for the treatment of psychological conditions among individuals.
Immediately after obtaining a medical degree at the University of Vienna, Sigmund Freud decided to work as a physician. He later expanded his knowledge by studying the works of Jean-Martin Charcot, who was a French neurologist. It was during this time that Freud developed an interest in the treatment of hysteria, which is an emotional disorder. Afterwards, Josef Breuer, one of Freud's mentors, introduced him to one patient's case study. The patient's name was Bertha Pappenheim, although she was simply known as "Anna O.". The patient suffered from various symptoms including paralysis, tactile anesthesia and a nervous cough. The two scientists discovered that Anna suffered from various traumatic experiences, which they believed had a significant contribution to her mental illness. Breuer and Freud encouraged the patient to talk freely about her symptoms and experiences. Since there was no known specific cause for Anna's difficulties, they simply allowed her to express her feelings and thoughts through talking. In 1895, the Studies on Hysteria was published, which was the outcome of their analysis on the improvement on Anna's condition by implementing the so-called "talking cure". Freud explored deeper into the human mind and sexuality, and this allowed him to publish several works including Three Essays on the Theory of Sexuality and The Interpretation of Dreams . Both of these written works by Freud became known worldwide, but his study of the psychosexual stages left a more lasting impact on critics and scholars alike. His theory was also met with much controversy and skepticism, yet this has a massive influence on the field of psychology up to this modern era.
Contributions
Sigmund Freud mainly worked on formulating theories that impact the human mind, mental disorders and sexuality. His works provided a deeper understanding on abnormal and clinical psychology, as well as the stages of human development. Some of his scholarly publications included The Ego and the Id , Moses and Monotheism , Three Essays on the Theory of Sexuality , Studies on Hysteria, Fragment of an Analysis of a Case of Hysteria, Civilization and Its Discontents , and The Interpretation of Dreams . He believed that mental disorders were rooted to cultural differences aside from physiological causes, as presented in his case studies. Although Freud initially worked with Breuer, the two parted ways because the latter believed that much of Freud's preoccupations were on the sexual origins of neuroses. They were unable to settle the differences in their viewpoints, and this triggered Freud to go deeper into his study. He also published his work "The Interpretation of Dreams", and he maintained the belief that a person's dreams reveal so much about the inner conflicts within. While he may have refined his theories and gained popularity with his publications, his contemporaries agreed on the assumption that Freud was more focused on sexuality as one of the topics of his studies. Nevertheless, Freud's fame increased worldwide as he received numerous invitations to deliver lectures in various parts of the United States, beginning 1909.
Sigmund Freud admitted that he had gone through conflicts within himself, which started during his early years. His father's death had an impact on him, and he went through feelings of guilt and shame, as well. He recalled how he viewed his father as his rival to the love and affection of his mother, which caused him to develop negative emotions. He reflected on this experience he had as a child and used it as one of his basis and inspiration in developing the theory on infantile sexuality and the concept of Oedipus Complex. There were several theories that Freud established, which are still recognized even up to this day. He also inspired several scholars and scientists during his time. For instance, Charles Darwin's theory on the evolution of man had some fascinating links to the study of Freud on human behavior. Then, there was this scientific theory by Helmholtz, which referred to energy and its constant quality in any physical system. This was related to Freud's analysis of the structural components of the human mind. Thus, the theories and scientific works of Freud may have been criticized and praised at the same time by his contemporaries, yet these are evidences of his strong influence in the field of psychology. Sigmund Freud battled with a serious illness during the last years of his life. He developed oral cancer, which caused him to struggle physically and emotionally. In 1939, while he was living in exile in England, he requested from his doctor a lethal dose of the drug morphine to end his sufferings. This resulted to the death of this controversial and influential scientist whose works remain with us until this very day.
Top of page
Collection Sigmund Freud Papers
Featured content, about this collection.
Digitization of this collection was made possible by The Polonsky Foundation .
The papers of psychoanalyst Sigmund Freud (1856-1939) span the years from about the 6th century B.C.E. (a small Greek statue) to 1998, with the bulk of material dating from 1871 to 1939. The digitized collection documents Freud's founding of psychoanalysis, the maturation of psychoanalytic theory, the refinement of its clinical technique, and the proliferation of its adherents and critics. Many facets of Freud's life and work are reflected, including his early medical and clinical training; his relationship with family, friends, colleagues, students, and patients; his association with early psychoanalytic societies; his perspectives on analytical training; and his numerous writings.
The physical collection, consisting in its entirety of 48,600 items, is located in the Library of Congress Manuscript Division and is organized in ten series as described in the collection's finding aid ( PDF and HTML ), updated with links to the digital content. The collection material is mostly in German, with some English and French. The digital edition comprises the contents of more than two thousand folders. Digitized in their entirety are those series described below containing papers that Freud or members of his family would have either created or owned. Also available digitally are interviews conducted by K. R. Eissler, a founder of the Sigmund Freud Archives (SFA), with Freud's associates, patients, and family members from the 1950s to the 1970s. Early interest in a digital edition of the Freud Papers and ongoing counsel from the SFA helped bring this digital project to fruition.
Omitted from the digital edition is the largely posthumous, supplemental material about Freud's life found in the Supplemental File series and parts of the Addition and Oversize series.
For additional background on the collection's provenance, see the Brief History of the Collection under the Articles and Essays tab.
Description of Series
Family papers, 1851-1978.
Correspondence, legal documents, estate records, writings, school records, immigration papers, certificates, genealogical data, a photograph, and printed matter documenting the lives and relationships of members of the Freud and Bernays families. Divided into three subseries, each arranged alphabetically therein by name of family member: Correspondence with Freud, Correspondence between Others, and a Subject File.
The Correspondence with Freud subseries consists of letters exchanged between Freud and family members including his mother Amalia Freud, his wife Martha Freud, and their children Ernst L. Freud, Martin Freud, Mathilde Freud Hollitscher, Oliver Freud, Sophie Freud Halberstadt, and Anna Freud, the only one of Sigmund Freud's children to become a psychoanalyst. Also included are letters to and from his sisters, brothers, nieces, nephews, grandchildren, and in-laws, including his sister-in-law and confidante Minna Bernays. Correspondence written by family members to people other than Freud are filed in the Correspondence between Others subseries. Also included in this subseries is correspondence between family members and with persons outside the family. Finally, the Subject File subseries contains legal documents, certificates, estate records, school records, writings, and printed matter documenting the lives of individual family members.
General Correspondence, 1871-1996
Correspondence including original letters, photocopies, transcripts, translations, and related background material between Sigmund Freud and his friends, professional associates, students, patients, and the public. Arranged alphabetically by name of correspondent and therein chronologically. Unidentified correspondence is filed at the end of the series.
Nearly six hundred correspondents are represented in the series. At times, their correspondence is limited to a single letter to or from Freud. In other cases, the correspondence is extensive, revealing Freud as a prolific correspondent who frequently chastised others for a lack of similar diligence. Included is correspondence with Karl Abraham, Alfred Adler, Franz Alexander, A. A. Brill, M. Eitingon, Sándor Ferenczi, Wilhelm Fliess, Eduard Hitschmann, Ernest Jones, C. G. Jung, Oskar Pfister, Otto Rank, Theodor Reik, Hanns Sachs, Ernst Simmel, Wilhelm Stekel, and Edoardo Weiss, among many others.
Prominent women in the field represented in the series include Lou Andreas-Salomé, Ruth Mack Brunswick, Emma Eckstein, Jeanne Lampl-de Groot, and Joan Riviere. Notable among Freud's patients with whom he corresponded is Sergius Pankejeff whom Freud referred to as the "Wolf-Man." Other prominent correspondents include Albert Einstein with whom Freud corresponded on the nature of war, Carl Koller who shared Freud's interest in the medical uses of cocaine, and novelist and essayist Thomas Mann.
Subject File, 1856-1988
School, university, and military records; patient case files and record book; calendars; notes and notebooks; birth, citizenship, and marriage certificates; biographical data; birthday greetings; condolence letters; photocopies of book annotations and marginalia; financial and estate records; wills; and clippings and other printed matter. Arranged alphabetically by name of organization or institution, subject, or type of material and therein chronologically.
The Subject File series contains a wide variety of records documenting many aspects of Freud's life. It includes patient case files from the Allgemeines Krankenhaus in Vienna and the Bellevue Sanatorium in Kreuzlingen, Switzerland, largely during the 1880s. Copies of book annotations and marginalia by Freud and others provide glimpses into the development of psychoanalytic theory. Freud's career is highlighted in a large file of newspaper and magazine clippings as well as material concerning the Goethe Prize he received in 1930 and the Nobel Prize which he coveted but never received. Calendars kept by Freud record his daily activities from 1916 to 1918. Freud's early life is documented by biographical data, birth and marriage certificates, and gymnasium, university, and military records. His departure from Nazi-controlled Austria and immigration to London in 1938 is tracked through American diplomatic cables and newspaper clippings. The series also contains letters and telegrams written on his death just over a year after his arrival in England.
Writings, 1877-1985
Writings by Freud, including holograph manuscripts, typescripts, galley proofs, printed publications, and photocopies. Arranged chronologically largely by year of first publication and therein according to the bibliographic sequence established by James Strachey in Indexes and Bibliographies , volume 24 of The Standard Edition of the Complete Psychological Works of Sigmund Freud (London: Hogarth Press and Institute of Psycho-analysis, 1974) and, for works published after 1974, by Ingeborg Meyer-Palmedo and Gerhard Fichtner, Freud-Bibliographie mit Werkkonkordanz (Frankfurt am Main: S. Fischer Verlag, 1989). Because of the large format of many of these items, the material has been filed in the Oversize series.
The writings range chronologically from an 1877 article on Freud's early research on eels to portions of his last major work, Der Mann Moses und die monotheistische Religion, published shortly before his death. Included in the series are articles, case histories, portions of books, published letters, lecture notes, prefaces, introductions, a travel journal, chronologies, obituaries, bibliographic notes, and casual jottings.
Interviews and Recollections, 1914-1998
Interviews with Freud associates, patients, and family members conducted by K. R. Eissler, a founder and longtime secretary of the Sigmund Freud Archives, and recollections about Freud contained in correspondence, writings, and notes sent to or collected by Eissler. Arranged in two parts: Set A contains interviews and recollections that opened in the years prior to 2016, and Set B contains interviews that became fully opened in October 2016. Material within each set is organized as interviews and recollections and alphabetically therein by name of individual.
Most of the interviews date from the 1950s. Included are transcripts, some with corrections by the interviewee, and summaries of interviews, usually made when the subject requested that the interview not be tape recorded. Among those interviewed by Eissler are family members Anna Freud Bernays, Anna Freud, Ernestine Drucker Freud, Harry Freud, Oliver Freud, and Judith Bernays Heller; prominent associates such as Franz Alexander, Ludwig Binswanger, Felix Deutsch, Max Graf, Eduard Hitschmann, Edith Banfield Jackson, Ludwig Jekels, C. G. Jung, Oskar Pfister, Theodor Reik, Joan Riviere, Philipp Sarasin, Hermann Swoboda, and Edoardo Weiss; and patients including Sergius Pankejeff. Also included in the series are recollections about Freud contained in letters, writings, and notes either addressed to or collected by Eissler.
Addition, 1912-1983
Correspondence, exhibit material, photographs, a case history, an index, lists, and printed matter. Arranged in groupings that correspond to other series in the collection and therein alphabetically by name of person or organization, topic, or type of material.
Digitized within this series are photocopies of Freud's correspondence with writer Arnold Zweig, derestricted in 2010 and filed in the Addition rather than in the General Correspondence series because of the volume of the material. The legibility of the photocopies varies considerably. Omitted from the digital edition is posthumous, supplemental material about Freud's life and work.
Artifacts and Paintings, Circa 6th Century B.C.E.-1936
Pocket watch, a small Greek statue, and an oil portrait painting of Freud. Arranged by type of material.
The series contains Freud's pocket watch which he gave to his personal physician Max Schur and a small Greek statue which Freud kept on his desk and later gave to Angelika Frink. Presented here are photographs of both artifacts from multiple views. Also included are photographs of an original oil portrait of Freud by Wilhelm Victor Krausz contained in the collection.
Oversize, 1859-1985
Writings, university and military records, legal documents, correspondence, patient case files, notes, exhibit material, newspaper clippings, family tree, sketch, photograph, and map and chart. Arranged and described according to the series, containers, and folders from which the items were removed.
This series contains material removed from its original series because of its large physical size. Included are items from the Family Papers, General Correspondence, Subject File, and Writings series. The bulk of the series consists of Freud's writings which are housed in their entirety in this series because of their large format. Omitted from the digital edition is the posthumous material from the Supplemental File series.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- BOOK REVIEW
- 26 June 2024
Freudian scripts and sensory slips: Books in brief
- Andrew Robinson 0
Andrew Robinson’s many books include Lost Languages: The Enigma of the World’s Undeciphered Scripts and Einstein on the Run: How Britain Saved the World’s Greatest Scientist . He is based in London.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
You have full access to this article via your institution.

Nicky Hayes Yale Univ. Press (2024)
Aristotle proposed that humans have five senses, but ignored internal ones. Today — as Nicky Hayes, president of the British Psychological Society, describes in her engaging global history from ancient Greece onwards — neurologists count more than 40 human senses used to receive information. The study of people “only becomes psychology when it is fully backed up by research evidence”. That said, it must include more than statistical methods, and must value asking subjects about their experiences, she argues.

Robert Zatorre Oxford Univ. Press (2024)
Charles Darwin appears twice in cognitive neuroscientist Robert Zatorre’s investigation of music. In 1871, Darwin pondered music’s apparent irrelevance to human survival as “most mysterious”, but he later admitted that listening regularly to music might have kept parts of his “atrophied” brain “active”. In Zatorre’s view, “to understand musical pleasure” we must grasp both the brain’s “perceptual/cognitive system” and its “reward system”. His pioneering book, based on profound research, is technical but always accessible.

Frank Tallis Abacus (2024)
Psychoanalysis, proposed by Sigmund Freud in Vienna in the 1890s, is probably science’s most controversial field. “Few major thinkers have been attacked and vilified more than Sigmund Freud,” emphasizes clinical psychologist Frank Tallis, who is overall an admirer, and author of a Freud-inspired detective series, the Liebermann Papers , adapted for television as Vienna Blood. Still, he often criticizes Freud in this biography, which is also a study of Vienna’s golden age, around the turn of the twentieth century.

Salman Khan Viking (2024)
Khan Academy is a non-profit online educational organization with more than 150 million learners in some 50 languages. It was started in the United States in 2006 by Salman Khan, who studied computer science at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology in Cambridge, and is the son of immigrants from Bangladesh. His practical, inspiring book considers how artificial intelligence can transform education — mostly for the better — and “create a new golden age for humanity, a time that will make today look like a dark age”.

Judith Butler Allen Lane (2024)
In the past decade, gender has been attacked by conservatives from many fields, notes philosopher and gender-studies scholar Judith Butler. This includes Pope Francis in his 2015 comment, quoted by Butler, that teaching gender in schools is “ideological colonization … think of Hitler Youth”. The book’s purpose is, however, neither primarily argumentative nor philosophical. Instead, it considers: “What kind of phantasm has gender become, and what anxieties, fears and hatreds does it collect and mobilize?”
Nature 630 , 812 (2024)
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-024-02084-3
Competing Interests
The author declares no competing interests.

Ms Anaria’s classroom rules for well-behaved kindergartners when alien ambassadors dock with the wrong ship
Futures 26 JUN 24

Lights in the storm
Futures 19 JUN 24
![biography of sigmund freud pdf Plastic-eating fungus caused doomsday[2][3]](https://images.nature.com/w140h79/magazine-assets/d41586-024-01723-z/d41586-024-01723-z_27198146.jpg)
Plastic-eating fungus caused doomsday[2][3]
Futures 12 JUN 24
Osaka University Immunology Frontier Research Center Postdoctoral Researcher
IFReC, Osaka University in Japan offers Advanced Postdoc Positions for Immunology, Cell Biology, Bioinformatics and Bioimaging.
Suita Campus, Osaka University in Osaka, Japan
Immunology Frontier Research Center, Osaka University
PostDoc Researcher, Magnetic Recording Materials Group, National Institute for Materials Science
Starting date would be after January 2025, but it is negotiable.
Tsukuba, Japan (JP)
National Institute for Materials Science
Tenure-Track/Tenured Faculty Positions
Tenure-Track/Tenured Faculty Positions in the fields of energy and resources.
Suzhou, Jiangsu, China
School of Sustainable Energy and Resources at Nanjing University
Postdoctoral Associate- Statistical Genetics
Houston, Texas (US)
Baylor College of Medicine (BCM)
Senior Research Associate (Single Cell/Transcriptomics Senior Bioinformatician)
Metabolic Research Laboratories at the Clinical School, University of Cambridge are recruiting 3 senior bioinformatician specialists to create a dynam
Cambridge, Cambridgeshire (GB)
University of Cambridge
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
We’re fighting to restore access to 500,000+ books in court this week. Join us!
Internet Archive Audio

- This Just In
- Grateful Dead
- Old Time Radio
- 78 RPMs and Cylinder Recordings
- Audio Books & Poetry
- Computers, Technology and Science
- Music, Arts & Culture
- News & Public Affairs
- Spirituality & Religion
- Radio News Archive

- Flickr Commons
- Occupy Wall Street Flickr
- NASA Images
- Solar System Collection
- Ames Research Center

- All Software
- Old School Emulation
- MS-DOS Games
- Historical Software
- Classic PC Games
- Software Library
- Kodi Archive and Support File
- Vintage Software
- CD-ROM Software
- CD-ROM Software Library
- Software Sites
- Tucows Software Library
- Shareware CD-ROMs
- Software Capsules Compilation
- CD-ROM Images
- ZX Spectrum
- DOOM Level CD

- Smithsonian Libraries
- FEDLINK (US)
- Lincoln Collection
- American Libraries
- Canadian Libraries
- Universal Library
- Project Gutenberg
- Children's Library
- Biodiversity Heritage Library
- Books by Language
- Additional Collections

- Prelinger Archives
- Democracy Now!
- Occupy Wall Street
- TV NSA Clip Library
- Animation & Cartoons
- Arts & Music
- Computers & Technology
- Cultural & Academic Films
- Ephemeral Films
- Sports Videos
- Videogame Videos
- Youth Media
Search the history of over 866 billion web pages on the Internet.
Mobile Apps
- Wayback Machine (iOS)
- Wayback Machine (Android)
Browser Extensions
Archive-it subscription.
- Explore the Collections
- Build Collections
Save Page Now
Capture a web page as it appears now for use as a trusted citation in the future.
Please enter a valid web address
- Donate Donate icon An illustration of a heart shape
The life and work of Sigmund Freud
Bookreader item preview, share or embed this item, flag this item for.
- Graphic Violence
- Explicit Sexual Content
- Hate Speech
- Misinformation/Disinformation
- Marketing/Phishing/Advertising
- Misleading/Inaccurate/Missing Metadata
![[WorldCat (this item)] [WorldCat (this item)]](https://archive.org/images/worldcat-small.png)
plus-circle Add Review comment Reviews
506 Previews
14 Favorites
DOWNLOAD OPTIONS
No suitable files to display here.
EPUB and PDF access not available for this item.
IN COLLECTIONS
Uploaded by Tracey Gutierres on December 24, 2013
SIMILAR ITEMS (based on metadata)

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Sigmund Freud (born May 6, 1856, Freiberg, Moravia, Austrian Empire [now Příbor, Czech Republic]—died September 23, 1939, London, England) was an Austrian neurologist and the founder of psychoanalysis. (Read Sigmund Freud's 1926 Britannica essay on psychoanalysis.) Freud may justly be called the most influential intellectual legislator of ...
A renowned psychologist, physiologist and great thinker during the early 20th century, Sigmund Freud is referred to as the father of psychoanalysis. He formulated several theories throughout his lifetime including the concepts of infantile sexuality, repression and the unconscious mind. Freud also explored on the structure of the mind, and ...
It will thus be obvious that Civilization and its Discontents is a work whose interest ranges far beyond sociology. Considerable portions of the earlier (1930) translation of this work were included in Rickman's Civilization, War and Death: Selections from Three Works by Sigmund Freud (1939, 26-81). —————————————.
Sigmund Freud's 29 major works in epub and pdf format. [1895] Studies In Hysteria [1900] The Interpretation of Dreams ... Sigmund Freud [1909] Analysis Of A Phobia In A Five-year-old Boy (The Little Hans Case History)(James Strachey Translation 1955)_daisy.zip
Sigmund Freud was an Austrian neurologist who developed psychoanalysis, a method through which an analyst unpacks unconscious conflicts based on the free associations, dreams and fantasies of the ...
The Standard Edition of the Complete Psychological Works of Sigmund Freud (Ed. J. Strachey with Anna Freud), 24 vols. London: 1953-1964. b. Works on Freud and Freudian Psychoanalysis. Abramson, J.B. Liberation and Its Limits: The Moral and Political Thought of Freud. New York: Free Press, 1984. Bettlelheim, B. Freud and Man's Soul. Knopf, 1982.
At a public ceremony in the Moravian town of Freiberg (Pfibor) on 25 October 1931, a plaque was unveiled celebrating the birth of Sigmund Freud on 6 May 1856. Freud himself, now 75 years old and suffering from cancer of the jaw and heart trouble, was unable to attend in person: his youngest daughter Anna read. his speech Of"thanks in ~s place.
Originally published: London : Hogarth Press, 1953, under title: Sigmund Freud: life and work Bibliogr V.1. The formative years and the great discoveries, 1856-1900.--V.2. Years of maturity, 1901-1919.--V.3. The last phase, 1919-1939 Notes. Cut-off text on some pages due too tight binding. ... PDF access not available for this item.
oned, and his legacy of psychoanalysis relegated to an 'imposture'. Alas, with the recent ascent of the chemical theory of mental disease and discovery of p. werful medications, much of Freudianism and its talk therapy have faded.EARLY YEARS Sigmund Freud was born on May 6, 1856 in Freiberg, Moravia (part of the Czech Republic today) to ...
Psychoanalysis continues to have an enormous influence on modern psychology and psychiatry. Sigmund Freud's theories and work helped shape current views of dreams, childhood, personality, memory, sexuality, and therapy. Freud's work also laid the foundation for many other theorists to formulate ideas, while others developed new theories in ...
Biography Sigmund Freud was born May 6, 1856, in a small town -- Freiberg -- in Moravia. His father was a wool merchant with a keen mind and a good sense of humor. His mother was a lively woman, her husband's second wife and 20 years younger. She was 21 years old when she gave birth to her first son, her darling, Sigmund. Sigmund had two older
PDF | A brief biography of Sigmund Freud | Find, read and cite all the research you need on ResearchGate
Sigmund Freud's Theories & Contributions. Psychoanalytic Theory: Freud is best known for developing psychoanalysis, a therapeutic technique for treating mental health disorders by exploring unconscious thoughts and feelings. Unconscious Mind: Freud (1900, 1905) developed a topographical model of the mind, describing the features of the mind ...
This collection of twenty-four volumes is the first full paperback publication of the standard edition of The Complete Psychological Works of Sigmund Freud in English Includes:Moses and Monotheism: Three Essays (1934-38)An Outline of Psycho-Analysis (1938)Analysis Terminable and Interminable (1937)Constructions in Analysis (1937)Splitting of the Ego in the Process of Defence (1938)Some ...
Sigmund Freud was born on May 6, 1856, in Freiberg, Moravia (now Czech Republic). Sigmund was the first child of his twice-widowed father's third marriage. His mother, Amalia Nathanson, was nineteen years old when she married Jacob Freud, aged thirty-nine. Sigmund's two stepbrothers from his father's first marriage were approximately the same ...
The standard edition of the complete psychological works of Sigmund Freud by Freud, Sigmund, 1856-1939; Strachey, James; Freud, Anna, 1895-1982; Richards, Angela. Publication date 1981 Topics Psychoanalysis Publisher ... EPUB and PDF access not available for this item. IN COLLECTIONS
Sigmund Freud, 1856-1939. Sigmund Freud was born in 1856 in Moravia (now part of Czechoslovakia). Influenced by physiologist Hermann Helmholtz, he set out to apply the laws of physics to the human nervous system. His interest in neurology gradually gave way to pioneering efforts to understand unconscious influences on our behavior in illness ...
Biography-of-Sigmund-Freud - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free.
Free PDF EBooks. On Aphasia, 1891; Studies On Hysteria, 1895 ; The Interpretation of Dreams, 1900 ... Sigmund Freud Biography. Sigmund Freud was the man behind the concept and method of psychoanalysis, which was a means of delving into a person's inner conflicts that lie within the unconscious mind. This method is based on the understanding ...
The papers of psychoanalyst Sigmund Freud (1856-1939) span the years from about the 6th century B.C.E. (a small Greek statue) to 1998, with the bulk of material dating from 1871 to 1939. The digitized collection documents Freud's founding of psychoanalysis, the maturation of psychoanalytic theory, the refinement of its clinical technique, and ...
Biography of Sigmund Freud - Free download as Word Doc (.doc), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. Sigmund Freud pioneered the study of the human personality, and founded the modern specialty of personality psychology. While at the University of Vienna medical school, he discovered the anesthetic properties of cocaine during surgery.
Download PDF. A Little History of Psychology ... Psychoanalysis, proposed by Sigmund Freud in Vienna in the 1890s, is probably science's most controversial field. ... Still, he often criticizes ...
Biography of Sigmund Freud - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. Biography of Sigmund Freud
The life and work of Sigmund Freud by Jones, Ernest, 1879-1958. Publication date 1953 Topics Freud, Sigmund, 1856-1939 Publisher New York, Basic Books Collection internetarchivebooks; inlibrary; printdisabled Contributor ... EPUB and PDF access not available for this item. IN COLLECTIONS